Proximity bias occurs when managers favor employees who are physically closer, often overlooking remote or hybrid workers, while affinity bias leads to preferential treatment of individuals who share similar backgrounds or interests. Both biases can hinder diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts in the workplace by influencing decision-making and performance evaluations. Explore deeper insights on managing and mitigating proximity and affinity biases to improve organizational fairness and productivity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between proximity bias and affinity bias is crucial for effective management because it helps leaders recognize distinct unconscious preferences that affect team dynamics and decision-making. Proximity bias favors individuals physically closer to a manager, potentially overlooking remote talent, while affinity bias leads to favoritism based on shared interests or backgrounds. Identifying these biases enables managers to foster diversity, equity, and inclusion within their organizations by creating fairer evaluation processes. This awareness directly improves hiring, promotions, and collaboration, enhancing overall organizational performance.
Comparison Table
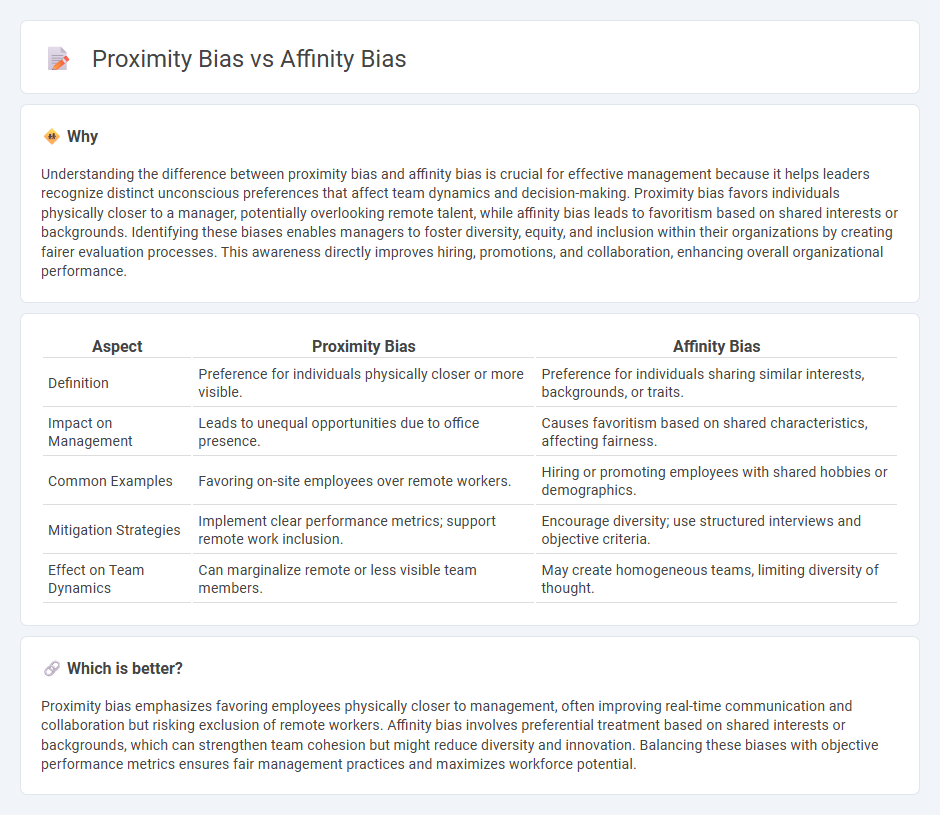
| Aspect | Proximity Bias | Affinity Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preference for individuals physically closer or more visible. | Preference for individuals sharing similar interests, backgrounds, or traits. |
| Impact on Management | Leads to unequal opportunities due to office presence. | Causes favoritism based on shared characteristics, affecting fairness. |
| Common Examples | Favoring on-site employees over remote workers. | Hiring or promoting employees with shared hobbies or demographics. |
| Mitigation Strategies | Implement clear performance metrics; support remote work inclusion. | Encourage diversity; use structured interviews and objective criteria. |
| Effect on Team Dynamics | Can marginalize remote or less visible team members. | May create homogeneous teams, limiting diversity of thought. |
Which is better?
Proximity bias emphasizes favoring employees physically closer to management, often improving real-time communication and collaboration but risking exclusion of remote workers. Affinity bias involves preferential treatment based on shared interests or backgrounds, which can strengthen team cohesion but might reduce diversity and innovation. Balancing these biases with objective performance metrics ensures fair management practices and maximizes workforce potential.
Connection
Proximity bias influences managers to favor employees who work physically closer, leading to unequal opportunities and skewed performance evaluations. Affinity bias causes managers to prefer individuals with similar backgrounds or interests, reinforcing favoritism within close-knit groups. Together, these biases create a cycle where proximity and shared traits amplify preferential treatment, undermining diversity and inclusion in management decisions.
Key Terms
Unconscious bias
Affinity bias occurs when individuals favor others who share similar characteristics, backgrounds, or interests, leading to preferential treatment in hiring or promotion decisions. Proximity bias arises when managers favor employees they physically see more often, often disadvantaging remote or hybrid workers. Explore deeper insights on how these unconscious biases impact workplace diversity and inclusion strategies.
Inclusion
Affinity bias leads individuals to favor others who share similar characteristics, backgrounds, or interests, potentially limiting diversity and inclusion in workplaces. Proximity bias emerges when people favor those physically or virtually closer, often neglecting remote or less visible colleagues, which can hinder equitable opportunities. Explore strategies to mitigate these biases and foster a truly inclusive environment.
Workplace diversity
Affinity bias leads employees to favor colleagues who share similar backgrounds, interests, or experiences, potentially limiting workplace diversity by creating homogeneous groups. Proximity bias occurs when individuals preferentially engage with those physically or digitally closer to them, often neglecting remote or geographically distant team members. Exploring strategies to mitigate these biases can enhance inclusivity and foster a more diverse work environment--learn more about effective diversity management practices.
Source and External Links
What is affinity bias? - HiBob - Affinity bias is the unconscious tendency to prefer people who share similar backgrounds, interests, or experiences, driven by cognitive shortcuts like the halo effect and conflict avoidance, which can negatively impact inclusivity and empathy in workplaces.
Affinity bias - Wikipedia - Affinity bias, also known as similarity bias or the "mini-me syndrome," is an implicit cognitive bias favoring others like ourselves, often affecting hiring and promotion decisions and potentially limiting diversity and creativity.
Affinity Bias: When Familiar Choices Kill Fresh Thinking - SHRM - Affinity bias reinforces sameness by making people prefer those with similar backgrounds and views, which can undermine diversity, innovation, and long-term organizational performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com