Hybrid workforce combines full-time employees working both remotely and onsite, enhancing flexibility and collaboration within organizations, while gig workforce consists of independent contractors or freelancers offering specialized skills on demand. Organizations leveraging hybrid models benefit from workforce stability and cultural cohesion, whereas gig models provide scalability and cost efficiency for project-based needs. Explore how these workforce strategies impact productivity and talent management in evolving business environments.
Why it is important
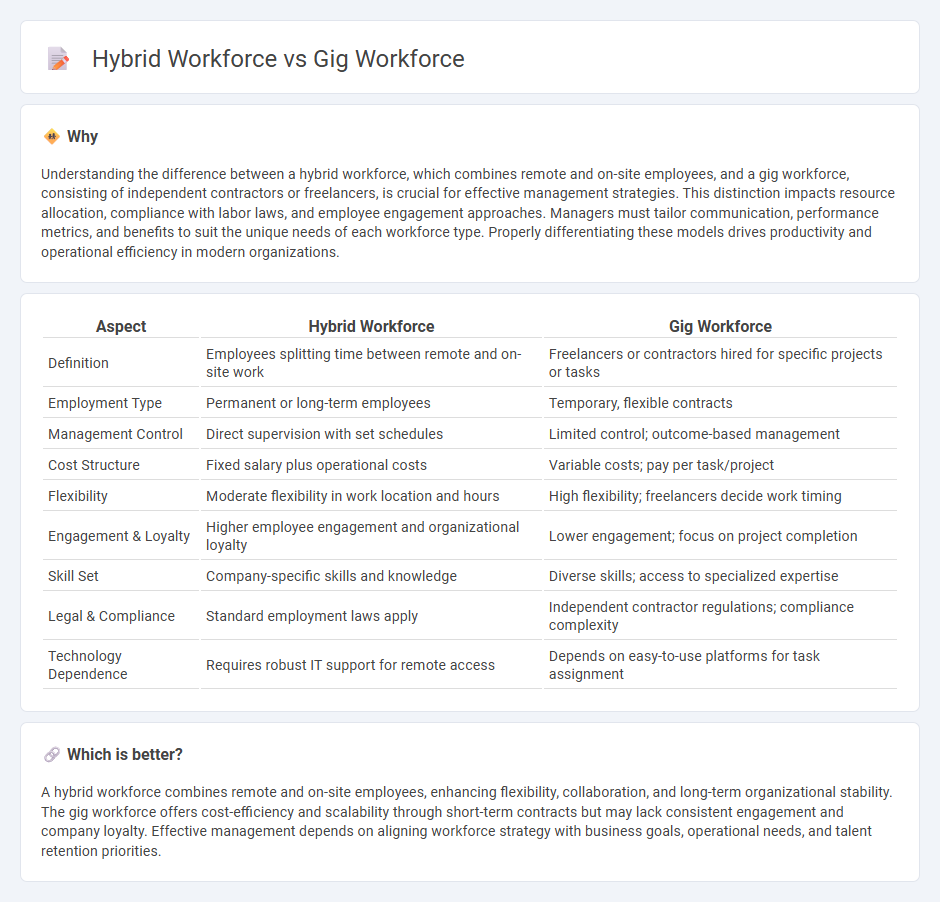
Understanding the difference between a hybrid workforce, which combines remote and on-site employees, and a gig workforce, consisting of independent contractors or freelancers, is crucial for effective management strategies. This distinction impacts resource allocation, compliance with labor laws, and employee engagement approaches. Managers must tailor communication, performance metrics, and benefits to suit the unique needs of each workforce type. Properly differentiating these models drives productivity and operational efficiency in modern organizations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Hybrid Workforce | Gig Workforce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees splitting time between remote and on-site work | Freelancers or contractors hired for specific projects or tasks |
| Employment Type | Permanent or long-term employees | Temporary, flexible contracts |
| Management Control | Direct supervision with set schedules | Limited control; outcome-based management |
| Cost Structure | Fixed salary plus operational costs | Variable costs; pay per task/project |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility in work location and hours | High flexibility; freelancers decide work timing |
| Engagement & Loyalty | Higher employee engagement and organizational loyalty | Lower engagement; focus on project completion |
| Skill Set | Company-specific skills and knowledge | Diverse skills; access to specialized expertise |
| Legal & Compliance | Standard employment laws apply | Independent contractor regulations; compliance complexity |
| Technology Dependence | Requires robust IT support for remote access | Depends on easy-to-use platforms for task assignment |
Which is better?
A hybrid workforce combines remote and on-site employees, enhancing flexibility, collaboration, and long-term organizational stability. The gig workforce offers cost-efficiency and scalability through short-term contracts but may lack consistent engagement and company loyalty. Effective management depends on aligning workforce strategy with business goals, operational needs, and talent retention priorities.
Connection
The hybrid workforce integrates remote and on-site employees, enhancing flexibility and productivity, while the gig workforce consists of independent contractors engaged for specific projects or tasks. Both workforce models rely on digital platforms and technology to enable seamless collaboration, task management, and communication across diverse locations. Organizations leveraging these approaches achieve scalable staffing solutions, access to specialized skills, and improved cost efficiency in talent management.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Gig workforce offers unmatched flexibility by allowing workers to choose projects and schedules independently, catering to varying personal and professional needs. Hybrid workforce combines remote and on-site work, providing employees flexibility while maintaining some structure and team collaboration. Explore how these workforce models maximize flexibility and impact organizational efficiency.
Employment Structure
A gig workforce consists of independent contractors or freelancers hired for specific tasks, offering flexibility without long-term commitments. In contrast, a hybrid workforce blends traditional full-time employees with remote or gig workers, promoting adaptability while maintaining core operational stability. Explore the differences in employment structures to optimize your organization's staffing strategy.
Worker Autonomy
The gig workforce offers high worker autonomy by enabling individuals to choose projects, set schedules, and work independently without traditional employer constraints. In contrast, the hybrid workforce balances remote and on-site work, providing employees with flexibility but typically within structured organizational guidelines. Explore how these models impact productivity and worker satisfaction to understand their benefits fully.
Source and External Links
Insights Into the Gig Workforce in Businesses - This report provides insights into the gig workforce, highlighting its prevalence across various industries and the challenges faced by companies in managing these workers.
Gig Worker - Gig workers are independent contractors or temporary workers often involved in on-demand jobs, with a growing presence in economies worldwide.
Gig Economy Statistics - This article presents statistics on the gig economy, including its size, growth, and the projected increase in gig workers globally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com