The internal gig economy leverages a company's existing workforce by matching employees with short-term projects or roles based on their skills and availability, enhancing flexibility and talent utilization. In contrast, the external gig economy relies on freelance or contract workers outside the organization, offering access to diverse expertise and cost-efficiency but posing challenges in integration and retention. Discover how balancing internal and external gig economies can transform your human resources strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between the internal gig economy and external gig economy is crucial for Human Resources to effectively manage talent allocation and workforce flexibility. The internal gig economy involves leveraging current employees for short-term projects, enhancing employee engagement and retention. The external gig economy taps into freelance or contract workers outside the organization, providing access to diverse skills and cost efficiency. This distinction helps HR optimize resource planning, compliance, and strategic hiring decisions.
Comparison Table
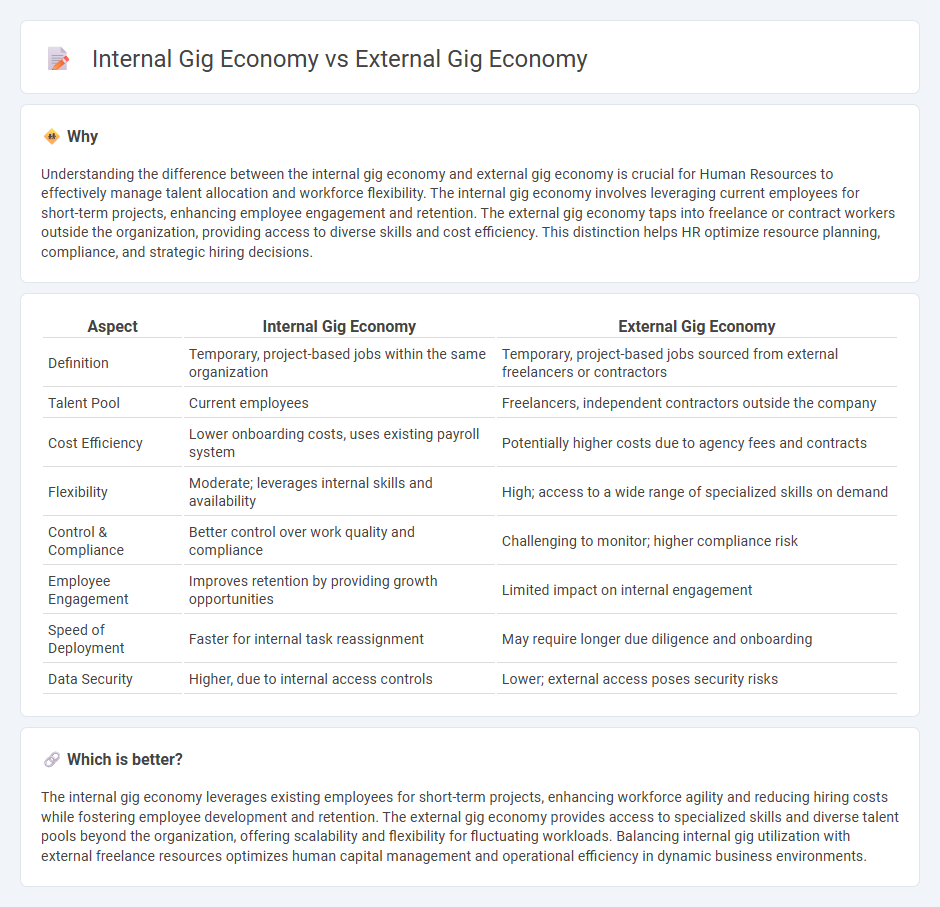
| Aspect | Internal Gig Economy | External Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary, project-based jobs within the same organization | Temporary, project-based jobs sourced from external freelancers or contractors |
| Talent Pool | Current employees | Freelancers, independent contractors outside the company |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower onboarding costs, uses existing payroll system | Potentially higher costs due to agency fees and contracts |
| Flexibility | Moderate; leverages internal skills and availability | High; access to a wide range of specialized skills on demand |
| Control & Compliance | Better control over work quality and compliance | Challenging to monitor; higher compliance risk |
| Employee Engagement | Improves retention by providing growth opportunities | Limited impact on internal engagement |
| Speed of Deployment | Faster for internal task reassignment | May require longer due diligence and onboarding |
| Data Security | Higher, due to internal access controls | Lower; external access poses security risks |
Which is better?
The internal gig economy leverages existing employees for short-term projects, enhancing workforce agility and reducing hiring costs while fostering employee development and retention. The external gig economy provides access to specialized skills and diverse talent pools beyond the organization, offering scalability and flexibility for fluctuating workloads. Balancing internal gig utilization with external freelance resources optimizes human capital management and operational efficiency in dynamic business environments.
Connection
The internal gig economy leverages a company's existing workforce by offering short-term projects and flexible roles, while the external gig economy connects organizations with freelance professionals outside the company. Both systems enhance workforce agility, enable rapid talent acquisition, and reduce hiring costs by tapping into specialized skills on demand. Integrating internal and external gig economies fosters a seamless talent ecosystem that maximizes resource optimization and supports dynamic business needs.
Key Terms
Talent Marketplace
External gig economy leverages freelance platforms such as Upwork and Fiverr to source specialized talent on-demand, enhancing flexibility and reducing long-term hiring costs. Internal gig economy utilizes a Talent Marketplace within organizations, enabling employees to access project-based opportunities that optimize skill deployment and increase workforce agility. Explore how internal Talent Marketplaces transform workforce management and boost employee engagement.
Flexible Workforce
The external gig economy leverages freelance talent through platforms like Upwork and Fiverr, offering companies scalable and diverse skill sets on demand, while the internal gig economy utilizes existing employees to undertake flexible, project-based tasks within the organization. Internal gig platforms such as Rover at Deloitte enhance employee engagement and optimize workforce agility by matching skills to short-term projects without external recruitment costs. Explore how businesses are integrating flexible workforce models to boost productivity and employee satisfaction.
Project-Based Assignments
External gig economy leverages freelance platforms like Upwork and Fiverr, connecting businesses with specialized talent for short-term, project-based assignments to enhance flexibility and cost-efficiency. Internal gig economy utilizes a company's existing workforce to allocate internal projects, fostering skill development and resource optimization without the overhead of external hiring. Explore how companies strategically blend both models to maximize project-based performance and agility.
Source and External Links
The Gig Economy: Flexibility or Fragility? - The external gig economy offers flexibility but often results in worker isolation, lack of unionization, and precarious conditions while companies benefit by minimizing labor costs and avoiding employee protections.
Gig economy: Threat or opportunity? - External gig opportunities attract and retain top talent by allowing employees to showcase diverse skills and achieve personal milestones without leaving their organizations.
HR Issues: The Gig Economy - Research Guides - CUNY - The external gig economy comprises contingent and alternative work arrangements such as freelancers and independent contractors, lacking formal employment contracts and official government statistical definitions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com