Silent quitting signifies employees reducing effort to basic tasks without formally resigning, often due to disengagement or unmet expectations. Burnout is a state of chronic physical and emotional exhaustion from prolonged workplace stress, impacting productivity and well-being. Explore the key differences, causes, and solutions to silent quitting and burnout within Human Resources.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between silent quitting and burnout is crucial for effective human resources management to tailor interventions and support employee well-being. Silent quitting involves employees disengaging and doing the bare minimum without formally resigning, which can signal dissatisfaction or lack of motivation. Burnout is a state of chronic physical and emotional exhaustion caused by prolonged work stress, requiring distinct recovery and workload adjustments. Recognizing these differences helps HR implement targeted strategies for retention, productivity, and mental health support.
Comparison Table
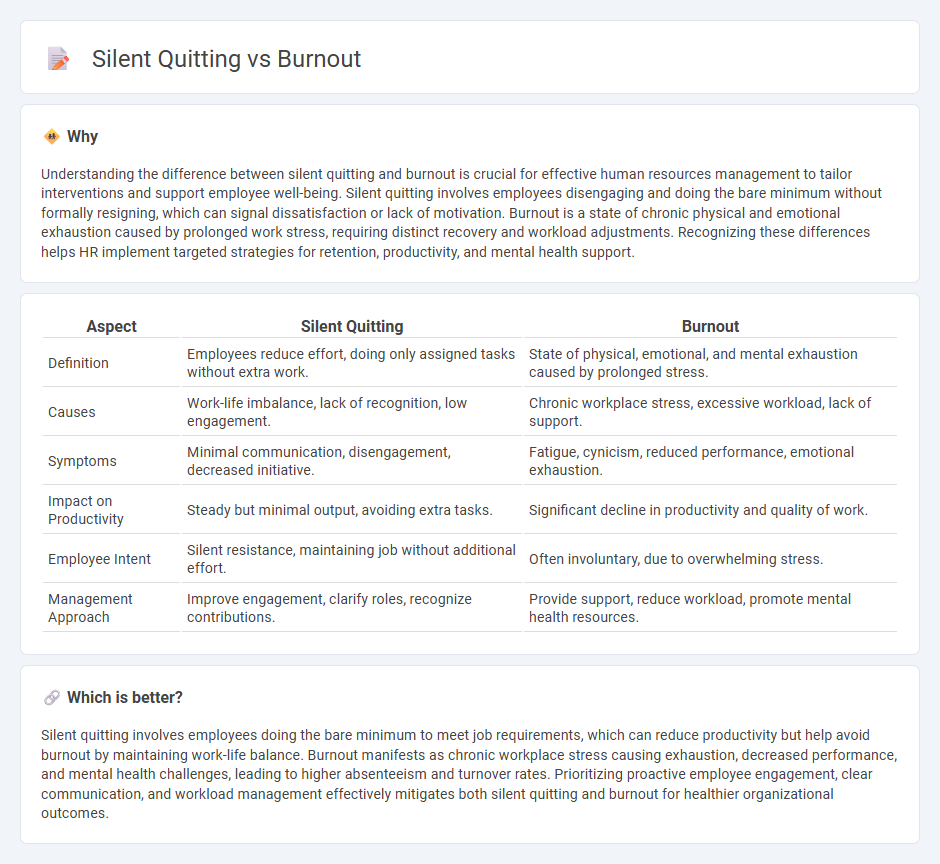
| Aspect | Silent Quitting | Burnout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees reduce effort, doing only assigned tasks without extra work. | State of physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged stress. |
| Causes | Work-life imbalance, lack of recognition, low engagement. | Chronic workplace stress, excessive workload, lack of support. |
| Symptoms | Minimal communication, disengagement, decreased initiative. | Fatigue, cynicism, reduced performance, emotional exhaustion. |
| Impact on Productivity | Steady but minimal output, avoiding extra tasks. | Significant decline in productivity and quality of work. |
| Employee Intent | Silent resistance, maintaining job without additional effort. | Often involuntary, due to overwhelming stress. |
| Management Approach | Improve engagement, clarify roles, recognize contributions. | Provide support, reduce workload, promote mental health resources. |
Which is better?
Silent quitting involves employees doing the bare minimum to meet job requirements, which can reduce productivity but help avoid burnout by maintaining work-life balance. Burnout manifests as chronic workplace stress causing exhaustion, decreased performance, and mental health challenges, leading to higher absenteeism and turnover rates. Prioritizing proactive employee engagement, clear communication, and workload management effectively mitigates both silent quitting and burnout for healthier organizational outcomes.
Connection
Silent quitting often stems from chronic burnout, where employees disengage and do only the minimum required tasks to cope with overwhelming stress and exhaustion. Burnout reduces motivation and productivity, leading to a withdrawal from discretionary efforts and decreased job satisfaction. Human Resources must address burnout proactively through workload management and mental health support to prevent silent quitting and retain talent.
Key Terms
Employee Engagement
Employee engagement significantly declines in both burnout and silent quitting, impacting overall productivity and organizational morale. Burnout occurs due to prolonged workplace stress, leading to emotional exhaustion, whereas silent quitting reflects employees doing only the minimum required, disengaging from extra responsibilities. Explore effective strategies to enhance employee engagement and mitigate these challenges.
Work-Life Balance
Burnout results from prolonged workplace stress leading to physical and emotional exhaustion, while silent quitting reflects disengagement by doing the minimum required. Both phenomena indicate poor work-life balance, impacting productivity and mental health. Explore effective strategies to restore balance and prevent burnout or silent quitting in your organization.
Job Satisfaction
Burnout manifests as chronic workplace stress leading to exhaustion, while silent quitting reflects disengagement marked by minimal effort and withdrawal from extra responsibilities. Both phenomena significantly reduce job satisfaction, affecting productivity and employee well-being in sectors with high-pressure environments. Explore effective strategies to enhance job satisfaction and combat burnout and silent quitting in your workplace.
Source and External Links
Burnout phenomenon: neurophysiological factors, clinical - This article discusses burnout as a distinct occupational phenomenon characterized by emotional exhaustion, physical fatigue, and cognitive weariness, often resulting from chronic workplace stress.
Burnout: Symptoms, Treatment, and Coping Strategy Tips - This webpage provides guidance on recognizing burnout stages, including the honeymoon phase, stress onset, chronic stress, and burnout, along with strategies for prevention and recovery.
Job burnout: How to spot it and take action - This Mayo Clinic article outlines job burnout symptoms, such as emotional exhaustion, and offers tips for identifying and addressing burnout to protect physical and mental health.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com