Internal gig economy offers organizations agility and cost-efficiency by leveraging a flexible workforce for project-based roles, contrasting with permanent employment that provides stability and long-term talent development. Companies adopting internal gig models benefit from rapid skill matching and workforce optimization while managing fluctuating demands. Explore how blending internal gig economy strategies with traditional employment can enhance overall HR effectiveness.
Why it is important
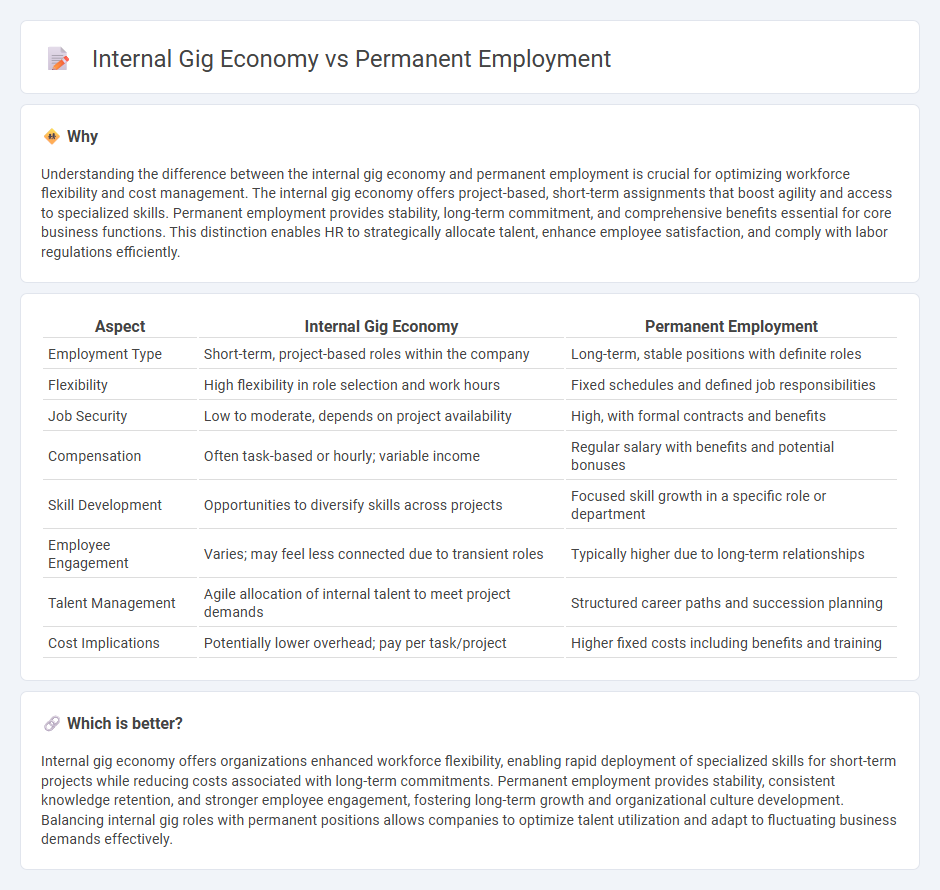
Understanding the difference between the internal gig economy and permanent employment is crucial for optimizing workforce flexibility and cost management. The internal gig economy offers project-based, short-term assignments that boost agility and access to specialized skills. Permanent employment provides stability, long-term commitment, and comprehensive benefits essential for core business functions. This distinction enables HR to strategically allocate talent, enhance employee satisfaction, and comply with labor regulations efficiently.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Internal Gig Economy | Permanent Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Type | Short-term, project-based roles within the company | Long-term, stable positions with definite roles |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in role selection and work hours | Fixed schedules and defined job responsibilities |
| Job Security | Low to moderate, depends on project availability | High, with formal contracts and benefits |
| Compensation | Often task-based or hourly; variable income | Regular salary with benefits and potential bonuses |
| Skill Development | Opportunities to diversify skills across projects | Focused skill growth in a specific role or department |
| Employee Engagement | Varies; may feel less connected due to transient roles | Typically higher due to long-term relationships |
| Talent Management | Agile allocation of internal talent to meet project demands | Structured career paths and succession planning |
| Cost Implications | Potentially lower overhead; pay per task/project | Higher fixed costs including benefits and training |
Which is better?
Internal gig economy offers organizations enhanced workforce flexibility, enabling rapid deployment of specialized skills for short-term projects while reducing costs associated with long-term commitments. Permanent employment provides stability, consistent knowledge retention, and stronger employee engagement, fostering long-term growth and organizational culture development. Balancing internal gig roles with permanent positions allows companies to optimize talent utilization and adapt to fluctuating business demands effectively.
Connection
The internal gig economy reshapes human resources by allowing permanent employees to engage in short-term, project-based tasks within their organization, optimizing workforce flexibility and talent utilization. This model enhances employee skill development and job satisfaction while maintaining the stability associated with permanent employment. Integrating internal gig roles within HR strategies supports agile workforce management and drives organizational innovation.
Key Terms
Job Security
Permanent employment provides stable income, comprehensive benefits, and clear career progression, enhancing job security for employees. In contrast, the internal gig economy offers flexible, project-based roles within organizations but often lacks long-term job guarantees and traditional safety nets. Explore how businesses balance these models to optimize workforce stability and adaptability.
Flexibility
Permanent employment offers stable work schedules and consistent income, often limiting flexibility in task variety and working hours. The internal gig economy allows employees to undertake short-term projects within their organization, providing greater adaptability and control over workloads. Explore how businesses balance flexibility and stability through these evolving employment models.
Career Development
Permanent employment offers structured career development pathways with clear promotion and skill-building opportunities within a single organization, fostering long-term professional growth. The internal gig economy provides flexible project-based roles that enable employees to diversify experience and rapidly acquire new skills across departments, enhancing adaptability and innovation. Explore how these models reshape career trajectories and maximize your professional potential.
Source and External Links
Permanent Jobs: What to Know Before Accepting - This article provides insights into the benefits and aspects of permanent jobs, including job security, employee benefits, and career growth opportunities.
Permanent Employment - Permanent employment involves working for an employer without a predetermined end date, typically offering benefits like health care and paid time off.
Permanent Employment: Definition, Advantages and Differences - This resource defines permanent employment, outlines its advantages, and explains how it differs from other types of employment arrangements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com