Distributed workforce refers to employees working from various geographic locations, often independently, while virtual teams collaborate through digital platforms despite physical separation. Effective management of these models requires optimizing communication technology, fostering trust, and aligning goals to enhance productivity. Explore strategies to successfully lead both distributed workforces and virtual teams for improved organizational performance.
Why it is important
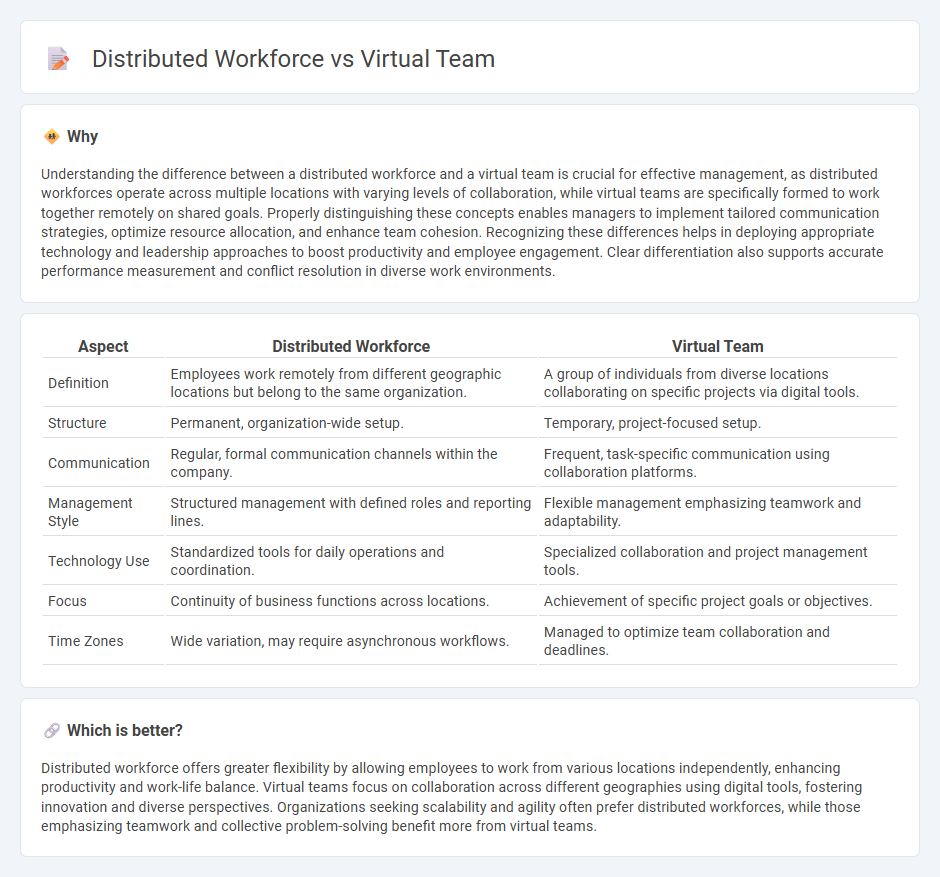
Understanding the difference between a distributed workforce and a virtual team is crucial for effective management, as distributed workforces operate across multiple locations with varying levels of collaboration, while virtual teams are specifically formed to work together remotely on shared goals. Properly distinguishing these concepts enables managers to implement tailored communication strategies, optimize resource allocation, and enhance team cohesion. Recognizing these differences helps in deploying appropriate technology and leadership approaches to boost productivity and employee engagement. Clear differentiation also supports accurate performance measurement and conflict resolution in diverse work environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Distributed Workforce | Virtual Team |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees work remotely from different geographic locations but belong to the same organization. | A group of individuals from diverse locations collaborating on specific projects via digital tools. |
| Structure | Permanent, organization-wide setup. | Temporary, project-focused setup. |
| Communication | Regular, formal communication channels within the company. | Frequent, task-specific communication using collaboration platforms. |
| Management Style | Structured management with defined roles and reporting lines. | Flexible management emphasizing teamwork and adaptability. |
| Technology Use | Standardized tools for daily operations and coordination. | Specialized collaboration and project management tools. |
| Focus | Continuity of business functions across locations. | Achievement of specific project goals or objectives. |
| Time Zones | Wide variation, may require asynchronous workflows. | Managed to optimize team collaboration and deadlines. |
Which is better?
Distributed workforce offers greater flexibility by allowing employees to work from various locations independently, enhancing productivity and work-life balance. Virtual teams focus on collaboration across different geographies using digital tools, fostering innovation and diverse perspectives. Organizations seeking scalability and agility often prefer distributed workforces, while those emphasizing teamwork and collective problem-solving benefit more from virtual teams.
Connection
Distributed workforce relies on virtual teams to collaborate and execute tasks across different geographic locations using digital communication tools and platforms. Virtual teams enable seamless coordination, knowledge sharing, and project management despite physical separation, enhancing organizational flexibility and productivity. Effective management of virtual teams within a distributed workforce requires robust communication strategies, technology integration, and trust-building practices.
Key Terms
Communication Technology
Virtual teams utilize advanced communication technology such as video conferencing, instant messaging, and collaborative platforms like Slack and Microsoft Teams to enable real-time interaction despite geographic separation. Distributed workforces rely on these tools combined with asynchronous communication methods, including email and project management software like Trello and Asana, to maintain productivity across different time zones. Explore how these communication technologies shape collaboration efficiency in both virtual teams and distributed workforces.
Collaboration
Virtual teams leverage real-time communication tools to enhance collaboration, enabling members to work synchronously despite geographical distances. Distributed workforces often operate asynchronously, relying on structured workflows and project management software to maintain productivity across different time zones. Explore how adopting specific collaboration strategies can optimize performance in both virtual teams and distributed workforces.
Geographic Dispersion
A virtual team operates across multiple geographic locations, collaborating through digital tools to achieve common goals, while a distributed workforce consists of employees working remotely but may not be directly connected as a unified team. Geographic dispersion in virtual teams necessitates structured communication and coordination strategies to overcome time zone differences and cultural diversity. Explore how geographic dispersion impacts productivity and collaboration in virtual versus distributed work setups.
Source and External Links
Virtual Team - A virtual team is a group of individuals working together from different geographic locations using communication technology to collaborate on tasks.
Examples of Virtual Teams - Provides examples of successful virtual teams, including networked and parallel teams, highlighting their benefits and applications.
Managing Virtual Teams - Offers strategies for managing virtual teams, focusing on communication, performance management, team building, and technology tools.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com