Diagnostic mapping focuses on visually identifying patterns and relationships within complex business processes, enabling clearer understanding of issues. Root cause analysis delves deeper by systematically uncovering fundamental problems that trigger recurring challenges. Explore these approaches to enhance organizational problem-solving and strategic decision-making.
Why it is important
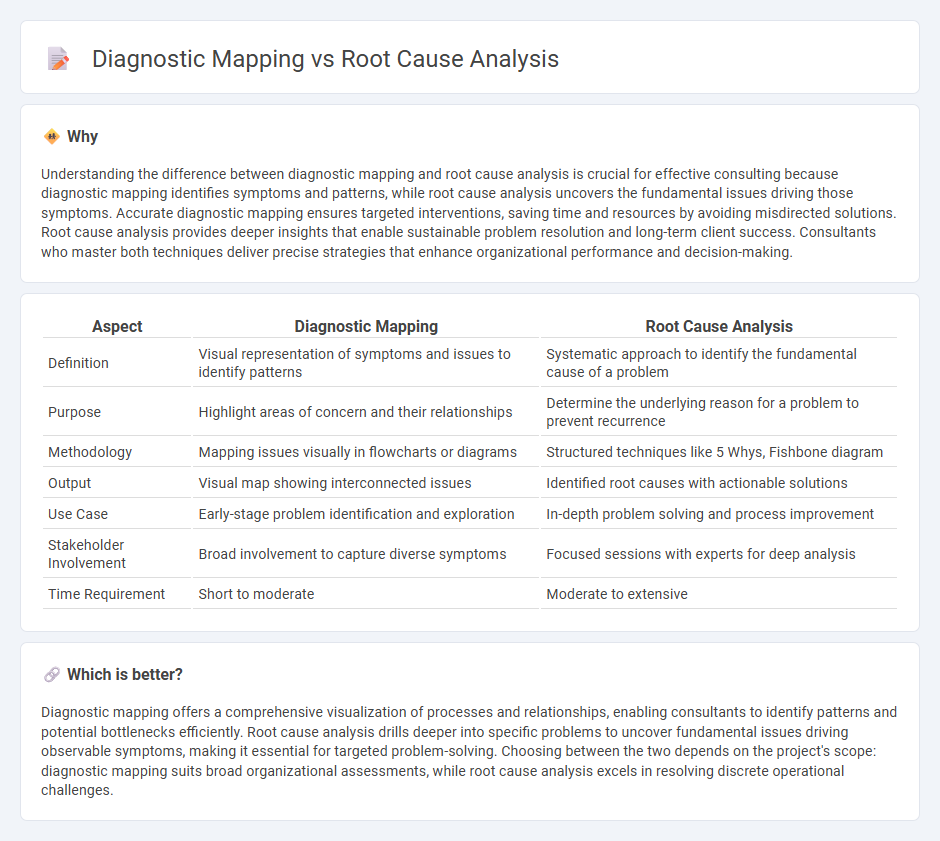
Understanding the difference between diagnostic mapping and root cause analysis is crucial for effective consulting because diagnostic mapping identifies symptoms and patterns, while root cause analysis uncovers the fundamental issues driving those symptoms. Accurate diagnostic mapping ensures targeted interventions, saving time and resources by avoiding misdirected solutions. Root cause analysis provides deeper insights that enable sustainable problem resolution and long-term client success. Consultants who master both techniques deliver precise strategies that enhance organizational performance and decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Diagnostic Mapping | Root Cause Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visual representation of symptoms and issues to identify patterns | Systematic approach to identify the fundamental cause of a problem |
| Purpose | Highlight areas of concern and their relationships | Determine the underlying reason for a problem to prevent recurrence |
| Methodology | Mapping issues visually in flowcharts or diagrams | Structured techniques like 5 Whys, Fishbone diagram |
| Output | Visual map showing interconnected issues | Identified root causes with actionable solutions |
| Use Case | Early-stage problem identification and exploration | In-depth problem solving and process improvement |
| Stakeholder Involvement | Broad involvement to capture diverse symptoms | Focused sessions with experts for deep analysis |
| Time Requirement | Short to moderate | Moderate to extensive |
Which is better?
Diagnostic mapping offers a comprehensive visualization of processes and relationships, enabling consultants to identify patterns and potential bottlenecks efficiently. Root cause analysis drills deeper into specific problems to uncover fundamental issues driving observable symptoms, making it essential for targeted problem-solving. Choosing between the two depends on the project's scope: diagnostic mapping suits broad organizational assessments, while root cause analysis excels in resolving discrete operational challenges.
Connection
Diagnostic mapping systematically identifies patterns and relationships within organizational processes, providing a visual framework that highlights areas of concern. Root cause analysis delves deeper into these pinpointed issues by uncovering the fundamental problems driving symptoms in business performance. Together, these tools enable consultants to craft targeted strategies that address core challenges, maximizing operational efficiency and outcomes.
Key Terms
**Root cause analysis:**
Root cause analysis (RCA) systematically identifies underlying causes of problems to prevent recurrence and improve processes. It involves techniques such as the 5 Whys, fishbone diagrams, and fault tree analysis to trace issues back to their origin. Explore deeper insights into RCA methods and applications for effective problem-solving.
Causal Factors
Root cause analysis identifies underlying causes of problems by systematically tracing back from observed symptoms to primary sources, while diagnostic mapping visually links symptoms to potential causal factors for clarity in complex systems. Both techniques focus on uncovering causal factors but root cause analysis dives deeper into cause-effect relationships, whereas diagnostic mapping provides a broad overview of possible causes and their interactions. Explore detailed methodologies to optimize your troubleshooting and decision-making processes.
Fishbone Diagram
Root cause analysis identifies underlying problems causing a specific issue, while diagnostic mapping visually organizes factors influencing those problems. The Fishbone Diagram, or Ishikawa Diagram, is a key tool in diagnostic mapping, categorizing causes into groups like Methods, Materials, and Environment for systematic investigation. Explore more to master applying Fishbone Diagram for effective problem-solving.
Source and External Links
Root Cause Analysis Explained: Definition, Examples, and Methods - Root cause analysis (RCA) is the process of discovering the root causes of problems to identify appropriate solutions, commonly using techniques like the 5 Whys to drill down through layers of causes until the underlying issue is found.
How to do Root Cause Analysis? Everything You Need to Know - RCA involves a structured investigatory process that starts by clearly defining the problem, documenting specific symptoms and impacts, and then applying methods to uncover the underlying causes systematically.
Root Cause Analysis: A Quick Guide - ProjectManager - Root cause analysis uses problem-solving tools like the Five Whys technique, where repeatedly asking "why" helps trace back from a symptom to the root cause, enabling teams to identify and resolve the fundamental problem rather than just its effects.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com