Holacracy implements a structured system of self-management with defined roles and governance processes, promoting agility and transparency within organizations. Distributed leadership disperses decision-making authority across team members, fostering collaboration and empowerment without rigid hierarchical control. Explore further to understand which approach best aligns with your organization's culture and goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between holacracy and distributed leadership is crucial for effective organizational design and decision-making processes. Holacracy offers a structured framework with defined roles and governance meetings, promoting transparency and accountability. Distributed leadership emphasizes shared influence and collaboration across team members without rigid role assignments. Knowing these distinctions enables leaders to choose the best approach for fostering innovation, agility, and employee empowerment within their specific organizational context.
Comparison Table
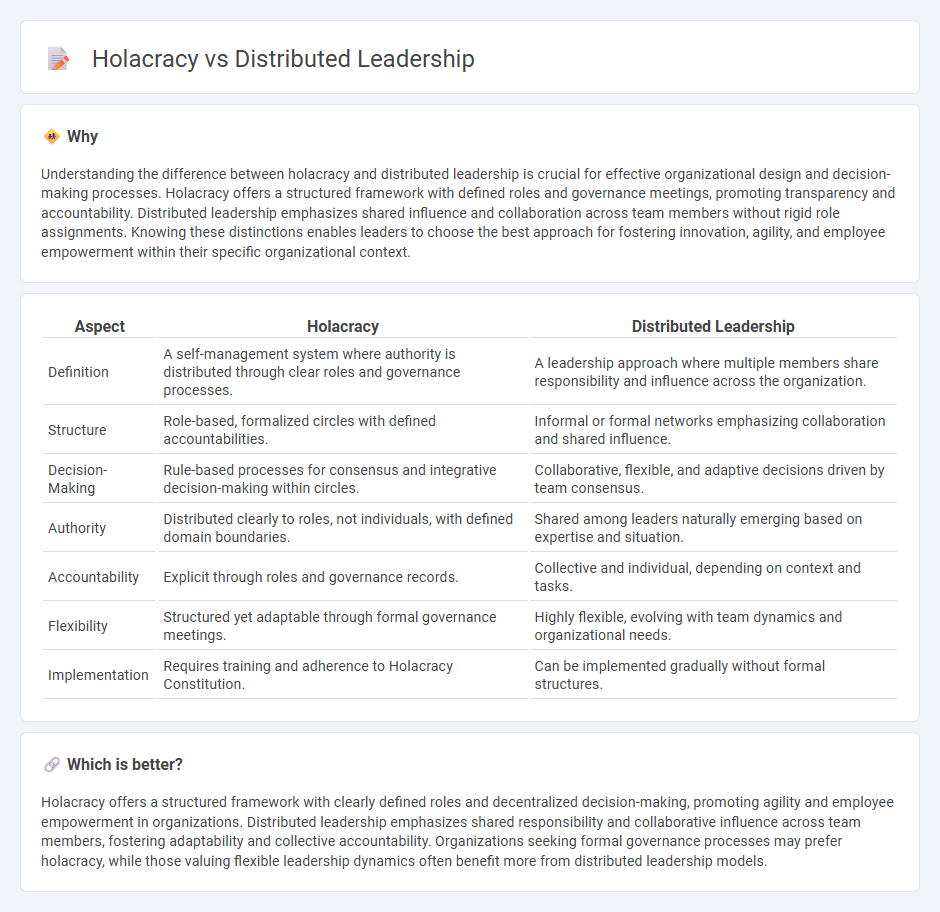
| Aspect | Holacracy | Distributed Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A self-management system where authority is distributed through clear roles and governance processes. | A leadership approach where multiple members share responsibility and influence across the organization. |
| Structure | Role-based, formalized circles with defined accountabilities. | Informal or formal networks emphasizing collaboration and shared influence. |
| Decision-Making | Rule-based processes for consensus and integrative decision-making within circles. | Collaborative, flexible, and adaptive decisions driven by team consensus. |
| Authority | Distributed clearly to roles, not individuals, with defined domain boundaries. | Shared among leaders naturally emerging based on expertise and situation. |
| Accountability | Explicit through roles and governance records. | Collective and individual, depending on context and tasks. |
| Flexibility | Structured yet adaptable through formal governance meetings. | Highly flexible, evolving with team dynamics and organizational needs. |
| Implementation | Requires training and adherence to Holacracy Constitution. | Can be implemented gradually without formal structures. |
Which is better?
Holacracy offers a structured framework with clearly defined roles and decentralized decision-making, promoting agility and employee empowerment in organizations. Distributed leadership emphasizes shared responsibility and collaborative influence across team members, fostering adaptability and collective accountability. Organizations seeking formal governance processes may prefer holacracy, while those valuing flexible leadership dynamics often benefit more from distributed leadership models.
Connection
Holacracy and distributed leadership both promote decentralized decision-making to enhance organizational agility and employee empowerment. Holacracy structures authority through defined roles and circles, enabling teams to self-manage without traditional hierarchies. Distributed leadership spreads leadership responsibilities across members, fostering collaboration and shared accountability aligned with holacracy's dynamic governance framework.
Key Terms
Decision-making authority
Distributed leadership disperses decision-making authority across multiple levels within an organization, enabling teams and individuals to exercise autonomy in their areas of expertise. Holacracy formalizes this dispersion through defined roles and circles, creating structured yet flexible decision-making processes without traditional management hierarchies. Explore deeper insights into how these models shape organizational dynamics and empower employee autonomy.
Role fluidity
Distributed leadership emphasizes shared authority among team members, allowing for flexible role adaptations based on expertise and situational needs, promoting dynamic collaboration. Holacracy implements role fluidity through defined but adaptable roles in a structured governance system, enabling continuous role evolution within organizational circles. Explore more to understand how role fluidity transforms organizational agility in both models.
Hierarchical structure
Distributed leadership disperses decision-making authority across various levels in a traditional hierarchical structure, promoting collaboration while maintaining clear reporting lines. Holacracy eliminates conventional hierarchies by implementing self-organizing teams called circles, where authority is decentralized and roles are fluid. Explore how these models redefine organizational hierarchy to enhance agility and accountability.
Source and External Links
Distributed Leadership: Definition and Key Concepts - Distributed leadership emphasizes teamwork and autonomy, allowing team members to contribute to organizational success and innovation without strict hierarchical control.
What Is Distributed Leadership? - This management approach empowers individuals across an organization to take ownership of leadership responsibilities, fostering a democratic and equitable culture.
What is Distributed Leadership? - Distributed leadership involves shared responsibility and power, promoting synergy and teamwork to achieve organizational goals through collective leadership efforts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com