Emotional salary encompasses non-monetary benefits such as work-life balance, recognition, and personal growth that significantly impact employee satisfaction and retention in Human Resources. Base pay refers to the fixed monetary compensation employees receive, forming the foundation of their total remuneration package. Discover how leveraging emotional salary alongside base pay can enhance workforce motivation and loyalty.
Why it is important
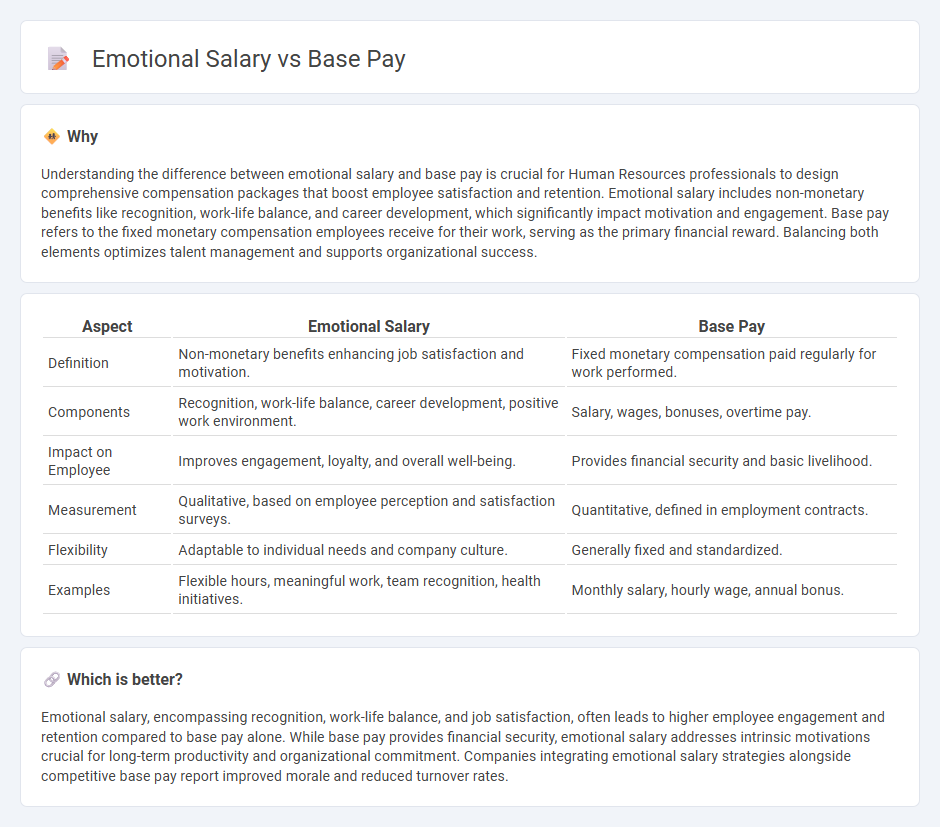
Understanding the difference between emotional salary and base pay is crucial for Human Resources professionals to design comprehensive compensation packages that boost employee satisfaction and retention. Emotional salary includes non-monetary benefits like recognition, work-life balance, and career development, which significantly impact motivation and engagement. Base pay refers to the fixed monetary compensation employees receive for their work, serving as the primary financial reward. Balancing both elements optimizes talent management and supports organizational success.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Emotional Salary | Base Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-monetary benefits enhancing job satisfaction and motivation. | Fixed monetary compensation paid regularly for work performed. |
| Components | Recognition, work-life balance, career development, positive work environment. | Salary, wages, bonuses, overtime pay. |
| Impact on Employee | Improves engagement, loyalty, and overall well-being. | Provides financial security and basic livelihood. |
| Measurement | Qualitative, based on employee perception and satisfaction surveys. | Quantitative, defined in employment contracts. |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to individual needs and company culture. | Generally fixed and standardized. |
| Examples | Flexible hours, meaningful work, team recognition, health initiatives. | Monthly salary, hourly wage, annual bonus. |
Which is better?
Emotional salary, encompassing recognition, work-life balance, and job satisfaction, often leads to higher employee engagement and retention compared to base pay alone. While base pay provides financial security, emotional salary addresses intrinsic motivations crucial for long-term productivity and organizational commitment. Companies integrating emotional salary strategies alongside competitive base pay report improved morale and reduced turnover rates.
Connection
Emotional salary, encompassing non-monetary benefits like recognition, work-life balance, and job satisfaction, complements base pay by enhancing overall employee motivation and retention. Research shows that employees receiving a competitive base salary alongside strong emotional rewards demonstrate higher productivity and loyalty. Integrating emotional salary with base pay strategies creates a holistic compensation package that drives engagement and reduces turnover rates in human resources management.
Key Terms
Compensation
Base pay constitutes the fixed monetary compensation an employee receives for their work, serving as the primary financial incentive in compensation structures. Emotional salary encompasses non-monetary benefits such as recognition, work-life balance, and a positive workplace culture, significantly impacting employee motivation and retention. Explore more to understand how integrating both enhances overall employee satisfaction and productivity.
Benefits
Base pay provides the fundamental financial compensation employees receive for their work hours, directly impacting their livelihood and financial stability. Emotional salary encompasses non-monetary benefits such as recognition, work-life balance, professional growth opportunities, and positive workplace culture, which significantly contribute to employee motivation and satisfaction. Explore how blending base pay with emotional salary benefits can transform employee engagement and retention strategies.
Employee Engagement
Base pay provides the essential financial compensation employees expect, while emotional salary encompasses non-monetary benefits such as recognition, work-life balance, and personal growth opportunities that significantly boost employee engagement. Companies that prioritize emotional salary alongside competitive base pay report higher retention rates and increased productivity. Discover how balancing these elements can enhance your workforce motivation and commitment.
Source and External Links
2025 Military Pay Charts - Basic pay is the primary compensation for service members, varying by paygrade and years of service; for example, an enlisted E-1 receives $2,319.00/month, while a senior officer O-4 with over 10 years earns $9,075.00/month in 2025.
Basic Pay - Defined by law or regulation as the fixed rate of pay excluding bonuses, allowances, or overtime, but including certain differentials and premium pay based on job conditions or locality.
Basic Pay - The fundamental and typically largest component of military pay, determined by rank/grade and years of service, and standard across all military members.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com