Corporate venturing involves established companies investing in or partnering with startups to accelerate innovation and market expansion. Spin-offs occur when a company creates an independent entity from its existing assets or technology to pursue new business opportunities. Discover how these strategic approaches differ and drive business growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between corporate venturing and spin-offs is crucial for strategic business growth and innovation management. Corporate venturing involves established companies investing in or partnering with startups to access new technologies or markets, while spin-offs are independent entities created from existing company divisions to focus on specialized products or services. Knowing these distinctions helps executives allocate resources effectively and foster tailored innovation ecosystems. Clear differentiation also guides legal, financial, and operational decision-making to maximize value creation.
Comparison Table
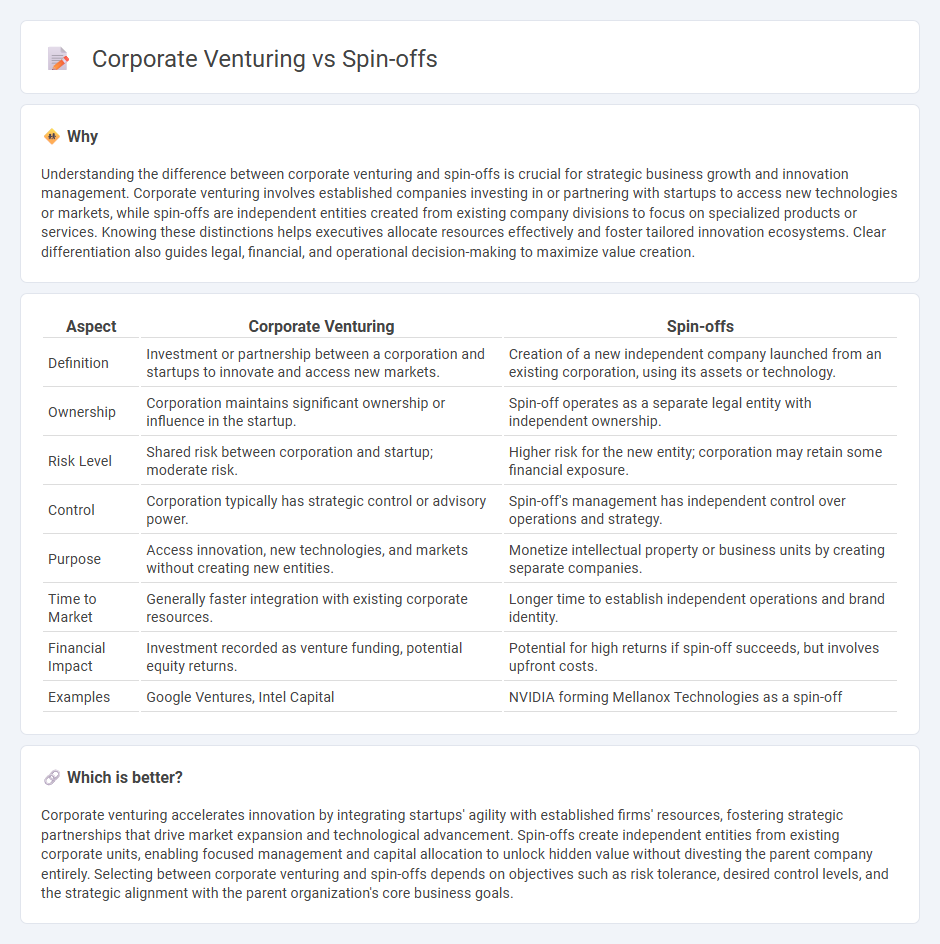
| Aspect | Corporate Venturing | Spin-offs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment or partnership between a corporation and startups to innovate and access new markets. | Creation of a new independent company launched from an existing corporation, using its assets or technology. |
| Ownership | Corporation maintains significant ownership or influence in the startup. | Spin-off operates as a separate legal entity with independent ownership. |
| Risk Level | Shared risk between corporation and startup; moderate risk. | Higher risk for the new entity; corporation may retain some financial exposure. |
| Control | Corporation typically has strategic control or advisory power. | Spin-off's management has independent control over operations and strategy. |
| Purpose | Access innovation, new technologies, and markets without creating new entities. | Monetize intellectual property or business units by creating separate companies. |
| Time to Market | Generally faster integration with existing corporate resources. | Longer time to establish independent operations and brand identity. |
| Financial Impact | Investment recorded as venture funding, potential equity returns. | Potential for high returns if spin-off succeeds, but involves upfront costs. |
| Examples | Google Ventures, Intel Capital | NVIDIA forming Mellanox Technologies as a spin-off |
Which is better?
Corporate venturing accelerates innovation by integrating startups' agility with established firms' resources, fostering strategic partnerships that drive market expansion and technological advancement. Spin-offs create independent entities from existing corporate units, enabling focused management and capital allocation to unlock hidden value without divesting the parent company entirely. Selecting between corporate venturing and spin-offs depends on objectives such as risk tolerance, desired control levels, and the strategic alignment with the parent organization's core business goals.
Connection
Corporate venturing drives innovation by investing in or partnering with startups, while spin-offs emerge as independent entities created from parent companies to commercialize new technologies. Both strategies enable corporations to accelerate growth, access novel markets, and leverage entrepreneurial agility. Spin-offs often result from successful corporate venturing initiatives focused on developing breakthrough ideas outside traditional structures.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Spin-offs involve a parent company creating an independent entity by redistributing ownership to existing shareholders, ensuring clear distinction between the new company's assets and liabilities. Corporate venturing typically entails the parent company retaining significant ownership or equity stake while investing in or partnering with innovative startups to leverage new technologies and markets. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which ownership structure suits your strategic business goals best.
Resource Allocation
Spin-offs allocate resources independently, allowing focused investment in innovation and growth without the constraints of the parent company's operational priorities. Corporate venturing integrates resource allocation within the larger organizational strategy, often balancing risk with existing business objectives. Explore how resource allocation strategies differ to optimize innovation outcomes in both models.
Strategic Autonomy
Spin-offs enable companies to achieve strategic autonomy by creating independent entities that can innovate with flexibility and focus, often accelerating growth in niche markets. Corporate venturing involves investing in or partnering with startups to leverage external innovation while maintaining some level of control, balancing risk and strategic alignment. Explore detailed strategies and case studies to understand how each approach can drive competitive advantage and long-term success.
Source and External Links
Spinoff (media) - A spin-off is a narrative work derived from an existing work focusing on different aspects, often featuring a supporting character in a new storyline or setting, and can include books, TV shows, films, and games.
What is a Spin-Off in Film & TV -- Definition & Examples - Spin-offs share the same universe as the original but explore different characters or storylines, often retaining stylistic elements to appeal to existing fans and expand the narrative world.
Spin-Off | M&A Definition + Examples - In business, a spin-off occurs when a parent company creates a new independent company by separating a division or subsidiary, exemplified by eBay spinning off PayPal in 2015.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com