Compassion fatigue and burnout are critical issues affecting professionals in human resources and caregiving roles, with compassion fatigue arising from prolonged exposure to others' suffering and burnout stemming from chronic workplace stress and exhaustion. Both conditions lead to decreased productivity, emotional exhaustion, and increased turnover rates, highlighting the importance of early identification and intervention. Explore effective strategies to recognize and manage compassion fatigue versus burnout to maintain workforce well-being and resilience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between compassion fatigue and burnout is crucial for human resources professionals to implement targeted wellness programs and provide effective employee support. Compassion fatigue primarily affects caregivers due to prolonged exposure to others' trauma, while burnout stems from chronic workplace stress and overload. Accurate identification ensures timely interventions that enhance employee mental health, productivity, and retention. HR must leverage this knowledge to tailor strategies that address specific emotional and occupational challenges within the workforce.
Comparison Table
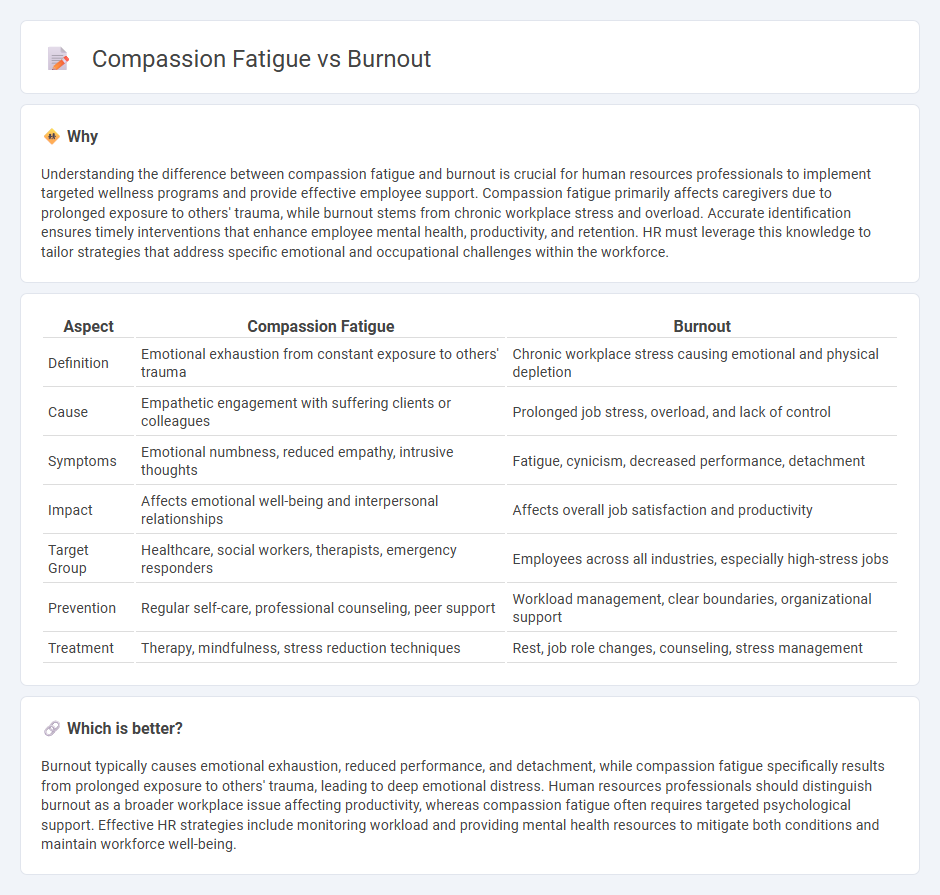
| Aspect | Compassion Fatigue | Burnout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional exhaustion from constant exposure to others' trauma | Chronic workplace stress causing emotional and physical depletion |
| Cause | Empathetic engagement with suffering clients or colleagues | Prolonged job stress, overload, and lack of control |
| Symptoms | Emotional numbness, reduced empathy, intrusive thoughts | Fatigue, cynicism, decreased performance, detachment |
| Impact | Affects emotional well-being and interpersonal relationships | Affects overall job satisfaction and productivity |
| Target Group | Healthcare, social workers, therapists, emergency responders | Employees across all industries, especially high-stress jobs |
| Prevention | Regular self-care, professional counseling, peer support | Workload management, clear boundaries, organizational support |
| Treatment | Therapy, mindfulness, stress reduction techniques | Rest, job role changes, counseling, stress management |
Which is better?
Burnout typically causes emotional exhaustion, reduced performance, and detachment, while compassion fatigue specifically results from prolonged exposure to others' trauma, leading to deep emotional distress. Human resources professionals should distinguish burnout as a broader workplace issue affecting productivity, whereas compassion fatigue often requires targeted psychological support. Effective HR strategies include monitoring workload and providing mental health resources to mitigate both conditions and maintain workforce well-being.
Connection
Compassion fatigue and burnout are interconnected phenomena frequently experienced by Human Resources professionals due to continuous exposure to employee stress and organizational challenges. Compassion fatigue arises from the emotional strain of empathetic engagement with colleagues' hardships, leading to diminished empathy and emotional exhaustion. Burnout encompasses a broader spectrum of chronic workplace stress characterized by feelings of cynicism, reduced efficacy, and physical and mental depletion resulting from sustained job demands and resource shortages.
Key Terms
Emotional exhaustion
Emotional exhaustion manifests differently in burnout and compassion fatigue, with burnout arising from prolonged workplace stress leading to feelings of depletion and detachment. Compassion fatigue specifically affects caregivers, marked by emotional numbness and reduced capacity to empathize due to constant exposure to others' trauma. Explore the distinct emotional symptoms and coping strategies to better understand these conditions.
Secondary traumatic stress
Secondary traumatic stress, a key component of compassion fatigue, arises from exposure to others' trauma, leading to symptoms similar to post-traumatic stress disorder such as intrusive thoughts, avoidance, and heightened arousal. Burnout primarily results from chronic workplace stress characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced personal accomplishment, but lacks the trauma-specific stress response seen in secondary traumatic stress. Explore the distinctions and management strategies between burnout and compassion fatigue to better support mental health professionals and caregivers.
Work-life balance
Burnout and compassion fatigue both stem from prolonged workplace stress but differ in impact; burnout primarily relates to emotional exhaustion and reduced performance due to chronic job strain, while compassion fatigue results from exposure to others' trauma, commonly affecting healthcare professionals and caregivers. Effective strategies for maintaining work-life balance include setting clear boundaries, prioritizing self-care, and engaging in regular stress management practices to mitigate symptoms of both conditions. Explore comprehensive methods and expert insights to enhance your work-life balance and prevent burnout and compassion fatigue.
Source and External Links
Burnout: Symptoms, Treatment, and Coping Strategy Tips - Burnout is a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by excessive and prolonged stress, progressing through stages from initial enthusiasm to chronic stress and eventual detachment and health neglect.
How to Identify and Prevent Burnout - Healthline - Burnout develops gradually through phases such as over-ambition, neglecting self-care, withdrawal from social life, behavioral changes, and can culminate in depression or mental collapse, requiring different levels of intervention.
Job burnout: How to spot it and take action - Mayo Clinic - Job burnout involves feeling physically or emotionally drained, cynical, detached from work, and questioning your competence, often accompanied by physical symptoms and changes in behavior, but it is not classified as a medical diagnosis.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com