Digital lean transformation emphasizes optimizing processes by integrating digital tools to eliminate waste and enhance operational efficiency, focusing primarily on value stream improvement. Industry 4.0 adoption involves implementing advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and cyber-physical systems to create smart factories with interconnected production systems. Explore how consulting services can help businesses navigate these strategies for competitive advantage and sustainable growth.
Why it is important
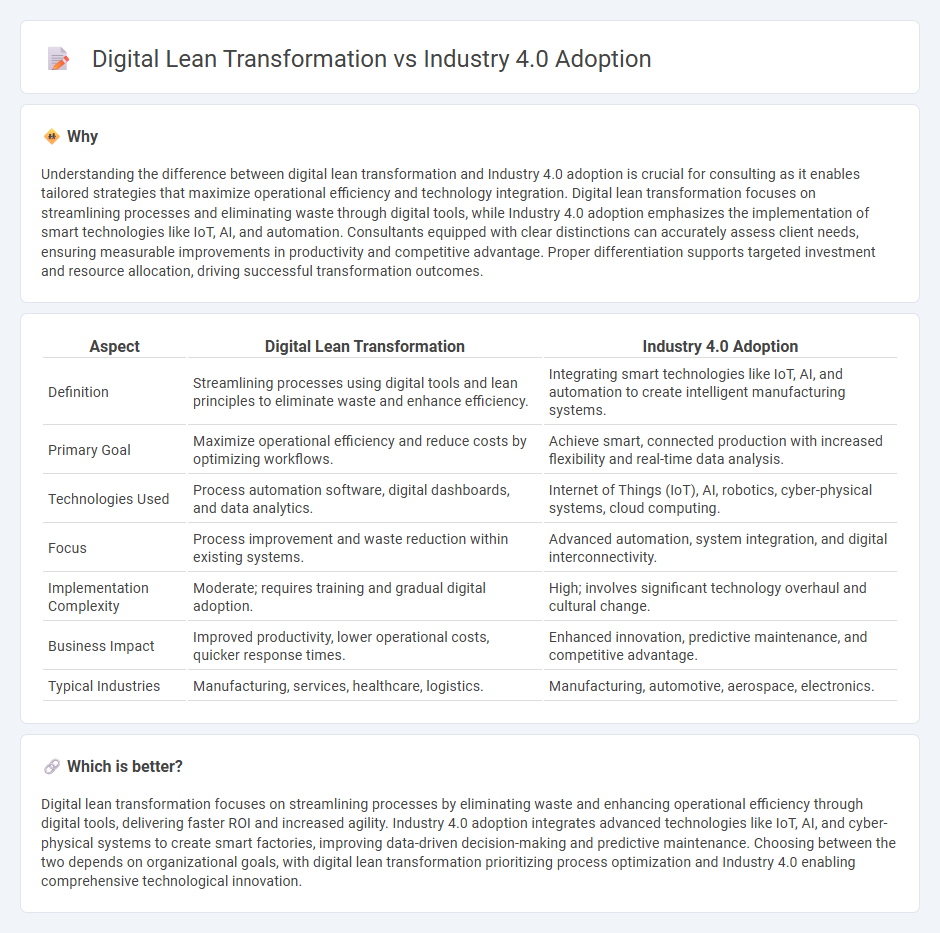
Understanding the difference between digital lean transformation and Industry 4.0 adoption is crucial for consulting as it enables tailored strategies that maximize operational efficiency and technology integration. Digital lean transformation focuses on streamlining processes and eliminating waste through digital tools, while Industry 4.0 adoption emphasizes the implementation of smart technologies like IoT, AI, and automation. Consultants equipped with clear distinctions can accurately assess client needs, ensuring measurable improvements in productivity and competitive advantage. Proper differentiation supports targeted investment and resource allocation, driving successful transformation outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Lean Transformation | Industry 4.0 Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Streamlining processes using digital tools and lean principles to eliminate waste and enhance efficiency. | Integrating smart technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to create intelligent manufacturing systems. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize operational efficiency and reduce costs by optimizing workflows. | Achieve smart, connected production with increased flexibility and real-time data analysis. |
| Technologies Used | Process automation software, digital dashboards, and data analytics. | Internet of Things (IoT), AI, robotics, cyber-physical systems, cloud computing. |
| Focus | Process improvement and waste reduction within existing systems. | Advanced automation, system integration, and digital interconnectivity. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate; requires training and gradual digital adoption. | High; involves significant technology overhaul and cultural change. |
| Business Impact | Improved productivity, lower operational costs, quicker response times. | Enhanced innovation, predictive maintenance, and competitive advantage. |
| Typical Industries | Manufacturing, services, healthcare, logistics. | Manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, electronics. |
Which is better?
Digital lean transformation focuses on streamlining processes by eliminating waste and enhancing operational efficiency through digital tools, delivering faster ROI and increased agility. Industry 4.0 adoption integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and cyber-physical systems to create smart factories, improving data-driven decision-making and predictive maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on organizational goals, with digital lean transformation prioritizing process optimization and Industry 4.0 enabling comprehensive technological innovation.
Connection
Digital lean transformation enhances operational efficiency by integrating Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, AI, and big data analytics. These technologies enable real-time data-driven decision-making and process automation, driving continuous improvement aligned with lean principles. The synergy between digital lean transformation and Industry 4.0 adoption accelerates productivity, reduces waste, and fosters agility in manufacturing and service industries.
Key Terms
Cyber-Physical Systems
Industry 4.0 adoption emphasizes integrating Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) to create interconnected, intelligent manufacturing environments that enable real-time data exchange between physical and digital assets. Digital lean transformation leverages these CPS technologies to streamline processes, reduce waste, and enhance operational efficiency through continuous improvement and automation. Explore further insights on how Cyber-Physical Systems drive the convergence of Industry 4.0 and digital lean strategies for modern enterprises.
Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) plays a critical role in both Industry 4.0 adoption and digital lean transformation by visualizing process flows and identifying waste across value chains. Integrating digital technologies such as IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and AI into VSM enhances decision-making and operational efficiency, driving continuous improvement in manufacturing systems. Explore how digital VSM tools accelerate Industry 4.0 initiatives and lean transformations to maximize productivity and competitive advantage.
Change Management
Industry 4.0 adoption integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and big data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes, while digital lean transformation emphasizes streamlining operations and reducing waste through digital tools and lean principles. Effective change management is critical for both approaches, ensuring employee engagement, aligning organizational culture, and sustaining continuous improvement. Explore our in-depth analysis to understand how strategic change management drives successful Industry 4.0 and digital lean initiatives.
Source and External Links
Adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies by organizations - Industry 4.0 adoption varies by technology, with IoT, CPS, machine-to-machine, and big data having very high implementation levels, while emerging technologies like digital twins and quantum computing remain in early adoption stages.
The rise of Industry 4.0 in 5 stats - Industry 4.0 adoption has accelerated significantly; as of 2022, 72% of companies have ongoing Industry 4.0/Smart Factory initiatives, reflecting widespread strategic implementation across enterprises.
What is industry 4.0 and the Fourth Industrial Revolution? - Industry 4.0 adoption differs by sector and infrastructure maturity, with operationally intensive industries like manufacturing transforming rapidly through automation and digitization, while cutting-edge innovations see slower uptake due to costs and complexity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com