Fractional employment offers companies flexible access to specialized skills on a part-time basis, optimizing workforce costs while enhancing productivity. Internships provide hands-on experience for students or recent graduates, fostering talent development and potential employee pipelines. Explore the benefits and differences between fractional employment and internships to optimize your human resources strategy.
Why it is important
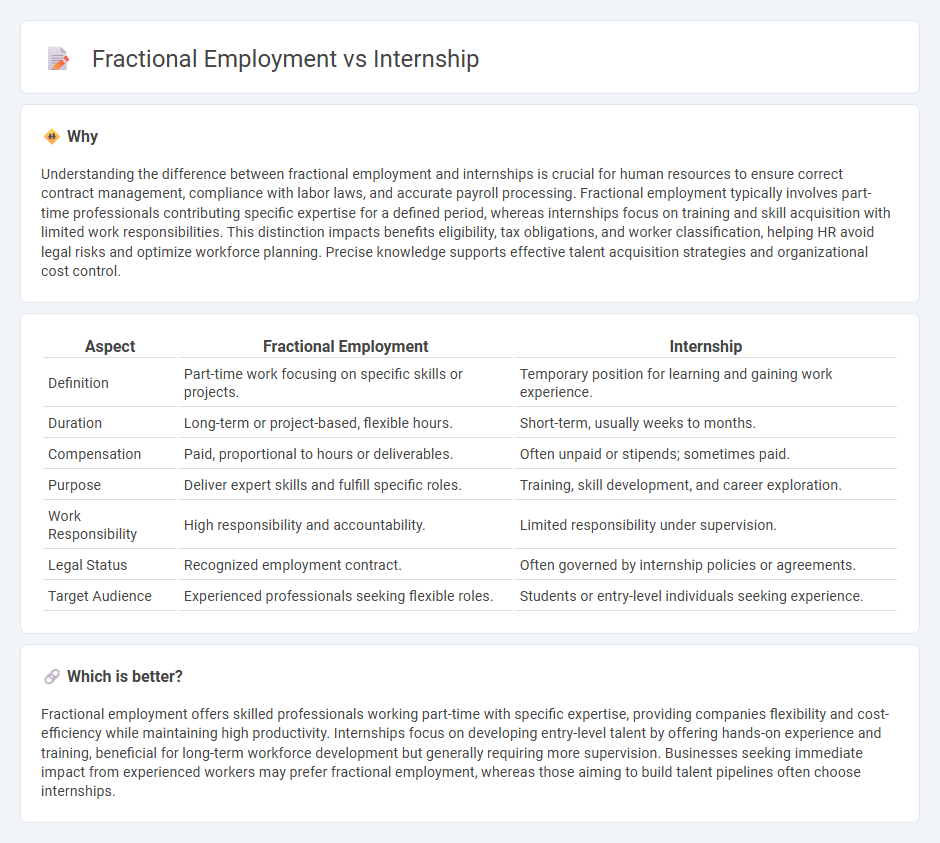
Understanding the difference between fractional employment and internships is crucial for human resources to ensure correct contract management, compliance with labor laws, and accurate payroll processing. Fractional employment typically involves part-time professionals contributing specific expertise for a defined period, whereas internships focus on training and skill acquisition with limited work responsibilities. This distinction impacts benefits eligibility, tax obligations, and worker classification, helping HR avoid legal risks and optimize workforce planning. Precise knowledge supports effective talent acquisition strategies and organizational cost control.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Employment | Internship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Part-time work focusing on specific skills or projects. | Temporary position for learning and gaining work experience. |
| Duration | Long-term or project-based, flexible hours. | Short-term, usually weeks to months. |
| Compensation | Paid, proportional to hours or deliverables. | Often unpaid or stipends; sometimes paid. |
| Purpose | Deliver expert skills and fulfill specific roles. | Training, skill development, and career exploration. |
| Work Responsibility | High responsibility and accountability. | Limited responsibility under supervision. |
| Legal Status | Recognized employment contract. | Often governed by internship policies or agreements. |
| Target Audience | Experienced professionals seeking flexible roles. | Students or entry-level individuals seeking experience. |
Which is better?
Fractional employment offers skilled professionals working part-time with specific expertise, providing companies flexibility and cost-efficiency while maintaining high productivity. Internships focus on developing entry-level talent by offering hands-on experience and training, beneficial for long-term workforce development but generally requiring more supervision. Businesses seeking immediate impact from experienced workers may prefer fractional employment, whereas those aiming to build talent pipelines often choose internships.
Connection
Fractional employment and internships both offer flexible work arrangements that enable organizations to access specialized skills without committing to full-time hires. Internships provide emerging talent with hands-on experience and potential pathways to fractional roles, while fractional employment allows businesses to engage skilled professionals part-time to meet specific project needs. This synergy helps companies optimize workforce resources, enhance talent development, and adapt to dynamic operational demands.
Key Terms
Duration
Internship durations typically range from a few weeks to six months, designed to provide short-term, practical experience for students or recent graduates. Fractional employment involves longer-term commitments, often spanning several months to years, where professionals contribute part-time to multiple companies or projects. Explore more to understand how duration impacts career development and project engagement.
Commitment level
Internships typically require a short-term commitment focused on gaining experience and skills, often lasting a few months. Fractional employment involves a part-time or project-based commitment where professionals contribute expertise with more flexibility and longer-term engagement. Explore the differences in commitment levels to determine which option best suits your career goals.
Compensation
Internship compensation typically involves stipends or academic credit, reflecting limited work hours and learning objectives, while fractional employment offers pro-rated salaries aligned with actual work contributions and professional qualifications. Interns may receive non-monetary benefits like mentorship and skill development, whereas fractional employees earn income proportionate to their part-time engagement under formal contracts. Explore further to understand the financial and legal nuances governing both internship stipends and fractional employment pay structures.
Source and External Links
Internship - Wikipedia - An internship is a temporary period of work experience offered by organizations to students or graduates seeking skills and exposure in a specific field, often serving as a pathway to future employment.
What Is an Internship? - UMBC Career Center - An internship is a supervised, structured professional learning experience that allows students to gain practical, relevant work experience in their field of study or career interest.
Internship Meaning and Definition: A NACE Guide - According to NACE, an internship is a form of experiential learning that integrates academic knowledge with practical application and skill development in a professional workplace setting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com