Urban air mobility revolutionizes logistics by enabling rapid transportation of goods across congested cities, reducing delivery times and operational costs. Last-mile delivery remains a critical challenge, focusing on the efficient distribution of packages from transportation hubs to final destinations, often hindered by traffic and infrastructure limitations. Explore how integrating urban air mobility can transform last-mile logistics and enhance supply chain efficiency.
Why it is important
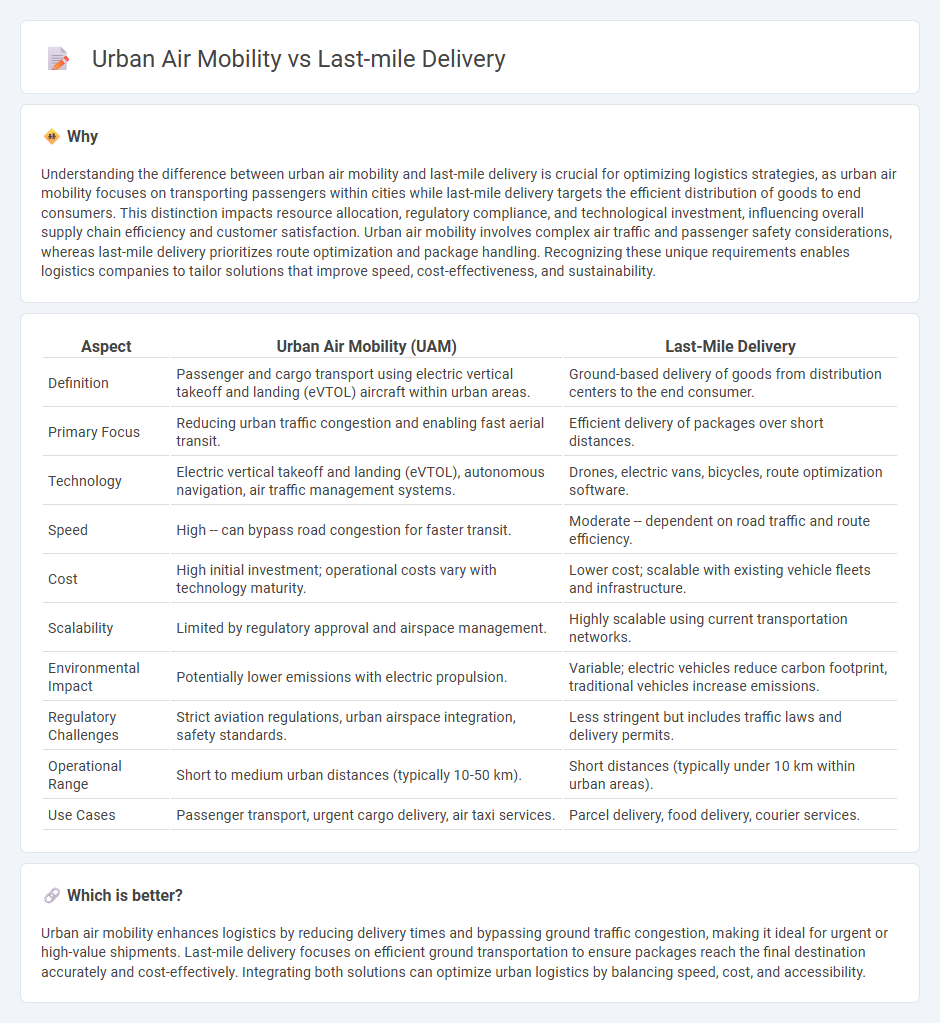
Understanding the difference between urban air mobility and last-mile delivery is crucial for optimizing logistics strategies, as urban air mobility focuses on transporting passengers within cities while last-mile delivery targets the efficient distribution of goods to end consumers. This distinction impacts resource allocation, regulatory compliance, and technological investment, influencing overall supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Urban air mobility involves complex air traffic and passenger safety considerations, whereas last-mile delivery prioritizes route optimization and package handling. Recognizing these unique requirements enables logistics companies to tailor solutions that improve speed, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Urban Air Mobility (UAM) | Last-Mile Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Passenger and cargo transport using electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft within urban areas. | Ground-based delivery of goods from distribution centers to the end consumer. |
| Primary Focus | Reducing urban traffic congestion and enabling fast aerial transit. | Efficient delivery of packages over short distances. |
| Technology | Electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL), autonomous navigation, air traffic management systems. | Drones, electric vans, bicycles, route optimization software. |
| Speed | High -- can bypass road congestion for faster transit. | Moderate -- dependent on road traffic and route efficiency. |
| Cost | High initial investment; operational costs vary with technology maturity. | Lower cost; scalable with existing vehicle fleets and infrastructure. |
| Scalability | Limited by regulatory approval and airspace management. | Highly scalable using current transportation networks. |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially lower emissions with electric propulsion. | Variable; electric vehicles reduce carbon footprint, traditional vehicles increase emissions. |
| Regulatory Challenges | Strict aviation regulations, urban airspace integration, safety standards. | Less stringent but includes traffic laws and delivery permits. |
| Operational Range | Short to medium urban distances (typically 10-50 km). | Short distances (typically under 10 km within urban areas). |
| Use Cases | Passenger transport, urgent cargo delivery, air taxi services. | Parcel delivery, food delivery, courier services. |
Which is better?
Urban air mobility enhances logistics by reducing delivery times and bypassing ground traffic congestion, making it ideal for urgent or high-value shipments. Last-mile delivery focuses on efficient ground transportation to ensure packages reach the final destination accurately and cost-effectively. Integrating both solutions can optimize urban logistics by balancing speed, cost, and accessibility.
Connection
Urban air mobility (UAM) enhances last-mile delivery by utilizing drones and electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft to bypass ground traffic congestion, significantly reducing delivery times in dense city environments. Integration of UAM with real-time logistics platforms improves route optimization and delivery accuracy, supporting faster and more efficient parcel distribution. These advancements contribute to sustainable urban logistics by lowering emissions and minimizing reliance on traditional delivery vehicles.
Key Terms
**Last-Mile Delivery:**
Last-mile delivery, a critical component of logistics, focuses on transporting goods from distribution centers to end consumers, emphasizing speed, cost-effectiveness, and reliability in urban environments. Innovations such as electric vans, autonomous ground vehicles, and advanced route optimization software are revolutionizing last-mile delivery by reducing emissions and operational expenses. Explore how integrating cutting-edge technologies is reshaping the future of urban logistics and customer satisfaction.
Route Optimization
Last-mile delivery relies heavily on ground-based route optimization algorithms to minimize distance, reduce fuel consumption, and meet narrow delivery windows in urban environments. Urban Air Mobility (UAM) introduces aerial route optimization to bypass congested streets, utilizing 3D airspace and real-time traffic data to enhance delivery speed and efficiency. Explore advanced route optimization technologies driving the future of both last-mile delivery and UAM services.
Parcel Tracking
Parcel tracking in last-mile delivery utilizes GPS and real-time data to optimize ground-based logistics, ensuring timely and accurate package arrival. Urban air mobility integrates UAVs and drones, enhancing parcel tracking through aerial surveillance and rapid data relay in congested urban environments. Explore emerging technologies redefining parcel tracking within these innovative delivery frameworks for comprehensive insights.
Source and External Links
Last mile delivery: solutions for your business | DHL Discover - Last mile delivery is the final stage of goods movement from a local distribution center to the end consumer, aiming for affordable, fast, and accurate delivery often via vans, bikes, or drop-off points, with innovations like drones being trialed.
What is Last-Mile Delivery? Logistics, Costs, and Top Carriers - Last-mile delivery involves transporting packages from a fulfillment center to the customer's door, focusing on speed and cost-efficiency, with tracking capabilities vital to customer satisfaction and delivery transparency.
Last Mile Delivery Logistics, Trends and Data for Retailers Explained - Last-mile delivery, the most expensive and time-consuming shipping phase, is critical for customer satisfaction and business growth, with effective strategies boosting speed, convenience, sales, and operational efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com