Algorithmic bias in marketing occurs when data-driven systems perpetuate existing prejudices, leading to unfair targeting or exclusion of specific consumer groups. Attribution modeling evaluates the effectiveness of different marketing channels, assigning credit to interactions that influence conversions based on user behavior and data analysis. Explore how understanding both algorithmic bias and attribution modeling can enhance fairness and accuracy in marketing strategies.
Why it is important
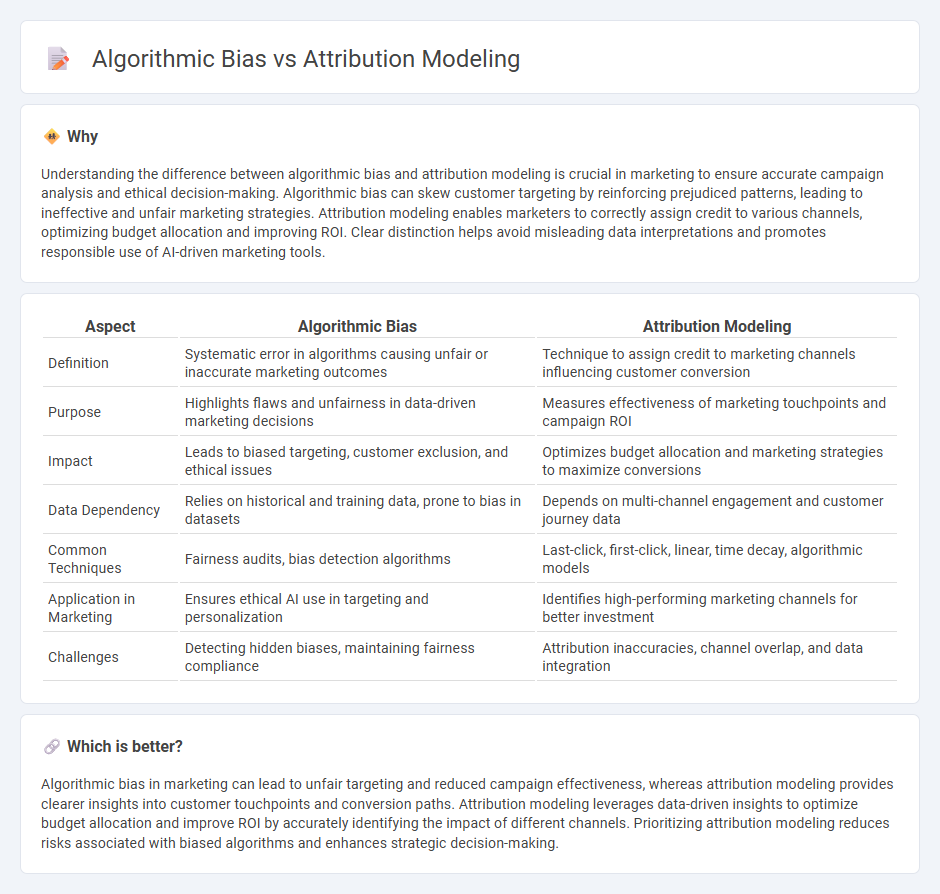
Understanding the difference between algorithmic bias and attribution modeling is crucial in marketing to ensure accurate campaign analysis and ethical decision-making. Algorithmic bias can skew customer targeting by reinforcing prejudiced patterns, leading to ineffective and unfair marketing strategies. Attribution modeling enables marketers to correctly assign credit to various channels, optimizing budget allocation and improving ROI. Clear distinction helps avoid misleading data interpretations and promotes responsible use of AI-driven marketing tools.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Bias | Attribution Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic error in algorithms causing unfair or inaccurate marketing outcomes | Technique to assign credit to marketing channels influencing customer conversion |
| Purpose | Highlights flaws and unfairness in data-driven marketing decisions | Measures effectiveness of marketing touchpoints and campaign ROI |
| Impact | Leads to biased targeting, customer exclusion, and ethical issues | Optimizes budget allocation and marketing strategies to maximize conversions |
| Data Dependency | Relies on historical and training data, prone to bias in datasets | Depends on multi-channel engagement and customer journey data |
| Common Techniques | Fairness audits, bias detection algorithms | Last-click, first-click, linear, time decay, algorithmic models |
| Application in Marketing | Ensures ethical AI use in targeting and personalization | Identifies high-performing marketing channels for better investment |
| Challenges | Detecting hidden biases, maintaining fairness compliance | Attribution inaccuracies, channel overlap, and data integration |
Which is better?
Algorithmic bias in marketing can lead to unfair targeting and reduced campaign effectiveness, whereas attribution modeling provides clearer insights into customer touchpoints and conversion paths. Attribution modeling leverages data-driven insights to optimize budget allocation and improve ROI by accurately identifying the impact of different channels. Prioritizing attribution modeling reduces risks associated with biased algorithms and enhances strategic decision-making.
Connection
Algorithmic bias in marketing influences attribution modeling by skewing the accuracy of customer journey data, leading to misallocated marketing budgets. Attribution models rely on data inputs that can reflect existing biases in digital platforms, causing certain channels or demographics to be overvalued or undervalued. Addressing algorithmic bias improves the precision of attribution models, enabling marketers to optimize campaigns based on fair and representative performance metrics.
Key Terms
**Attribution Modeling:**
Attribution modeling analyzes customer touchpoints to allocate credit for conversions, improving marketing ROI by identifying the most effective channels. It relies on data-driven algorithms to assess interaction patterns, yet can still reflect biases due to skewed data or flawed assumptions. Explore how advanced attribution models reduce bias and enhance decision-making in digital marketing.
Multi-Touch Attribution
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) offers a data-driven approach to allocating credit across multiple customer interactions, enhancing marketing effectiveness through comprehensive analysis of user touchpoints. Algorithmic bias, however, can skew MTA results by introducing systematic errors that favor certain customer segments or channels, potentially misleading decision-making processes. Explore how addressing algorithmic bias improves the accuracy and fairness of Multi-Touch Attribution models for better marketing outcomes.
Conversion Path
Attribution modeling analyzes the conversion path to determine which marketing efforts most effectively lead to sales, using data-driven techniques to assign credit across multiple touchpoints. Algorithmic bias in attribution models occurs when the data or algorithms disproportionately favor certain channels or customer segments, skewing the accuracy of conversion path insights. Explore how addressing algorithmic bias can optimize your attribution strategies and improve conversion path analysis.
Source and External Links
A Beginner's Guide to Attribution Model Frameworks - Amplitude - Attribution modeling is a framework that assigns credit to different marketing touchpoints and channels influencing a conversion, helping marketers understand and optimize their marketing efforts using single-touch or multi-touch models tailored to their business needs.
About attribution modeling - Campaign Manager 360 Help - Attribution modeling is the set of rules that assign credit for sales and conversions to specific touchpoints in a customer's conversion path, with models like Last Interaction or First Interaction determining how credit is distributed across marketing efforts.
Attribution models: What they are, why they matter, when to use them - CallRail - Multi-touch attribution models allocate credit to multiple touchpoints, including Linear, Time Decay, U-Shaped, W-Shaped, and Z-Shaped models, each distributing conversion credit differently based on the position and timing of customer interactions throughout the journey.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com