Roll-up acquisition strategies involve consolidating multiple smaller companies within the same industry to achieve economies of scale and increased market share. Partnership models focus on collaborative efforts between entities to leverage complementary strengths and share resources for mutual growth. Explore how these approaches can impact your entrepreneurial ventures by diving deeper into their unique benefits and challenges.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between roll-up acquisition and partnership is crucial for entrepreneurs to make informed strategic decisions that impact business growth and resource allocation. Roll-up acquisitions involve consolidating multiple smaller companies to achieve economies of scale and market dominance, whereas partnerships focus on collaborative efforts without ownership transfer. Knowing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs assess financial risks, control levels, and integration challenges. This insight enables optimized negotiation strategies and long-term value creation.
Comparison Table
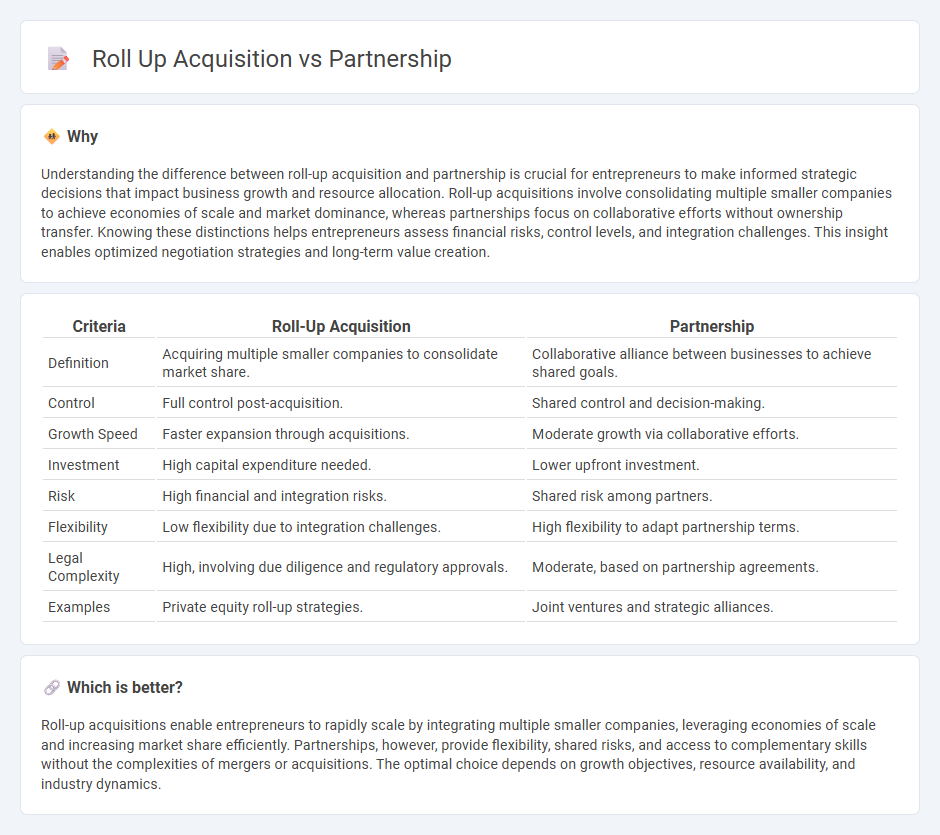
| Criteria | Roll-Up Acquisition | Partnership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquiring multiple smaller companies to consolidate market share. | Collaborative alliance between businesses to achieve shared goals. |
| Control | Full control post-acquisition. | Shared control and decision-making. |
| Growth Speed | Faster expansion through acquisitions. | Moderate growth via collaborative efforts. |
| Investment | High capital expenditure needed. | Lower upfront investment. |
| Risk | High financial and integration risks. | Shared risk among partners. |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility due to integration challenges. | High flexibility to adapt partnership terms. |
| Legal Complexity | High, involving due diligence and regulatory approvals. | Moderate, based on partnership agreements. |
| Examples | Private equity roll-up strategies. | Joint ventures and strategic alliances. |
Which is better?
Roll-up acquisitions enable entrepreneurs to rapidly scale by integrating multiple smaller companies, leveraging economies of scale and increasing market share efficiently. Partnerships, however, provide flexibility, shared risks, and access to complementary skills without the complexities of mergers or acquisitions. The optimal choice depends on growth objectives, resource availability, and industry dynamics.
Connection
Roll-up acquisitions consolidate multiple smaller companies within the same industry to achieve scale, efficiency, and increased market share, creating substantial value for entrepreneurs. Partnerships often serve as strategic alliances during or after roll-up processes, facilitating resource sharing, expertise exchange, and accelerated growth. Entrepreneurs leverage the synergy between roll-up acquisitions and partnerships to optimize operational integration and maximize competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Key Terms
Equity Ownership
Partnerships typically involve shared equity ownership where both parties contribute resources and hold proportional stakes, fostering collaborative decision-making. Roll-up acquisitions consolidate multiple companies under a single equity structure, often leading to majority ownership by the acquiring entity and streamlined control. Explore detailed comparisons of equity implications in partnerships versus roll-up acquisitions to optimize your investment strategy.
Control Structure
Partnerships typically involve shared control and decision-making between entities, allowing for collaborative strategies and resource pooling without full ownership transfer. Roll-up acquisitions centralize control by consolidating multiple smaller companies under one ownership, enabling streamlined management and unified operational direction. Explore deeper insights on how control structures impact business growth and strategic outcomes.
Integration Strategy
Partnerships emphasize collaborative integration strategies that preserve individual brand identities while leveraging shared resources and expertise for mutual growth. Roll-up acquisitions prioritize rapid consolidation of multiple entities under a unified operational framework to achieve economies of scale and streamlined processes. Explore detailed integration tactics to optimize success in your chosen growth approach.
Source and External Links
Partnership - Wikipedia - A partnership is an agreement where parties agree to cooperate to advance their mutual interests, typically involving sharing profits and responsibilities among individuals or organizations, often governed by specific laws like the Partnership Act 1932 in some countries.
Definition of Partnership: How They Work, Taxation and Types - A partnership is a legally binding agreement between two or more people who share responsibilities, ownership, and management of a business, combining their resources and skills for mutual benefit.
Partnership - Overview, Types of Partners, Types of Partnerships - A partnership is an unincorporated business structure formed and owned by two or more parties who share capital, labor, experience, profits, and liabilities, often governed by a partnership agreement detailing rights and responsibilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com