Blind hiring eliminates bias by removing personal information such as name, gender, and age from applications, focusing solely on candidates' skills and experience. Competency modeling identifies the specific skills, behaviors, and attributes required for successful performance in a job role, ensuring alignment with organizational goals. Discover how integrating blind hiring with competency modeling can enhance talent acquisition and foster workplace diversity.
Why it is important
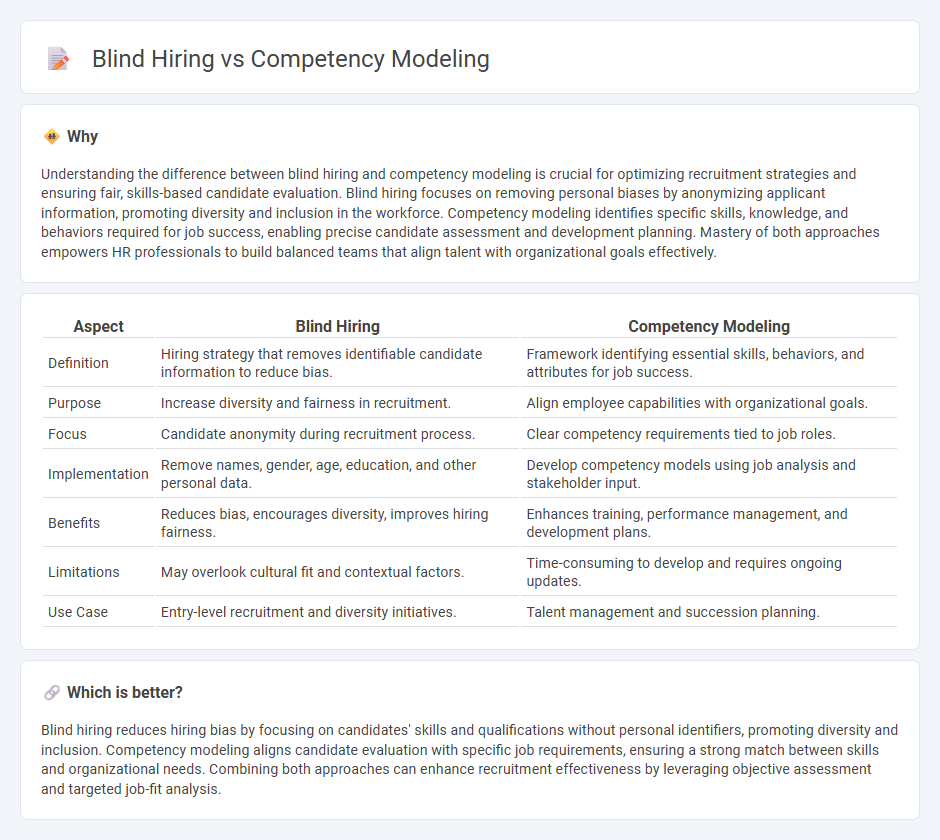
Understanding the difference between blind hiring and competency modeling is crucial for optimizing recruitment strategies and ensuring fair, skills-based candidate evaluation. Blind hiring focuses on removing personal biases by anonymizing applicant information, promoting diversity and inclusion in the workforce. Competency modeling identifies specific skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for job success, enabling precise candidate assessment and development planning. Mastery of both approaches empowers HR professionals to build balanced teams that align talent with organizational goals effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blind Hiring | Competency Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring strategy that removes identifiable candidate information to reduce bias. | Framework identifying essential skills, behaviors, and attributes for job success. |
| Purpose | Increase diversity and fairness in recruitment. | Align employee capabilities with organizational goals. |
| Focus | Candidate anonymity during recruitment process. | Clear competency requirements tied to job roles. |
| Implementation | Remove names, gender, age, education, and other personal data. | Develop competency models using job analysis and stakeholder input. |
| Benefits | Reduces bias, encourages diversity, improves hiring fairness. | Enhances training, performance management, and development plans. |
| Limitations | May overlook cultural fit and contextual factors. | Time-consuming to develop and requires ongoing updates. |
| Use Case | Entry-level recruitment and diversity initiatives. | Talent management and succession planning. |
Which is better?
Blind hiring reduces hiring bias by focusing on candidates' skills and qualifications without personal identifiers, promoting diversity and inclusion. Competency modeling aligns candidate evaluation with specific job requirements, ensuring a strong match between skills and organizational needs. Combining both approaches can enhance recruitment effectiveness by leveraging objective assessment and targeted job-fit analysis.
Connection
Blind hiring reduces bias by anonymizing candidate information, allowing for a focus on demonstrated skills and competencies. Competency modeling provides a structured framework to identify essential skills and behaviors needed for success in a role. Integrating blind hiring with competency modeling ensures candidate evaluation centers on objective qualifications rather than subjective factors, improving diversity and fit.
Key Terms
**Competency Modeling:**
Competency modeling identifies specific skills, behaviors, and attributes required for successful job performance, enabling organizations to align recruitment and training processes with strategic goals. This approach enhances employee development by providing clear performance expectations and criteria for career progression. Explore more insights on how competency modeling optimizes talent management and drives organizational success.
Job Analysis
Competency modeling emphasizes identifying specific skills, behaviors, and attributes required for a job through comprehensive job analysis, ensuring alignment between candidate capabilities and role expectations. Blind hiring removes demographic and personal information to reduce unconscious bias but may overlook critical competencies identified through job analysis. Explore how integrating robust job analysis enhances both competency modeling and blind hiring strategies for optimal talent acquisition.
Behavioral Indicators
Competency modeling emphasizes defining specific behavioral indicators that predict successful job performance, enabling organizations to identify candidates who align with desired skills and attributes. Blind hiring removes demographic and identity information to reduce bias but may overlook critical behavioral competencies essential for role fit. Explore how integrating behavioral indicators into blind hiring can enhance both fairness and effectiveness in talent acquisition.
Source and External Links
Competency Model: Complete Guide With Examples - This webpage provides a comprehensive guide on creating a competency model, including steps to define goals, identify key roles, conduct job analysis, and validate the model for effective organizational alignment.
What Is a Competency Model? - The AIHR blog offers expert guidance on developing a competency model, including defining competencies, identifying critical behaviors, and structuring the model to align with organizational goals.
Competency Models: Benefits, Types, Examples (+Template) - This article discusses the benefits of competency models, provides examples, and offers a template for developing an effective model that aligns with business objectives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com