Effective human resources strategies balance workforce motivation and productivity to foster sustainable business growth. Good jobs strategies emphasize employee training, job security, and fair wages to enhance job satisfaction and innovation, while lean production focuses on reducing waste and maximizing efficiency through streamlined processes and workforce flexibility. Explore how aligning human resources practices with organizational goals can drive competitive advantage.
Why it is important
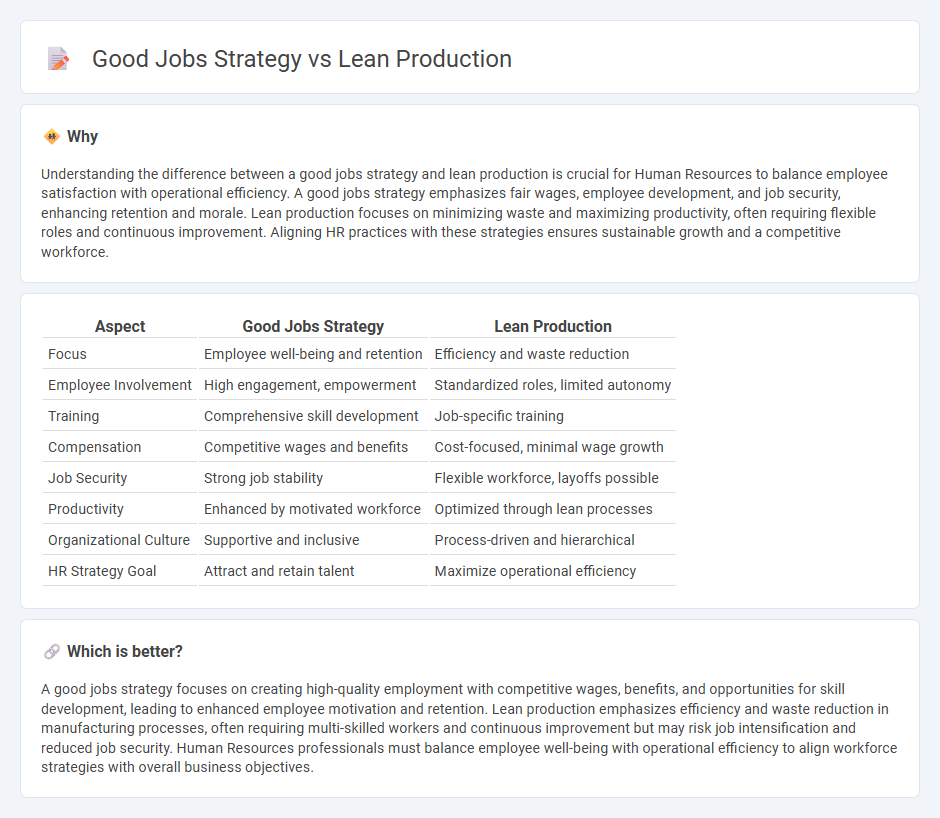
Understanding the difference between a good jobs strategy and lean production is crucial for Human Resources to balance employee satisfaction with operational efficiency. A good jobs strategy emphasizes fair wages, employee development, and job security, enhancing retention and morale. Lean production focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing productivity, often requiring flexible roles and continuous improvement. Aligning HR practices with these strategies ensures sustainable growth and a competitive workforce.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Good Jobs Strategy | Lean Production |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Employee well-being and retention | Efficiency and waste reduction |
| Employee Involvement | High engagement, empowerment | Standardized roles, limited autonomy |
| Training | Comprehensive skill development | Job-specific training |
| Compensation | Competitive wages and benefits | Cost-focused, minimal wage growth |
| Job Security | Strong job stability | Flexible workforce, layoffs possible |
| Productivity | Enhanced by motivated workforce | Optimized through lean processes |
| Organizational Culture | Supportive and inclusive | Process-driven and hierarchical |
| HR Strategy Goal | Attract and retain talent | Maximize operational efficiency |
Which is better?
A good jobs strategy focuses on creating high-quality employment with competitive wages, benefits, and opportunities for skill development, leading to enhanced employee motivation and retention. Lean production emphasizes efficiency and waste reduction in manufacturing processes, often requiring multi-skilled workers and continuous improvement but may risk job intensification and reduced job security. Human Resources professionals must balance employee well-being with operational efficiency to align workforce strategies with overall business objectives.
Connection
A good jobs strategy enhances employee engagement and productivity, which aligns closely with lean production principles focused on eliminating waste and optimizing workflows. Integrating lean production techniques in human resources management promotes continuous improvement, skill development, and efficient resource allocation. This synergy leads to higher job satisfaction, reduced turnover, and sustained organizational performance.
Key Terms
Workforce Flexibility
Lean production emphasizes workforce flexibility through multi-skilled employees and just-in-time labor deployment, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. Good jobs strategy prioritizes stable employment, fair wages, and employee well-being while fostering adaptability through continuous training and participative work environments. Explore how balancing these approaches optimizes both productivity and job quality.
Employee Empowerment
Lean production emphasizes employee empowerment by fostering continuous improvement and enabling workers to contribute ideas that enhance efficiency and reduce waste. Good jobs strategy prioritizes employee empowerment through fair wages, job security, and opportunities for skill development, creating a supportive work environment that values worker well-being. Discover more about how integrating these approaches can drive sustainable business success and workforce satisfaction.
Skill Development
Lean production emphasizes efficiency and waste reduction, often requiring workers to develop multi-functional skills through continuous training and problem-solving techniques. Good jobs strategy prioritizes comprehensive skill development, career progression, and job security, fostering employee motivation and long-term commitment. Explore how integrating skill development in both approaches can enhance productivity and worker satisfaction.
Source and External Links
Understanding Lean Manufacturing | KAIZEN Article - Lean Manufacturing is a framework focused on optimizing production by ensuring essential stability, production flow, and internal logistics flow to enhance quality and minimize costs through skilled labor, reliable machinery, quality materials, and standardized methods.
Lean Production - Lean Production is a management philosophy that maximizes customer value by eliminating waste such as overproduction, waiting, and defects while promoting continuous improvement (Kaizen) and Just-In-Time production.
Lean manufacturing - Lean manufacturing is a method aimed at reducing production and supplier response times by eliminating non-value adding activities and wastes, inspired by the Toyota Production System, focusing on efficiency, productivity, and continuous improvement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com