Reverse mentorship flips traditional learning by enabling younger employees to share digital skills and fresh perspectives with senior leaders, enhancing organizational agility and innovation. Apprenticeship emphasizes hands-on experience and guided skill development under expert supervision to build long-term professional competence. Explore how these dynamic approaches transform workforce growth and leadership development.
Why it is important
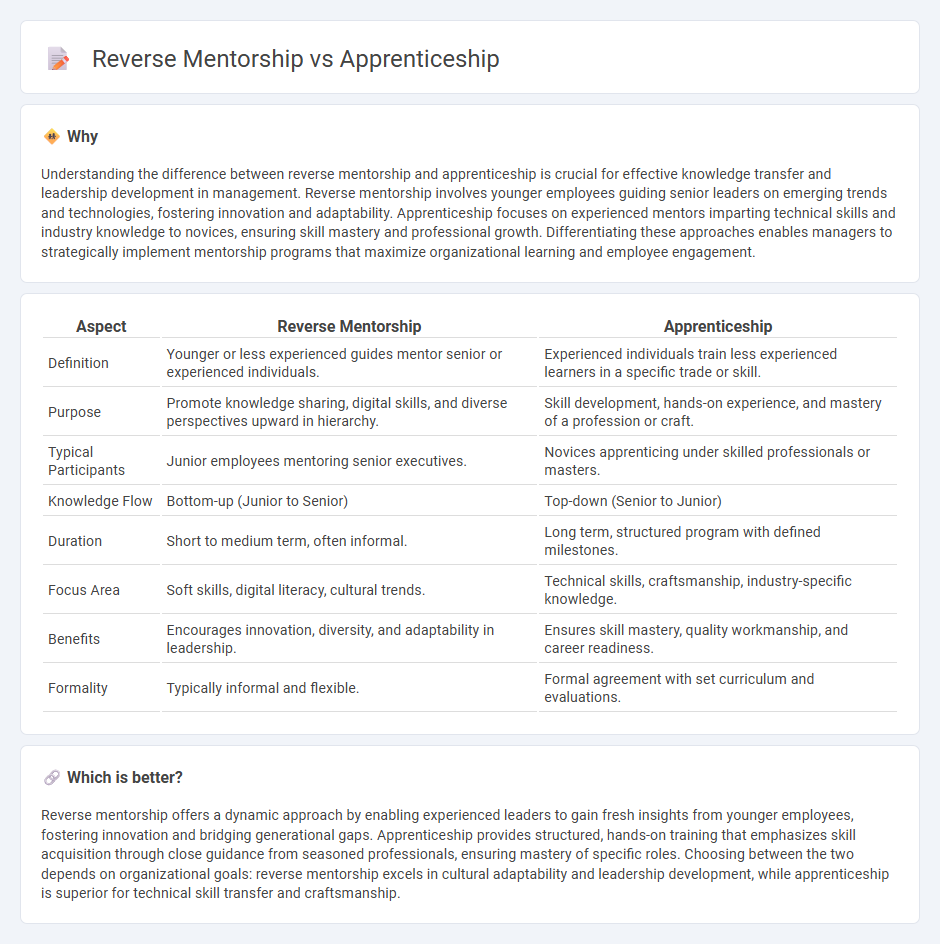
Understanding the difference between reverse mentorship and apprenticeship is crucial for effective knowledge transfer and leadership development in management. Reverse mentorship involves younger employees guiding senior leaders on emerging trends and technologies, fostering innovation and adaptability. Apprenticeship focuses on experienced mentors imparting technical skills and industry knowledge to novices, ensuring skill mastery and professional growth. Differentiating these approaches enables managers to strategically implement mentorship programs that maximize organizational learning and employee engagement.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Mentorship | Apprenticeship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Younger or less experienced guides mentor senior or experienced individuals. | Experienced individuals train less experienced learners in a specific trade or skill. |
| Purpose | Promote knowledge sharing, digital skills, and diverse perspectives upward in hierarchy. | Skill development, hands-on experience, and mastery of a profession or craft. |
| Typical Participants | Junior employees mentoring senior executives. | Novices apprenticing under skilled professionals or masters. |
| Knowledge Flow | Bottom-up (Junior to Senior) | Top-down (Senior to Junior) |
| Duration | Short to medium term, often informal. | Long term, structured program with defined milestones. |
| Focus Area | Soft skills, digital literacy, cultural trends. | Technical skills, craftsmanship, industry-specific knowledge. |
| Benefits | Encourages innovation, diversity, and adaptability in leadership. | Ensures skill mastery, quality workmanship, and career readiness. |
| Formality | Typically informal and flexible. | Formal agreement with set curriculum and evaluations. |
Which is better?
Reverse mentorship offers a dynamic approach by enabling experienced leaders to gain fresh insights from younger employees, fostering innovation and bridging generational gaps. Apprenticeship provides structured, hands-on training that emphasizes skill acquisition through close guidance from seasoned professionals, ensuring mastery of specific roles. Choosing between the two depends on organizational goals: reverse mentorship excels in cultural adaptability and leadership development, while apprenticeship is superior for technical skill transfer and craftsmanship.
Connection
Reverse mentorship and apprenticeship are connected through their focus on knowledge transfer and skill development across different experience levels. Reverse mentorship involves younger employees sharing digital expertise with senior leaders, while apprenticeships provide hands-on training under experienced professionals. Both approaches foster continuous learning, collaboration, and innovation within an organization's management framework.
Key Terms
Knowledge Transfer
Apprenticeship facilitates knowledge transfer by enabling experienced professionals to impart technical skills and industry insights to less experienced individuals through hands-on training. Reverse mentorship reverses this dynamic, allowing younger employees to share fresh perspectives, digital proficiency, and innovative ideas with senior leaders. Explore how both approaches maximize organizational learning and bridge skill gaps effectively.
Skill Development
Apprenticeship emphasizes skill development through hands-on experience guided by an expert, fostering practical knowledge in real-world settings. Reverse mentorship accelerates learning by pairing less experienced employees with senior leaders, promoting digital literacy and fresh perspectives. Explore how these approaches enhance workplace capabilities and drive continuous growth.
Intergenerational Learning
Intergenerational learning thrives through both apprenticeship, where younger individuals gain skills and knowledge from experienced elders, and reverse mentorship, which empowers younger generations to share digital expertise with senior counterparts. Apprenticeship emphasizes traditional skill transfer and long-term professional growth, while reverse mentorship leverages generational differences to foster innovation and adaptability in rapidly changing workplaces. Explore more insights into how these approaches enhance collaboration and learning across age groups.
Source and External Links
Apprenticeship.gov: Homepage - Central U.S. government resource connecting career seekers, employers, and educators to apprenticeship programs offering paid on-the-job training, classroom instruction, nationally recognized credentials, and strong career outcomes.
Montana Registered Apprenticeship - Offers earn-while-you-learn programs combining paid work experience and classroom training in skilled trades with apprenticeships requiring a minimum of 2,000 hours supervised on-the-job training in Montana.
Apprenticeship Utah - State-level apprenticeship program featuring an "earn and learn" model blending on-the-job learning and classroom instruction that leads to improved career prospects, wage increases, and portable industry-recognized credentials.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com