Borderless hiring empowers companies to access a global talent pool without geographic constraints, leveraging remote work and digital collaboration tools to enhance flexibility and reduce costs. Expatriate staffing involves relocating employees internationally, fostering direct control, cultural integration, and on-site expertise in foreign markets. Explore the advantages and challenges of both approaches to optimize your global workforce strategy.
Why it is important
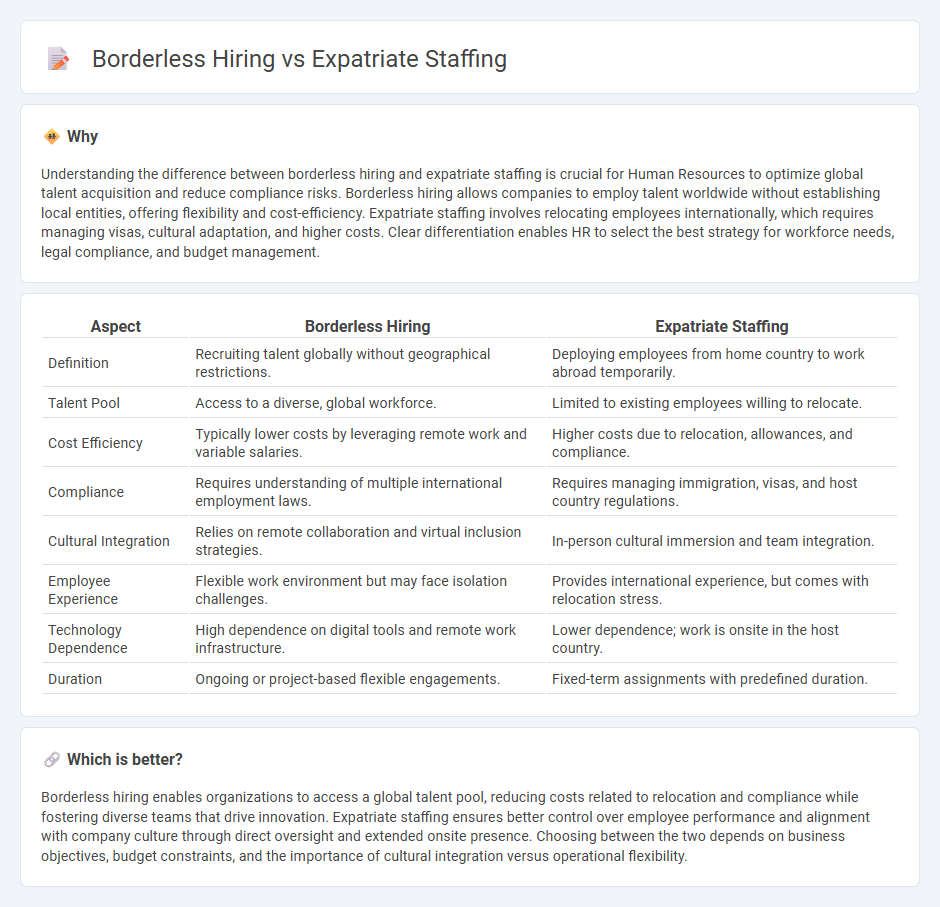
Understanding the difference between borderless hiring and expatriate staffing is crucial for Human Resources to optimize global talent acquisition and reduce compliance risks. Borderless hiring allows companies to employ talent worldwide without establishing local entities, offering flexibility and cost-efficiency. Expatriate staffing involves relocating employees internationally, which requires managing visas, cultural adaptation, and higher costs. Clear differentiation enables HR to select the best strategy for workforce needs, legal compliance, and budget management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Borderless Hiring | Expatriate Staffing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recruiting talent globally without geographical restrictions. | Deploying employees from home country to work abroad temporarily. |
| Talent Pool | Access to a diverse, global workforce. | Limited to existing employees willing to relocate. |
| Cost Efficiency | Typically lower costs by leveraging remote work and variable salaries. | Higher costs due to relocation, allowances, and compliance. |
| Compliance | Requires understanding of multiple international employment laws. | Requires managing immigration, visas, and host country regulations. |
| Cultural Integration | Relies on remote collaboration and virtual inclusion strategies. | In-person cultural immersion and team integration. |
| Employee Experience | Flexible work environment but may face isolation challenges. | Provides international experience, but comes with relocation stress. |
| Technology Dependence | High dependence on digital tools and remote work infrastructure. | Lower dependence; work is onsite in the host country. |
| Duration | Ongoing or project-based flexible engagements. | Fixed-term assignments with predefined duration. |
Which is better?
Borderless hiring enables organizations to access a global talent pool, reducing costs related to relocation and compliance while fostering diverse teams that drive innovation. Expatriate staffing ensures better control over employee performance and alignment with company culture through direct oversight and extended onsite presence. Choosing between the two depends on business objectives, budget constraints, and the importance of cultural integration versus operational flexibility.
Connection
Borderless hiring expands talent acquisition beyond geographic limits, directly feeding the expatriate staffing process by placing employees in international roles. Companies optimize global workforce agility by integrating borderless recruitment with expatriate assignments, ensuring cultural fit and compliance across diverse markets. This synergy enhances organizational competitiveness through seamless human resource deployment worldwide.
Key Terms
Global Mobility
Expatriate staffing involves relocating employees across borders with comprehensive support for visas, housing, and cultural integration, ensuring compliance with international labor laws. Borderless hiring leverages technology and flexible work arrangements to engage talent globally without the need for physical relocation, streamlining payroll, tax, and legal processes. Explore the nuances of global mobility strategies to optimize your organization's international workforce solutions.
Talent Acquisition
Expatriate staffing involves relocating employees internationally with visa sponsorship, ensuring compliance with local labor laws and cultural integration support, which can be time-consuming and costly. Borderless hiring leverages digital platforms to recruit talent globally without physical relocation, optimizing talent acquisition by reducing relocation expenses and minimizing legal complexities. Explore how these approaches can transform your talent acquisition strategy for global workforce agility.
Localization
Expatriate staffing involves relocating employees internationally, often requiring adaptation to local regulations and cultural norms, while borderless hiring emphasizes a global talent pool without geographic constraints, prioritizing flexibility and remote work. Localization in expatriate staffing ensures compliance and cultural integration, whereas borderless hiring leverages technology to manage diverse, decentralized teams effectively. Explore how businesses optimize workforce strategies by combining expatriate staffing and borderless hiring to enhance localization and global operations.
Source and External Links
14.2 Staffing Internationally - Expatriate staffing is a strategy where employees from the home country are sent to work in overseas locations, serving as a bridge for company culture and operations abroad, with advantages and disadvantages compared to hiring locals or third-country nationals.
What Is an Expatriate Employee? Pros & Cons - Expatriate employees are professionals temporarily working in a foreign country, providing operational consistency, company-specific expertise, talent gap solutions, and cultural bridge-building to support international business success.
Staffing Policy & HRM Issues in International Business - In international business, expatriate staffing involves placing foreign employees in key positions while aligning HR policies with local employment laws to balance expatriates' and local workers' contributions, as seen in countries like the UAE.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com