Ghost hiring involves discreetly recruiting specific talent to fill critical skill gaps without public job postings, enabling companies to maintain confidentiality and reduce competition. Mass hiring focuses on rapidly onboarding large numbers of employees to support organizational growth or seasonal demand, utilizing broad outreach and streamlined selection processes. Explore the distinct strategies and benefits of ghost hiring versus mass hiring to optimize your workforce management.
Why it is important
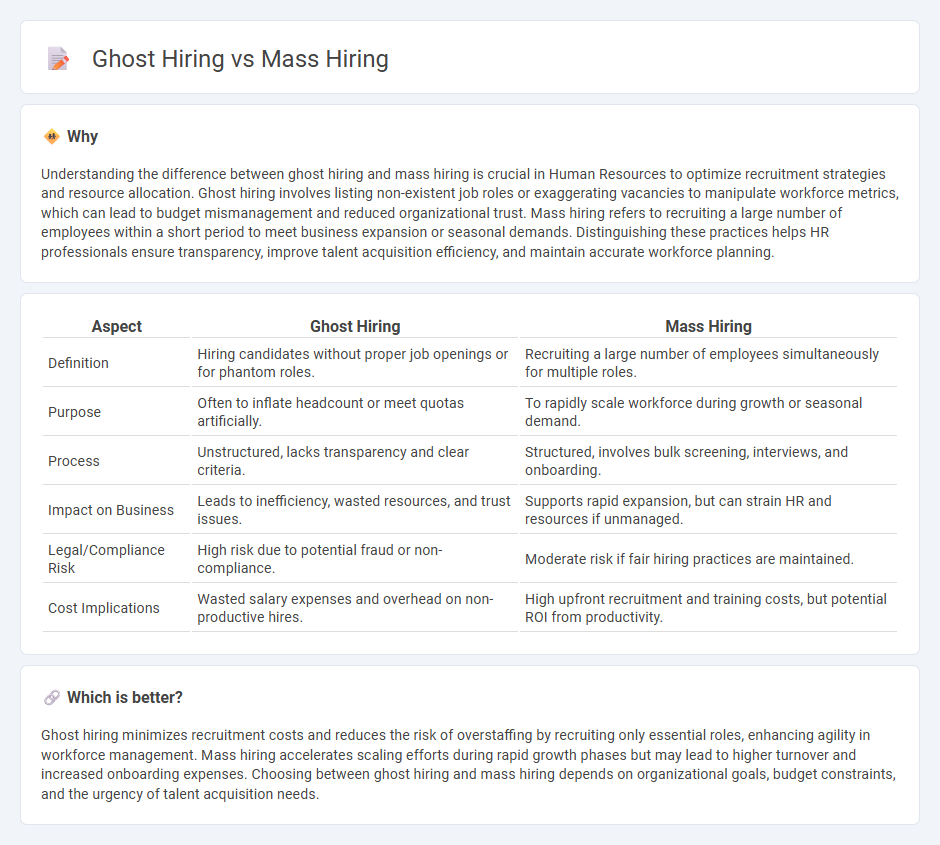
Understanding the difference between ghost hiring and mass hiring is crucial in Human Resources to optimize recruitment strategies and resource allocation. Ghost hiring involves listing non-existent job roles or exaggerating vacancies to manipulate workforce metrics, which can lead to budget mismanagement and reduced organizational trust. Mass hiring refers to recruiting a large number of employees within a short period to meet business expansion or seasonal demands. Distinguishing these practices helps HR professionals ensure transparency, improve talent acquisition efficiency, and maintain accurate workforce planning.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Hiring | Mass Hiring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring candidates without proper job openings or for phantom roles. | Recruiting a large number of employees simultaneously for multiple roles. |
| Purpose | Often to inflate headcount or meet quotas artificially. | To rapidly scale workforce during growth or seasonal demand. |
| Process | Unstructured, lacks transparency and clear criteria. | Structured, involves bulk screening, interviews, and onboarding. |
| Impact on Business | Leads to inefficiency, wasted resources, and trust issues. | Supports rapid expansion, but can strain HR and resources if unmanaged. |
| Legal/Compliance Risk | High risk due to potential fraud or non-compliance. | Moderate risk if fair hiring practices are maintained. |
| Cost Implications | Wasted salary expenses and overhead on non-productive hires. | High upfront recruitment and training costs, but potential ROI from productivity. |
Which is better?
Ghost hiring minimizes recruitment costs and reduces the risk of overstaffing by recruiting only essential roles, enhancing agility in workforce management. Mass hiring accelerates scaling efforts during rapid growth phases but may lead to higher turnover and increased onboarding expenses. Choosing between ghost hiring and mass hiring depends on organizational goals, budget constraints, and the urgency of talent acquisition needs.
Connection
Ghost hiring and mass hiring are connected through their impact on workforce planning and resource allocation in Human Resources. Ghost hiring, where positions are listed without intent to fill them immediately, often precedes mass hiring to forecast future talent needs or buffer against attrition. Both strategies influence recruitment cycles, budget distribution, and organizational growth by managing employee supply and demand proactively.
Key Terms
**Mass Hiring:**
Mass hiring involves recruiting a large number of candidates within a short timeframe to rapidly scale workforce capacity, often employed by retail, manufacturing, and call center industries facing high turnover rates. This process optimizes operational efficiency and reduces hiring costs per employee by leveraging bulk interviewing and automated screening tools. Discover effective strategies and best practices to enhance your mass hiring outcomes.
Recruitment Drive
Mass hiring involves recruiting a large number of candidates simultaneously to quickly fill numerous vacancies, ensuring workforce scalability and operational efficiency. Ghost hiring refers to creating job openings without an immediate intent to hire, often to build a talent pipeline or gauge market response. Explore the impact of these strategies on recruitment drive effectiveness and organizational growth.
Onboarding Process
Mass hiring expedites the recruitment of large talent pools but often challenges the onboarding process with limited personalization and increased administrative complexity. Ghost hiring, involving recruiting without immediate job openings, streamlines onboarding by preparing candidates in advance, reducing time-to-productivity when roles officially open. Explore detailed strategies to optimize onboarding efficiency in both hiring approaches.
Source and External Links
MassHire - Mass.gov - Provides a statewide network connecting businesses and jobseekers, offering job search tools, training programs, job fairs, and funding to help with mass hiring and workforce development in various high-growth industries.
Amazon Jobs Hiring Now - Hourly & Shift Jobs @ Amazon - Amazon is actively mass hiring for hourly positions including warehouse and delivery roles, offering increased pay, flexible schedules, and benefits, aiming to hire 250,000 people.
MassHire Springfield: Jobs, Training, Job Fairs, Employment - Connects job seekers with employers and training resources regionally with no cost job postings, supporting mass hiring initiatives with a focus on personalized employment assistance and workforce re-entry.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com