Fractional employment offers companies flexible access to specialized HR talent on a part-time basis, optimizing costs while maintaining control over workforce integration. Outsourced labor involves contracting external agencies or firms to manage entire HR functions or projects, often leading to greater scalability but less direct oversight. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to determine the best fit for your organization's HR strategy.
Why it is important
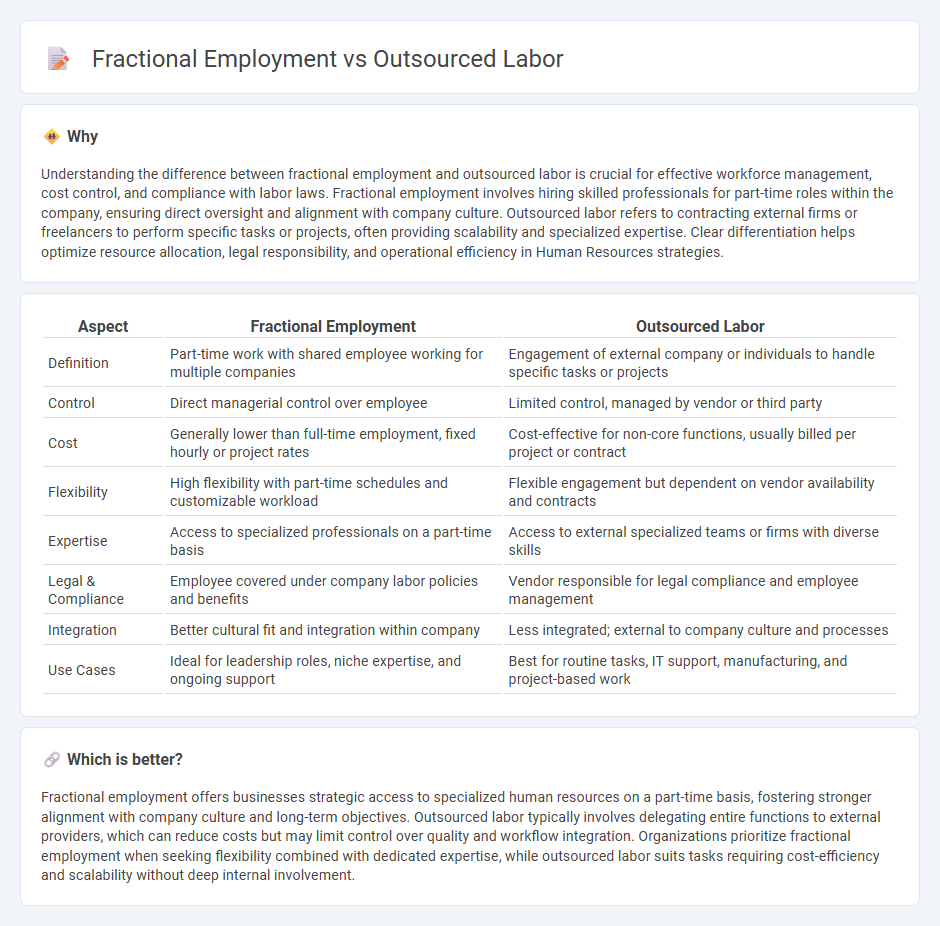
Understanding the difference between fractional employment and outsourced labor is crucial for effective workforce management, cost control, and compliance with labor laws. Fractional employment involves hiring skilled professionals for part-time roles within the company, ensuring direct oversight and alignment with company culture. Outsourced labor refers to contracting external firms or freelancers to perform specific tasks or projects, often providing scalability and specialized expertise. Clear differentiation helps optimize resource allocation, legal responsibility, and operational efficiency in Human Resources strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Employment | Outsourced Labor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Part-time work with shared employee working for multiple companies | Engagement of external company or individuals to handle specific tasks or projects |
| Control | Direct managerial control over employee | Limited control, managed by vendor or third party |
| Cost | Generally lower than full-time employment, fixed hourly or project rates | Cost-effective for non-core functions, usually billed per project or contract |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with part-time schedules and customizable workload | Flexible engagement but dependent on vendor availability and contracts |
| Expertise | Access to specialized professionals on a part-time basis | Access to external specialized teams or firms with diverse skills |
| Legal & Compliance | Employee covered under company labor policies and benefits | Vendor responsible for legal compliance and employee management |
| Integration | Better cultural fit and integration within company | Less integrated; external to company culture and processes |
| Use Cases | Ideal for leadership roles, niche expertise, and ongoing support | Best for routine tasks, IT support, manufacturing, and project-based work |
Which is better?
Fractional employment offers businesses strategic access to specialized human resources on a part-time basis, fostering stronger alignment with company culture and long-term objectives. Outsourced labor typically involves delegating entire functions to external providers, which can reduce costs but may limit control over quality and workflow integration. Organizations prioritize fractional employment when seeking flexibility combined with dedicated expertise, while outsourced labor suits tasks requiring cost-efficiency and scalability without deep internal involvement.
Connection
Fractional employment and outsourced labor both offer flexible workforce solutions by allowing companies to access specialized skills without full-time commitments, reducing operational costs and increasing efficiency. Fractional employment involves hiring professionals for a fraction of their time, often in strategic roles like HR management or finance, while outsourced labor delegates entire functions or projects to external providers. Both approaches support scalable human resource strategies, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to workload fluctuations and focus on core activities.
Key Terms
Contractual Agreements
Outsourced labor involves third-party companies managing entire business functions under comprehensive contractual agreements that specify deliverables, timelines, and service levels. Fractional employment contracts define part-time engagements with individual professionals, detailing specific project scopes and hourly commitments to align with organizational needs. Explore the nuances of contractual agreements to choose the best labor solution for your business goals.
Workforce Flexibility
Outsourced labor offers companies the ability to delegate entire projects or functions to external providers, enabling rapid scalability and cost control without increasing full-time headcount. Fractional employment provides access to specialized expertise on a part-time basis, granting businesses targeted skills and strategic input with flexible commitment levels. Explore how leveraging these workforce models can drive agility and efficiency in your organization.
Cost Structure
Outsourced labor typically incurs variable costs based on project scope and hourly rates, often including management fees and overhead expenses, making it flexible but potentially less predictable. Fractional employment usually involves fixed retainer fees for part-time access to highly skilled professionals, offering cost efficiency with consistent budgeting and scalable engagement. Explore these cost structures further to determine the best fit for your business needs.
Source and External Links
How Outsourcing Labor Can Help Your Company Survive Labor Challenges - Outsourcing labor is hiring third parties to perform tasks or services once done in-house, helping companies cope with labor shortages and changing work environments by accessing external expertise and reducing direct staffing burdens.
Domestic outsourcing is on the rise. What happens when the practice is banned? - Domestic outsourcing involves subcontracting workers rather than hiring directly, often used to cut labor costs, but tends to result in outsourced workers earning less than non-outsourced counterparts in similar roles.
Outsourcing Labor for Small Businesses: A Checklist - Outsourcing labor allows small businesses to reduce costs and access talent by contracting external parties, though effective outsourcing requires clear planning, onboarding, and communication to align with business needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com