Stakeholder capitalism emphasizes creating value for all parties affected by business activities, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities, rather than focusing solely on shareholder profits. Ethical leadership drives this approach by prioritizing transparency, fairness, and responsible decision-making to align corporate actions with broader societal goals. Explore how consulting empowers organizations to integrate stakeholder capitalism with ethical leadership for sustainable success.
Why it is important
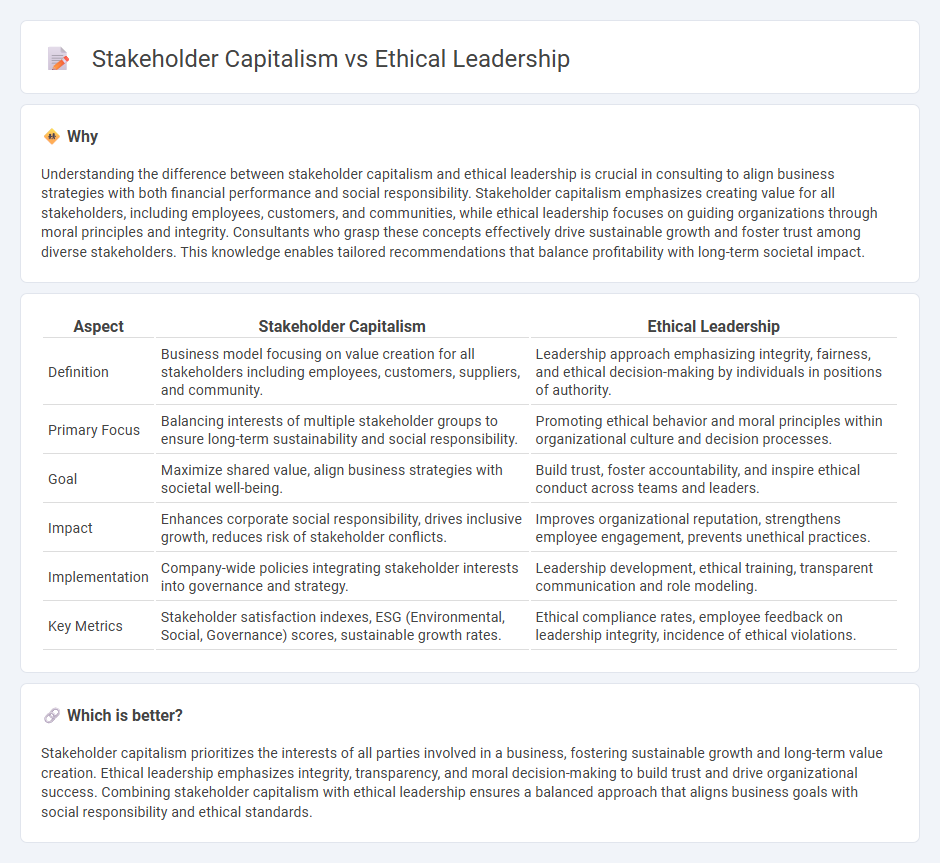
Understanding the difference between stakeholder capitalism and ethical leadership is crucial in consulting to align business strategies with both financial performance and social responsibility. Stakeholder capitalism emphasizes creating value for all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and communities, while ethical leadership focuses on guiding organizations through moral principles and integrity. Consultants who grasp these concepts effectively drive sustainable growth and foster trust among diverse stakeholders. This knowledge enables tailored recommendations that balance profitability with long-term societal impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Stakeholder Capitalism | Ethical Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business model focusing on value creation for all stakeholders including employees, customers, suppliers, and community. | Leadership approach emphasizing integrity, fairness, and ethical decision-making by individuals in positions of authority. |
| Primary Focus | Balancing interests of multiple stakeholder groups to ensure long-term sustainability and social responsibility. | Promoting ethical behavior and moral principles within organizational culture and decision processes. |
| Goal | Maximize shared value, align business strategies with societal well-being. | Build trust, foster accountability, and inspire ethical conduct across teams and leaders. |
| Impact | Enhances corporate social responsibility, drives inclusive growth, reduces risk of stakeholder conflicts. | Improves organizational reputation, strengthens employee engagement, prevents unethical practices. |
| Implementation | Company-wide policies integrating stakeholder interests into governance and strategy. | Leadership development, ethical training, transparent communication and role modeling. |
| Key Metrics | Stakeholder satisfaction indexes, ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) scores, sustainable growth rates. | Ethical compliance rates, employee feedback on leadership integrity, incidence of ethical violations. |
Which is better?
Stakeholder capitalism prioritizes the interests of all parties involved in a business, fostering sustainable growth and long-term value creation. Ethical leadership emphasizes integrity, transparency, and moral decision-making to build trust and drive organizational success. Combining stakeholder capitalism with ethical leadership ensures a balanced approach that aligns business goals with social responsibility and ethical standards.
Connection
Stakeholder capitalism emphasizes the importance of creating value for all stakeholders, including employees, customers, communities, and shareholders, which inherently requires ethical leadership to balance diverse interests fairly. Ethical leadership fosters transparency, accountability, and trust, enabling organizations to adopt stakeholder-driven strategies that promote long-term sustainability. This alignment ensures that decision-making prioritizes social responsibility alongside profitability, driving success in consulting engagements focused on corporate governance and organizational ethics.
Key Terms
Integrity
Ethical leadership prioritizes integrity by consistently adhering to moral principles and transparency in decision-making, ensuring trust within organizations. Stakeholder capitalism integrates integrity by balancing the interests of employees, customers, communities, and shareholders to create long-term value and accountability. Explore how these approaches shape sustainable business practices and organizational success.
Accountability
Ethical leadership emphasizes accountability through moral principles and transparent decision-making, ensuring leaders are responsible for their actions and impacts on society. Stakeholder capitalism prioritizes accountability by balancing the interests of shareholders, employees, customers, and communities to create long-term value and sustainable growth. Explore the intricate relationship between ethical leadership and stakeholder capitalism to understand their roles in fostering accountable business practices.
Transparency
Ethical leadership emphasizes transparency by fostering open communication, accountability, and trust between leaders and stakeholders, ensuring decisions align with moral values and societal expectations. Stakeholder capitalism promotes transparency through inclusive governance, integrating the concerns of employees, customers, suppliers, and communities into business strategies to enhance long-term value creation. Discover how transparency shapes responsible business practices and drives sustainable success.
Source and External Links
Ethical leadership - Wikipedia - Ethical leadership is directed by respect for ethical beliefs and values and the dignity and rights of others, acting as a role model through social learning and transactional fairness between leader and followers.
What is ethical leadership and its characteristics - Esade - Ethical leadership is based on moral principles such as integrity, transparency, and respect, with key characteristics including respect for individuals and honesty to build trust and openness in organizations.
Why Ethical Leadership is Important for Business Success - Ethico - Ethical leadership prioritizes respect, honesty, and integrity to foster transparency, trust, and accountability, guiding organizations toward sustainable long-term success and compliance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com