Ghost quitting refers to employees disengaging mentally while still physically present at work, leading to reduced productivity and morale. Absenteeism involves frequent, unplanned absences that disrupt workflow and increase operational costs. Explore how understanding these behaviors can improve workforce management and retention.
Why it is important
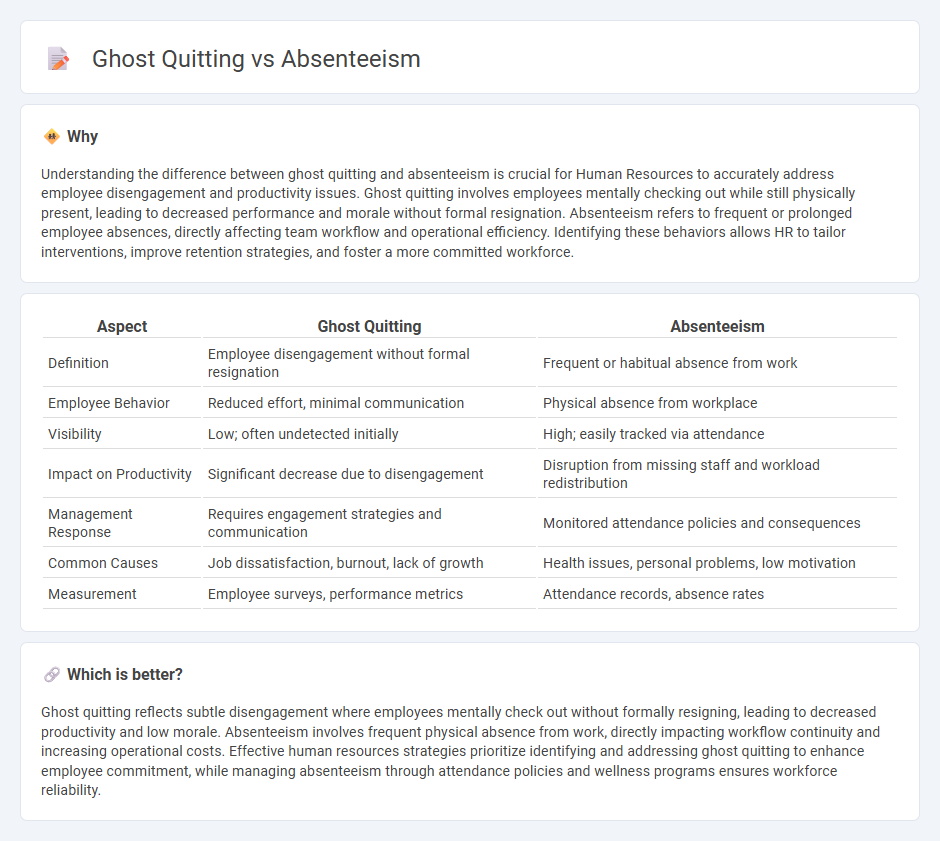
Understanding the difference between ghost quitting and absenteeism is crucial for Human Resources to accurately address employee disengagement and productivity issues. Ghost quitting involves employees mentally checking out while still physically present, leading to decreased performance and morale without formal resignation. Absenteeism refers to frequent or prolonged employee absences, directly affecting team workflow and operational efficiency. Identifying these behaviors allows HR to tailor interventions, improve retention strategies, and foster a more committed workforce.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Quitting | Absenteeism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee disengagement without formal resignation | Frequent or habitual absence from work |
| Employee Behavior | Reduced effort, minimal communication | Physical absence from workplace |
| Visibility | Low; often undetected initially | High; easily tracked via attendance |
| Impact on Productivity | Significant decrease due to disengagement | Disruption from missing staff and workload redistribution |
| Management Response | Requires engagement strategies and communication | Monitored attendance policies and consequences |
| Common Causes | Job dissatisfaction, burnout, lack of growth | Health issues, personal problems, low motivation |
| Measurement | Employee surveys, performance metrics | Attendance records, absence rates |
Which is better?
Ghost quitting reflects subtle disengagement where employees mentally check out without formally resigning, leading to decreased productivity and low morale. Absenteeism involves frequent physical absence from work, directly impacting workflow continuity and increasing operational costs. Effective human resources strategies prioritize identifying and addressing ghost quitting to enhance employee commitment, while managing absenteeism through attendance policies and wellness programs ensures workforce reliability.
Connection
Ghost quitting directly impacts absenteeism rates by creating a work environment where disengaged employees frequently miss work without formal notice. This behavior undermines team productivity and increases the burden on human resources to manage unplanned absences. Understanding the correlation between ghost quitting and absenteeism helps HR professionals develop targeted retention strategies and improve workforce stability.
Key Terms
Attendance Tracking
Absenteeism refers to employees frequently missing work without valid reasons, whereas ghost quitting involves employees disengaging and fulfilling minimal responsibilities without formally resigning. Effective attendance tracking systems use biometric data, real-time monitoring, and analytics to differentiate between these behaviors and improve workforce management. Explore advanced attendance solutions to enhance productivity and employee accountability.
Employee Engagement
Absenteeism directly impacts employee productivity and overall workplace morale, while ghost quitting erodes trust and commitment by quietly disengaging employees without formal resignation. Both phenomena highlight critical gaps in employee engagement strategies, necessitating proactive measures such as regular feedback, supportive management, and transparent communication. Explore effective solutions to enhance employee retention and foster a more engaged workforce.
Turnover
Absenteeism significantly impacts employee turnover by increasing operational costs and reducing productivity due to frequent unplanned absences. Ghost quitting, characterized by reduced engagement and effort while remaining employed, also elevates turnover risk by diminishing team morale and overall performance. Discover strategies to effectively manage absenteeism and ghost quitting to improve employee retention.
Source and External Links
Absenteeism - Absenteeism is a habitual pattern of absence from a duty or obligation without good reason, generally referring to unplanned absences and often seen as a management problem linked to poor individual performance or psychological and social adjustment to work.
Fighting Employee Absenteeism: 5 Expert Tips You Need ... - Absenteeism means chronic or habitual unplanned workplace absence, including lateness or early leaves, driven by factors like stress, mental health, and disengagement, with growing rates since the pandemic.
Absenteeism: Definition, Causes, and Remedies - Common causes of workplace absenteeism include lack of employee engagement, inflexible work conditions, poor physical and mental health, harassment, poor leadership, and job burnout.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com