Proximity bias refers to the tendency of managers to favor employees who work physically closer to them, impacting fairness in evaluation and resource allocation. Recency bias occurs when recent events disproportionately influence performance assessments, overshadowing long-term contributions. Explore deeper insights into how these biases affect management decisions and employee outcomes.
Why it is important
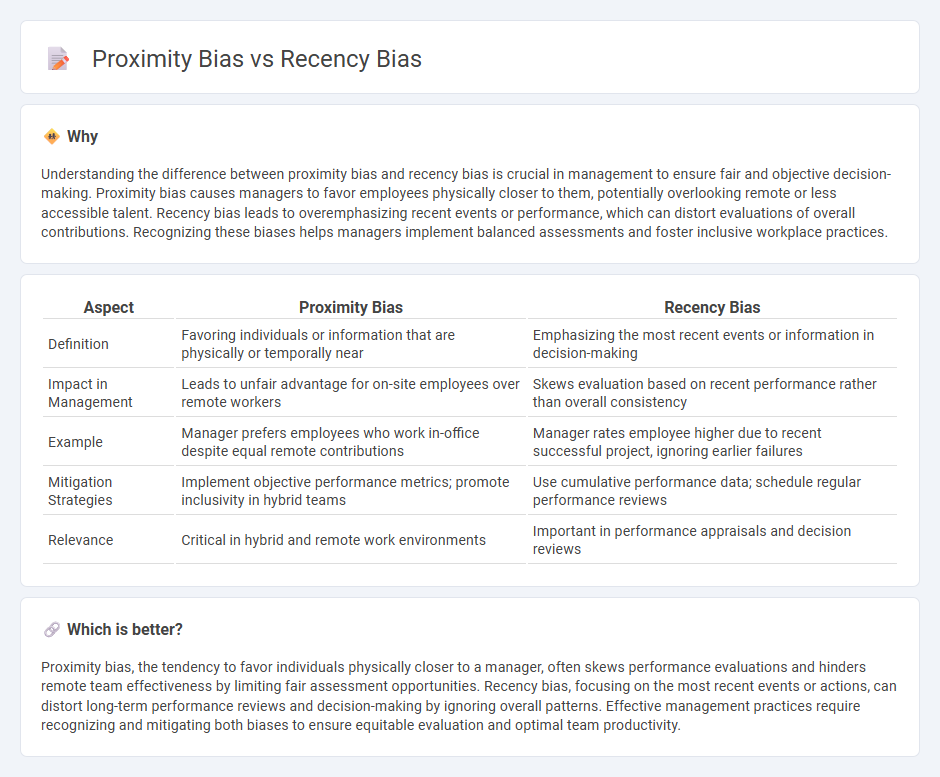
Understanding the difference between proximity bias and recency bias is crucial in management to ensure fair and objective decision-making. Proximity bias causes managers to favor employees physically closer to them, potentially overlooking remote or less accessible talent. Recency bias leads to overemphasizing recent events or performance, which can distort evaluations of overall contributions. Recognizing these biases helps managers implement balanced assessments and foster inclusive workplace practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Proximity Bias | Recency Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Favoring individuals or information that are physically or temporally near | Emphasizing the most recent events or information in decision-making |
| Impact in Management | Leads to unfair advantage for on-site employees over remote workers | Skews evaluation based on recent performance rather than overall consistency |
| Example | Manager prefers employees who work in-office despite equal remote contributions | Manager rates employee higher due to recent successful project, ignoring earlier failures |
| Mitigation Strategies | Implement objective performance metrics; promote inclusivity in hybrid teams | Use cumulative performance data; schedule regular performance reviews |
| Relevance | Critical in hybrid and remote work environments | Important in performance appraisals and decision reviews |
Which is better?
Proximity bias, the tendency to favor individuals physically closer to a manager, often skews performance evaluations and hinders remote team effectiveness by limiting fair assessment opportunities. Recency bias, focusing on the most recent events or actions, can distort long-term performance reviews and decision-making by ignoring overall patterns. Effective management practices require recognizing and mitigating both biases to ensure equitable evaluation and optimal team productivity.
Connection
Proximity bias and recency bias both influence management decisions by distorting perceptions of employee performance based on physical closeness or recent events. Proximity bias occurs when managers favor employees who are physically closer or more visible, while recency bias leads to overemphasizing recent behaviors or outcomes in evaluations. Together, these cognitive biases can undermine fair performance assessments and affect talent management strategies within organizations.
Key Terms
Decision-making
Recency bias causes decision-makers to overweight recent information, leading to skewed judgments based on the latest events rather than long-term data. Proximity bias, in contrast, influences decisions by favoring people or information that are physically or emotionally closer, often impacting workplace fairness and resource allocation. Explore detailed strategies to mitigate these cognitive biases in decision-making for more balanced outcomes.
Employee evaluation
Recency bias in employee evaluation causes managers to overemphasize recent events, overshadowing an employee's long-term performance, while proximity bias favors employees who work physically closer to evaluators, potentially disadvantaging remote or hybrid workers. Both biases distort fair assessments by prioritizing convenience or recent memories over comprehensive data. Explore strategies to mitigate these biases and ensure equitable performance reviews.
Workplace fairness
Recency bias causes employees to be judged primarily on their most recent performance, potentially overshadowing consistent past achievements and skewing workplace fairness. Proximity bias favors individuals who are physically closer or work in the same location as decision-makers, leading to unequal opportunities for remote or distributed team members. Explore effective strategies to mitigate these biases and promote equitable judgment in the workplace.
Source and External Links
Recency Bias | SKYbrary Aviation Safety - This webpage discusses recency bias as a tendency to weigh recent events more heavily than earlier ones, often influenced by cognitive ease and memory limitations.
What Is Recency Bias? | Definition & Examples - Scribbr - This article defines recency bias as a cognitive bias causing people to overemphasize recent experiences and apply them to future predictions, often ignoring statistical probability and history.
Recency bias - Wikipedia - Wikipedia describes recency bias as a cognitive bias giving greater importance to recent events over historic ones, relating it to memory biases and the serial-position effect.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com