Distributed workforce refers to employees working from multiple locations, often remotely, enhancing global reach and operational resilience. Flexible workforce emphasizes adaptable work hours and arrangements, promoting employee work-life balance and productivity. Explore the key distinctions and benefits of managing distributed versus flexible workforces.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between distributed workforce and flexible workforce is crucial for effective management because distributed workforce refers to employees working from multiple, often global, locations, while flexible workforce emphasizes adaptable schedules and work arrangements. Recognizing these distinctions helps managers implement appropriate communication, collaboration tools, and policies tailored to each workforce type. Properly managing diverse work models boosts productivity, employee satisfaction, and operational efficiency. Clear differentiation also aids in compliance with labor laws and optimizing resource allocation for business growth.
Comparison Table
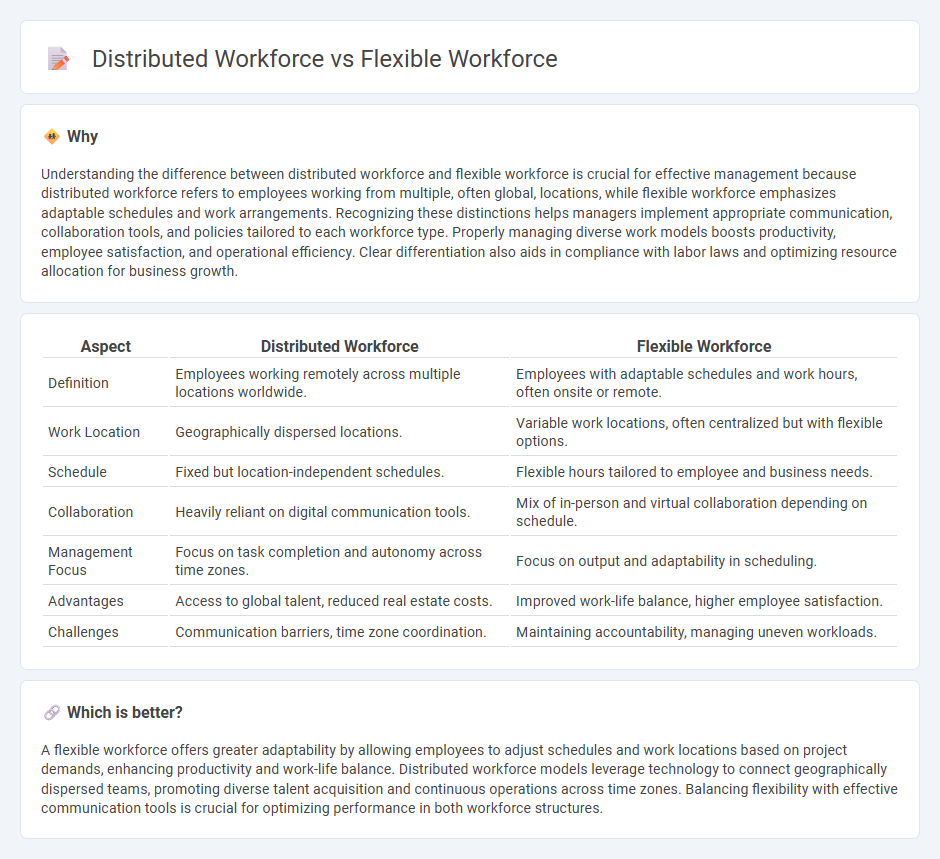
| Aspect | Distributed Workforce | Flexible Workforce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees working remotely across multiple locations worldwide. | Employees with adaptable schedules and work hours, often onsite or remote. |
| Work Location | Geographically dispersed locations. | Variable work locations, often centralized but with flexible options. |
| Schedule | Fixed but location-independent schedules. | Flexible hours tailored to employee and business needs. |
| Collaboration | Heavily reliant on digital communication tools. | Mix of in-person and virtual collaboration depending on schedule. |
| Management Focus | Focus on task completion and autonomy across time zones. | Focus on output and adaptability in scheduling. |
| Advantages | Access to global talent, reduced real estate costs. | Improved work-life balance, higher employee satisfaction. |
| Challenges | Communication barriers, time zone coordination. | Maintaining accountability, managing uneven workloads. |
Which is better?
A flexible workforce offers greater adaptability by allowing employees to adjust schedules and work locations based on project demands, enhancing productivity and work-life balance. Distributed workforce models leverage technology to connect geographically dispersed teams, promoting diverse talent acquisition and continuous operations across time zones. Balancing flexibility with effective communication tools is crucial for optimizing performance in both workforce structures.
Connection
A distributed workforce relies on flexible workforce strategies to effectively manage remote teams across diverse locations, enhancing productivity and employee satisfaction. Flexible workforce models enable organizations to adapt work schedules and processes, supporting seamless collaboration among distributed employees. Integrating these approaches drives operational efficiency and resilience in dynamic business environments.
Key Terms
Remote Work
A flexible workforce adapts to changing work schedules and locations, enabling employees to choose when and where they work, while a distributed workforce specifically refers to employees working from various geographic locations, often remotely. Remote work is a key factor for both models, promoting productivity and work-life balance by leveraging technology for seamless communication and collaboration. Explore more on how these workforce strategies can optimize remote work effectiveness and business outcomes.
Cross-functional Teams
Cross-functional teams thrive in both flexible and distributed workforce models by leveraging diverse skill sets and promoting collaboration across departments. Flexible workforces offer adaptability in scheduling and location, enhancing productivity and employee satisfaction, while distributed workforces enable global talent integration and real-time communication through digital tools. Explore how aligning your cross-functional teams with these workforce strategies can drive innovation and efficiency.
Agile Staffing
A flexible workforce adapts roles and hours based on project demands, enhancing agility within a centralized or local team structure. A distributed workforce spans multiple geographic locations, leveraging remote talent to maintain continuous operations and diverse skill sets. Explore how Agile Staffing integrates both models to maximize performance and responsiveness in dynamic markets.
Source and External Links
How to create a flexible workforce - A flexible workforce can scale up or down based on business needs, incorporating full-time, part-time, and temporary workers, supported by standardized procurement and technology platforms to maintain efficiency and employee well-being.
What is Flexible Workforce? - A flexible workforce consists of part-time, contract, or remote workers, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to changing demands, reduce costs, and access specialized skills while improving productivity and retention.
Flexible workforce solutions - Organizations can implement digital, automated solutions for managing flexible work arrangements, helping to meet employee expectations for hybrid and remote work while supporting compliance and workforce agility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com