Ghost hiring refers to the practice of listing job openings without genuine intent to fill them, often to gauge market availability or competitor strategies, whereas contingent hiring involves recruiting temporary or contract workers to meet fluctuating business demands. Companies utilizing contingent hiring benefit from workforce flexibility, cost efficiency, and access to specialized skills without long-term commitments. Explore further to understand the strategic impact and operational nuances of ghost versus contingent hiring.
Why it is important
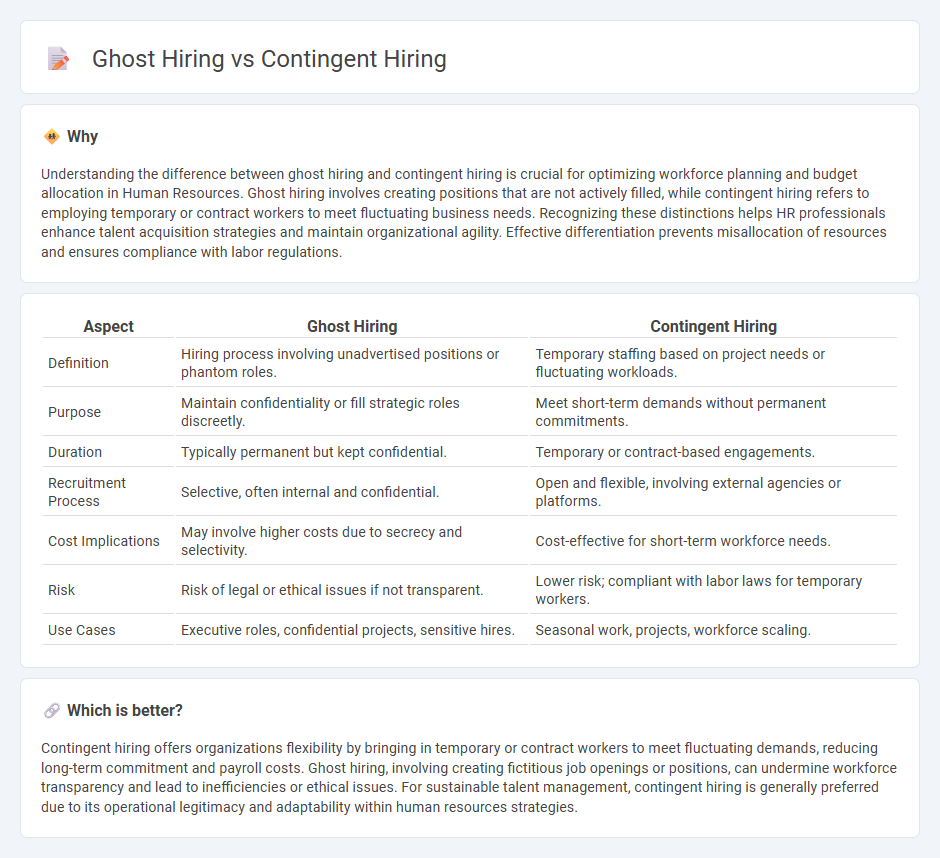
Understanding the difference between ghost hiring and contingent hiring is crucial for optimizing workforce planning and budget allocation in Human Resources. Ghost hiring involves creating positions that are not actively filled, while contingent hiring refers to employing temporary or contract workers to meet fluctuating business needs. Recognizing these distinctions helps HR professionals enhance talent acquisition strategies and maintain organizational agility. Effective differentiation prevents misallocation of resources and ensures compliance with labor regulations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Hiring | Contingent Hiring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring process involving unadvertised positions or phantom roles. | Temporary staffing based on project needs or fluctuating workloads. |
| Purpose | Maintain confidentiality or fill strategic roles discreetly. | Meet short-term demands without permanent commitments. |
| Duration | Typically permanent but kept confidential. | Temporary or contract-based engagements. |
| Recruitment Process | Selective, often internal and confidential. | Open and flexible, involving external agencies or platforms. |
| Cost Implications | May involve higher costs due to secrecy and selectivity. | Cost-effective for short-term workforce needs. |
| Risk | Risk of legal or ethical issues if not transparent. | Lower risk; compliant with labor laws for temporary workers. |
| Use Cases | Executive roles, confidential projects, sensitive hires. | Seasonal work, projects, workforce scaling. |
Which is better?
Contingent hiring offers organizations flexibility by bringing in temporary or contract workers to meet fluctuating demands, reducing long-term commitment and payroll costs. Ghost hiring, involving creating fictitious job openings or positions, can undermine workforce transparency and lead to inefficiencies or ethical issues. For sustainable talent management, contingent hiring is generally preferred due to its operational legitimacy and adaptability within human resources strategies.
Connection
Ghost hiring and contingent hiring are interconnected practices within Human Resources that address workforce flexibility and talent acquisition. Ghost hiring involves creating fictitious job requisitions or positions to attract candidates or assess talent pipelines without immediate hiring intent, while contingent hiring focuses on recruiting temporary or contract workers for short-term organizational needs. Both strategies enable companies to manage labor costs, respond swiftly to fluctuating demand, and optimize talent management through agile workforce planning.
Key Terms
Temporary Employment
Contingent hiring involves recruiting temporary employees to meet short-term business needs, optimizing workforce flexibility without long-term commitments. Ghost hiring refers to the practice of posting job openings without intent to fill them immediately, often used to gauge market interest or signal growth. Explore effective temporary employment strategies by understanding the distinctions between contingent and ghost hiring.
Phantom Job Posting
Contingent hiring involves recruiting temporary or project-based professionals, while ghost hiring refers to phantom job postings that companies list without intent to fill, often used to gauge market interest or increase talent pool visibility. Phantom job postings can mislead applicants and distort labor market analytics, complicating recruitment strategies for both employers and candidates. Explore more about the impact and identification of ghost hiring practices to optimize your talent acquisition approach.
Workforce Flexibility
Contingent hiring allows companies to quickly adjust workforce size by employing temporary or contract workers, optimizing labor costs and meeting fluctuating project demands. Ghost hiring, on the other hand, involves listing fictitious job openings to inflate hiring metrics or deter competitors, which can undermine workforce planning and trust. Explore how mastering these hiring strategies enhances workforce flexibility and business agility.
Source and External Links
Contingent Recruitment - BambooHR - Contingent hiring involves using recruitment agencies paid only when a candidate they present is hired, typically for roles filled on a contingency basis with no upfront fee to the company.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com