Resenteeism refers to employees physically present at work but disengaged or unproductive due to dissatisfaction or stress, while absenteeism involves frequent or habitual absence from the workplace. Understanding the distinction between these behaviors is crucial for effective workforce management and improving organizational performance. Explore strategies to identify and address both resenteeism and absenteeism to enhance employee well-being and productivity.
Why it is important
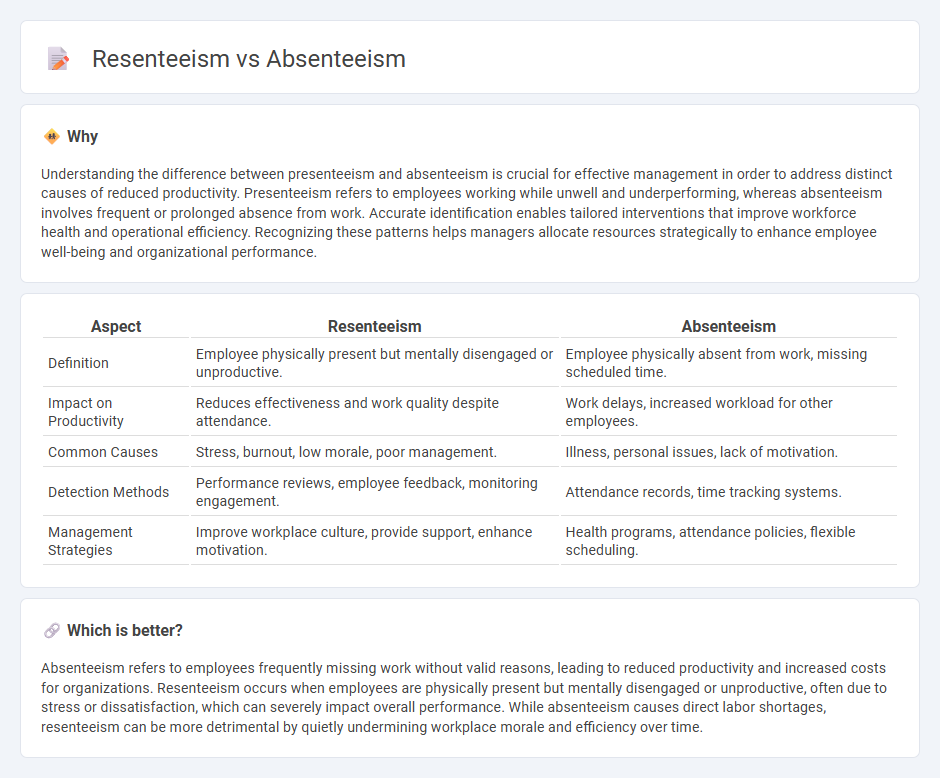
Understanding the difference between presenteeism and absenteeism is crucial for effective management in order to address distinct causes of reduced productivity. Presenteeism refers to employees working while unwell and underperforming, whereas absenteeism involves frequent or prolonged absence from work. Accurate identification enables tailored interventions that improve workforce health and operational efficiency. Recognizing these patterns helps managers allocate resources strategically to enhance employee well-being and organizational performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Resenteeism | Absenteeism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee physically present but mentally disengaged or unproductive. | Employee physically absent from work, missing scheduled time. |
| Impact on Productivity | Reduces effectiveness and work quality despite attendance. | Work delays, increased workload for other employees. |
| Common Causes | Stress, burnout, low morale, poor management. | Illness, personal issues, lack of motivation. |
| Detection Methods | Performance reviews, employee feedback, monitoring engagement. | Attendance records, time tracking systems. |
| Management Strategies | Improve workplace culture, provide support, enhance motivation. | Health programs, attendance policies, flexible scheduling. |
Which is better?
Absenteeism refers to employees frequently missing work without valid reasons, leading to reduced productivity and increased costs for organizations. Resenteeism occurs when employees are physically present but mentally disengaged or unproductive, often due to stress or dissatisfaction, which can severely impact overall performance. While absenteeism causes direct labor shortages, resenteeism can be more detrimental by quietly undermining workplace morale and efficiency over time.
Connection
Resenteeism and absenteeism are closely connected as both reflect employee disengagement and dissatisfaction within the workplace, often leading to reduced productivity and increased operational costs. Resenteeism occurs when employees physically attend work but are mentally disengaged or unproductive, while absenteeism involves frequent or prolonged absences from work. Addressing underlying issues such as workplace stress, poor management, and job dissatisfaction can effectively reduce both behaviors, enhancing overall organizational performance.
Key Terms
Employee Engagement
Absenteeism refers to frequent or habitual absence from work, negatively impacting overall productivity and team dynamics. Resenteeism occurs when employees are physically present but disengaged, leading to reduced efficiency and morale. Explore strategies to boost employee engagement and mitigate both absenteeism and presenteeism for a thriving workplace.
Workplace Culture
Absenteeism refers to frequent employee absences that disrupt workflow, while presenteeism occurs when employees are physically present but mentally disengaged due to stress or health issues, negatively impacting productivity. A positive workplace culture fosters employee well-being and engagement, reducing both absenteeism and presenteeism by promoting support, recognition, and open communication. Explore effective strategies to cultivate a thriving workplace culture and minimize absenteeism and presenteeism.
Job Satisfaction
Absenteeism refers to employees frequently missing work, while presenteeism involves attending work but underperforming due to disengagement or health issues, both negatively impacting job satisfaction and overall productivity. Low job satisfaction often correlates with higher absenteeism rates and increased presenteeism, leading to decreased morale, reduced quality of work, and costly organizational consequences. Explore effective strategies to enhance job satisfaction and mitigate both absenteeism and presenteeism for a more productive workforce.
Source and External Links
Absenteeism - Wikipedia - Absenteeism refers to a habitual pattern of unplanned and unjustified absences from a duty or obligation, often seen as an indicator of poor performance or a sign of underlying psychological, medical, or social issues.
Fighting Employee Absenteeism: 5 Expert Tips You Need to Know - Absenteeism is chronic or habitual workplace absence that is unplanned and unannounced, including lateness and early departures, and it disrupts trust and engagement within an organization.
Chronic absenteeism | American Federation of Teachers - Chronic absenteeism is defined as missing at least 10% of school days in a year for any reason, and it is a major cause of poor academic achievement, often linked to broader social and economic challenges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com