Digital twin simulation creates virtual replicas of physical systems for real-time monitoring and predictive analysis, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, driving productivity and reducing human error in business processes. Explore how integrating digital twin simulation with RPA can transform your organization's performance and innovation.
Why it is important
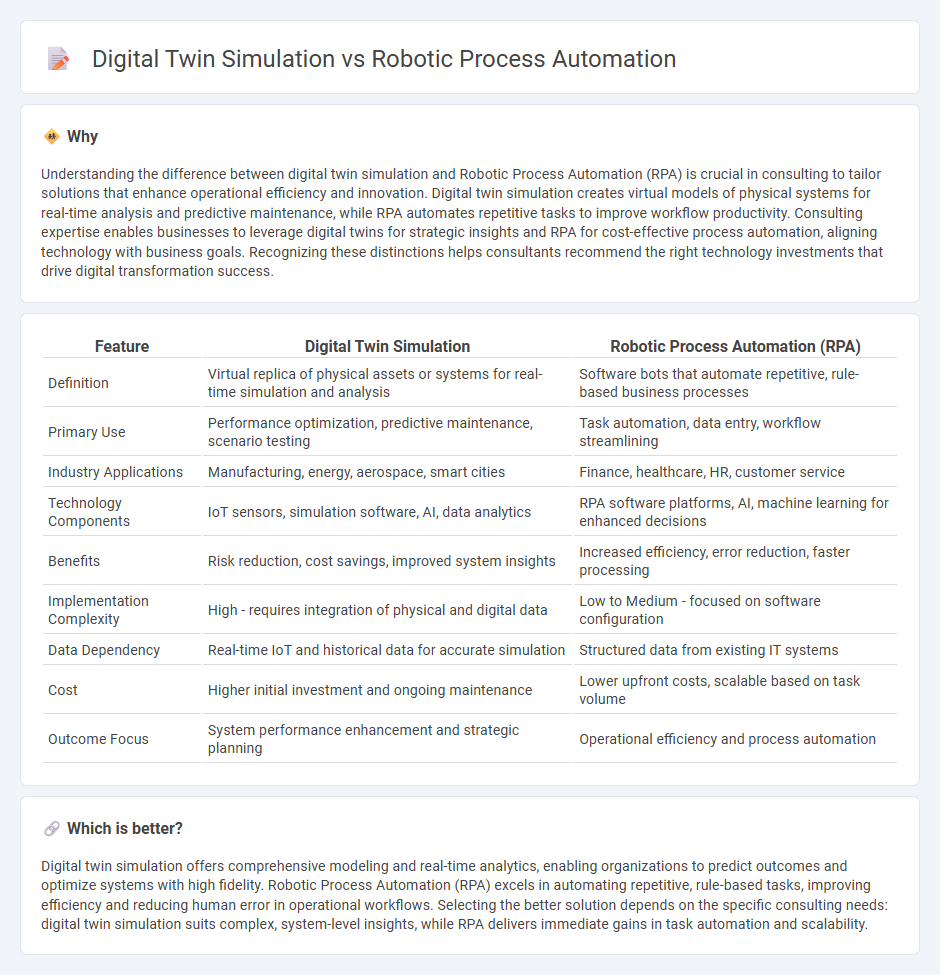
Understanding the difference between digital twin simulation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is crucial in consulting to tailor solutions that enhance operational efficiency and innovation. Digital twin simulation creates virtual models of physical systems for real-time analysis and predictive maintenance, while RPA automates repetitive tasks to improve workflow productivity. Consulting expertise enables businesses to leverage digital twins for strategic insights and RPA for cost-effective process automation, aligning technology with business goals. Recognizing these distinctions helps consultants recommend the right technology investments that drive digital transformation success.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Twin Simulation | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets or systems for real-time simulation and analysis | Software bots that automate repetitive, rule-based business processes |
| Primary Use | Performance optimization, predictive maintenance, scenario testing | Task automation, data entry, workflow streamlining |
| Industry Applications | Manufacturing, energy, aerospace, smart cities | Finance, healthcare, HR, customer service |
| Technology Components | IoT sensors, simulation software, AI, data analytics | RPA software platforms, AI, machine learning for enhanced decisions |
| Benefits | Risk reduction, cost savings, improved system insights | Increased efficiency, error reduction, faster processing |
| Implementation Complexity | High - requires integration of physical and digital data | Low to Medium - focused on software configuration |
| Data Dependency | Real-time IoT and historical data for accurate simulation | Structured data from existing IT systems |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance | Lower upfront costs, scalable based on task volume |
| Outcome Focus | System performance enhancement and strategic planning | Operational efficiency and process automation |
Which is better?
Digital twin simulation offers comprehensive modeling and real-time analytics, enabling organizations to predict outcomes and optimize systems with high fidelity. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, improving efficiency and reducing human error in operational workflows. Selecting the better solution depends on the specific consulting needs: digital twin simulation suits complex, system-level insights, while RPA delivers immediate gains in task automation and scalability.
Connection
Digital twin simulation enhances Robotic Process Automation (RPA) by creating precise virtual models of business processes, enabling real-time testing and optimization before deployment. This integration allows consultants to identify inefficiencies and predict the impact of automation on workflows, improving accuracy and reducing implementation risks. Leveraging both technologies accelerates digital transformation by providing actionable insights and scalable automation strategies.
Key Terms
Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking human interactions with software systems, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing errors in process automation. Digital twin simulation creates virtual replicas of physical processes, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and optimization through data-driven models. Explore more to understand how these technologies boost process automation capabilities.
Virtual Modeling
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive tasks through software bots, enhancing operational efficiency without replicating physical systems. Digital twin simulation creates a virtual model of real-world assets, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and scenario testing for improved decision-making. Explore how integrating RPA with digital twin simulation drives innovation in virtual modeling and business automation.
Operational Efficiency
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and accelerating process execution in industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. Digital twin simulation provides a virtual replica of physical systems, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized decision-making for complex operations. Explore how integrating RPA with digital twin technology can unlock unprecedented operational efficiency and innovation.
Source and External Links
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? - IBM - RPA is software technology that uses intelligent automation to perform repetitive office tasks like data extraction, form filling, and file movement, combining APIs and UI interactions to automate activities across software systems and freeing humans for complex work, with emerging integration of AI for more intelligent automation.
RPA - Robotic Process Automation Software & Services - Xerox - RPA uses bots to automate repetitive and standardized tasks in business workflows, including document processing, invoice management, customer service, HR onboarding, and supply chain operations, enhancing efficiency and accuracy across industries.
What is Robotic Process Automation - RPA Software - UiPath - RPA enables the building and deployment of software robots that emulate human interactions with digital systems for faster, consistent task execution, with AI advancements broadening its use to intelligent document processing and agentic automation beyond rule-based back-office tasks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com