Job crafting involves employees proactively modifying tasks, relationships, and perceptions to better align their work with personal strengths and interests, enhancing job satisfaction and performance. Role innovation goes beyond individual adjustments by encouraging the creation of new roles or redefinition of existing roles within an organization, fostering adaptability and competitive advantage. Explore innovative management strategies to boost engagement and organizational growth.
Why it is important
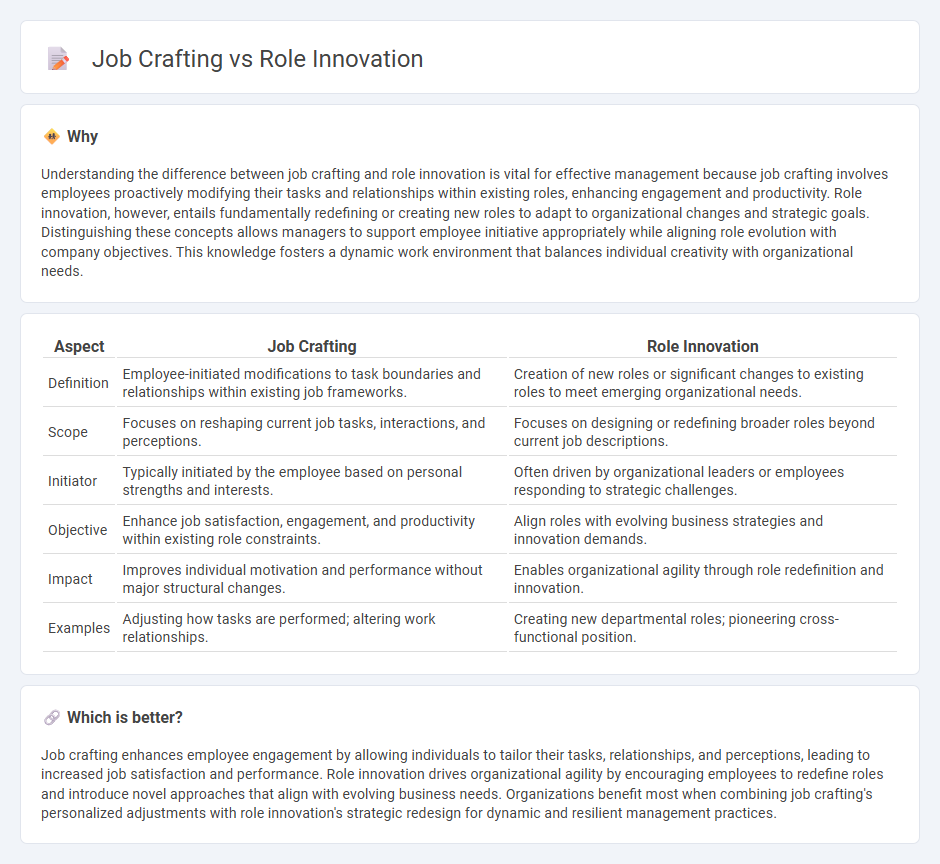
Understanding the difference between job crafting and role innovation is vital for effective management because job crafting involves employees proactively modifying their tasks and relationships within existing roles, enhancing engagement and productivity. Role innovation, however, entails fundamentally redefining or creating new roles to adapt to organizational changes and strategic goals. Distinguishing these concepts allows managers to support employee initiative appropriately while aligning role evolution with company objectives. This knowledge fosters a dynamic work environment that balances individual creativity with organizational needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Job Crafting | Role Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee-initiated modifications to task boundaries and relationships within existing job frameworks. | Creation of new roles or significant changes to existing roles to meet emerging organizational needs. |
| Scope | Focuses on reshaping current job tasks, interactions, and perceptions. | Focuses on designing or redefining broader roles beyond current job descriptions. |
| Initiator | Typically initiated by the employee based on personal strengths and interests. | Often driven by organizational leaders or employees responding to strategic challenges. |
| Objective | Enhance job satisfaction, engagement, and productivity within existing role constraints. | Align roles with evolving business strategies and innovation demands. |
| Impact | Improves individual motivation and performance without major structural changes. | Enables organizational agility through role redefinition and innovation. |
| Examples | Adjusting how tasks are performed; altering work relationships. | Creating new departmental roles; pioneering cross-functional position. |
Which is better?
Job crafting enhances employee engagement by allowing individuals to tailor their tasks, relationships, and perceptions, leading to increased job satisfaction and performance. Role innovation drives organizational agility by encouraging employees to redefine roles and introduce novel approaches that align with evolving business needs. Organizations benefit most when combining job crafting's personalized adjustments with role innovation's strategic redesign for dynamic and resilient management practices.
Connection
Job crafting empowers employees to reshape their tasks and interactions, fostering role innovation by encouraging the creation of new, adaptive responsibilities. Role innovation emerges when individuals proactively redefine their job boundaries, aligning personal strengths with organizational goals. This dynamic interplay enhances employee engagement, productivity, and organizational agility.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Role innovation enhances autonomy by allowing employees to redefine job boundaries and introduce novel tasks, fostering creativity and personal growth. Job crafting specifically targets autonomy through proactive adjustments in task boundaries, relationships, and cognitive framing to better align work with individual strengths and preferences. Explore how these approaches uniquely empower autonomy and drive workplace engagement.
Proactivity
Role innovation involves proactively redefining job responsibilities to create new value within an organization, emphasizing strategic change and long-term impact. Job crafting centers on employees actively modifying their tasks, relationships, and perceptions to enhance job satisfaction and performance in their current roles. Explore deeper insights to understand how proactivity drives both approaches in dynamic workplaces.
Task Redesign
Role innovation involves redefining job responsibilities through significant, creative changes to tasks, enhancing employee engagement and organizational adaptability. Job crafting focuses on employees making subtle, proactive adjustments to task boundaries, increasing job satisfaction and personal meaningfulness. Discover how task redesign strategies can transform work experiences and drive performance outcomes.
Source and External Links
Your Role in Innovation Depends on Where You Sit - This article discusses the roles individuals play in innovation based on their organizational position, focusing on creating and leading innovation efforts.
What Does an Innovation Manager Do? - An innovation manager is responsible for implementing strategies to increase efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness through innovative practices.
Jobs in Innovation: Our Field Guide - This guide explores various roles in the field of innovation, including innovation consultants, business designers, and chief innovation officers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com