Wellbeing auditing focuses on evaluating employee health, satisfaction, and workplace culture to enhance organizational performance and retention. Sustainability auditing assesses environmental impact, resource usage, and compliance with eco-friendly standards to ensure long-term corporate responsibility. Explore these auditing approaches to understand how they contribute to holistic organizational success.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between wellbeing auditing and sustainability auditing is essential for effective business strategy and compliance, as wellbeing auditing focuses on employee health and organizational culture, while sustainability auditing assesses environmental impact and resource management. Wellbeing audits measure factors like mental health, workplace safety, and employee satisfaction to enhance productivity and retention. Sustainability audits evaluate carbon footprint, waste reduction, and energy consumption to meet regulatory standards and promote corporate social responsibility. Clear differentiation ensures targeted improvements, optimized resource allocation, and enhanced stakeholder trust.
Comparison Table
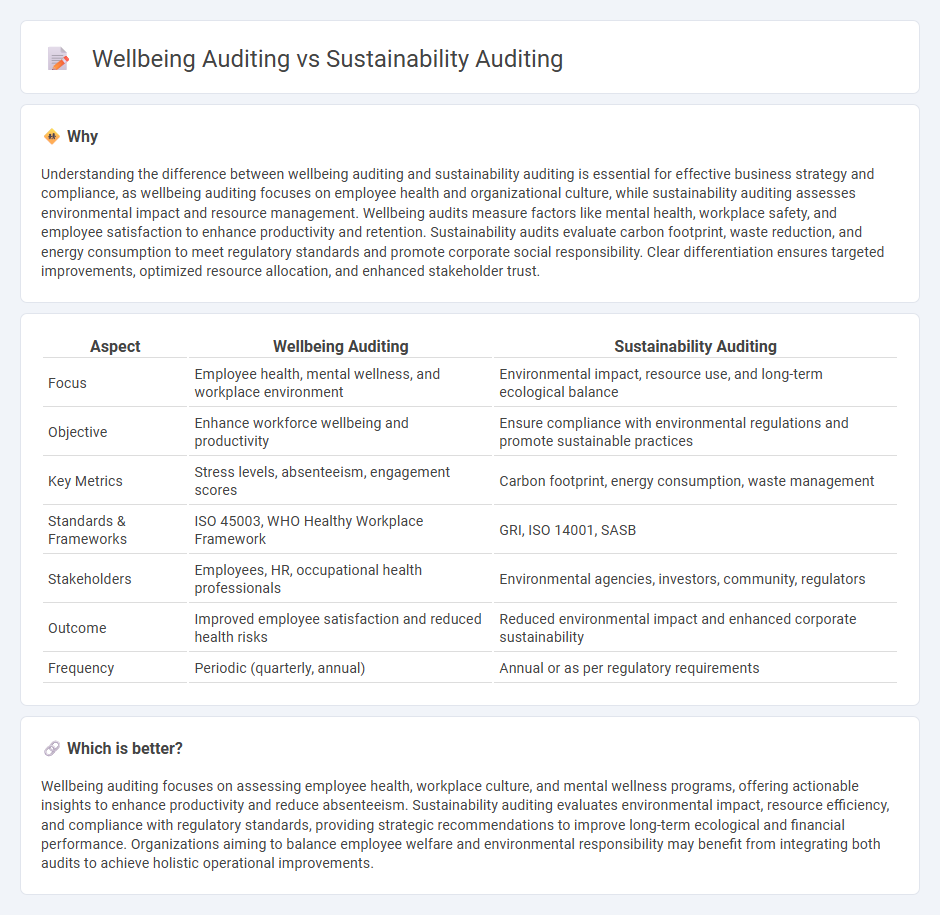
| Aspect | Wellbeing Auditing | Sustainability Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Employee health, mental wellness, and workplace environment | Environmental impact, resource use, and long-term ecological balance |
| Objective | Enhance workforce wellbeing and productivity | Ensure compliance with environmental regulations and promote sustainable practices |
| Key Metrics | Stress levels, absenteeism, engagement scores | Carbon footprint, energy consumption, waste management |
| Standards & Frameworks | ISO 45003, WHO Healthy Workplace Framework | GRI, ISO 14001, SASB |
| Stakeholders | Employees, HR, occupational health professionals | Environmental agencies, investors, community, regulators |
| Outcome | Improved employee satisfaction and reduced health risks | Reduced environmental impact and enhanced corporate sustainability |
| Frequency | Periodic (quarterly, annual) | Annual or as per regulatory requirements |
Which is better?
Wellbeing auditing focuses on assessing employee health, workplace culture, and mental wellness programs, offering actionable insights to enhance productivity and reduce absenteeism. Sustainability auditing evaluates environmental impact, resource efficiency, and compliance with regulatory standards, providing strategic recommendations to improve long-term ecological and financial performance. Organizations aiming to balance employee welfare and environmental responsibility may benefit from integrating both audits to achieve holistic operational improvements.
Connection
Wellbeing auditing and sustainability auditing are interconnected through their shared focus on long-term organizational health and ethical responsibility. Wellbeing audits evaluate employee health, satisfaction, and work-life balance, which directly influence sustainable business practices by fostering a resilient workforce. Sustainability audits assess environmental impact and resource management, while factoring in social aspects like employee wellbeing ensures holistic corporate sustainability and enhanced stakeholder trust.
Key Terms
Sustainability Auditing:
Sustainability auditing evaluates an organization's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance by examining resource use, waste management, and compliance with sustainability standards, aiming to reduce ecological footprints and enhance long-term viability. This audit analyzes carbon emissions, energy efficiency, and supply chain practices to ensure alignment with global sustainability frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Explore more to understand how sustainability auditing drives responsible business practices and supports strategic decision-making.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Sustainability auditing evaluates an organization's environmental performance by examining resource use, emissions, waste management, and compliance with environmental regulations, emphasizing long-term ecological balance. Wellbeing auditing assesses how workplace conditions affect employee health and satisfaction but intersects with environmental factors when evaluating exposure to pollutants or ergonomic risks. Explore the detailed methodologies and impacts of Environmental Impact Assessment within both auditing frameworks to understand their distinct yet complementary roles.
Carbon Footprint
Sustainability auditing rigorously evaluates an organization's carbon footprint, focusing on measuring greenhouse gas emissions across operations to ensure compliance with environmental standards and reduce overall impact. Wellbeing auditing, while centered on employee health and workplace conditions, integrates carbon footprint considerations to promote environmentally healthy environments that support human wellness. Explore detailed methodologies to understand how carbon footprint assessment differentiates these auditing approaches.
Source and External Links
What is a Sustainability Audit? - A sustainability audit critically evaluates how well a business addresses its sustainability goals by examining environmental impacts, CSR policies, supplier contracts, compliance, and providing a scorecard that highlights successes and gaps with recommendations for improvement.
The rise of sustainability and internal audit's role in auditing ESG - KPMG's sustainability audit methodology assesses an organization's ESG initiatives across defining policies, execution, and monitoring, including oversight, risk assessment, due diligence, implementation, and reporting to stakeholders.
Environmental Auditing and Certification Services - Environmental audits provide third-party verification to help organizations reduce energy use, waste, and pollution, ensure regulatory compliance, identify cost savings, and demonstrate environmental commitment through certification and assurance services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com