Regenerative business strategy focuses on restoring and enhancing natural ecosystems while creating sustainable economic value, prioritizing long-term environmental health and community resilience. ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) strategy emphasizes corporate responsibility and risk management through measurable criteria across environmental impact, social equity, and governance practices. Discover how regenerative approaches can complement or surpass traditional ESG frameworks for future-proof business growth.
Why it is important
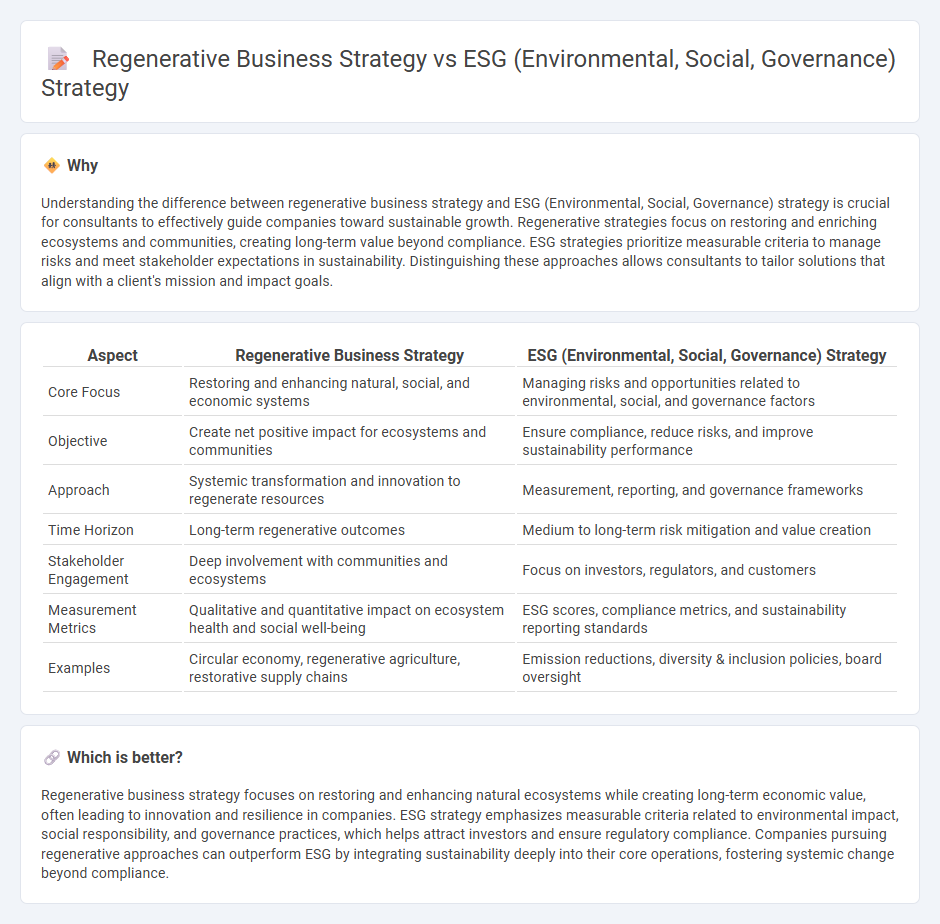
Understanding the difference between regenerative business strategy and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) strategy is crucial for consultants to effectively guide companies toward sustainable growth. Regenerative strategies focus on restoring and enriching ecosystems and communities, creating long-term value beyond compliance. ESG strategies prioritize measurable criteria to manage risks and meet stakeholder expectations in sustainability. Distinguishing these approaches allows consultants to tailor solutions that align with a client's mission and impact goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Regenerative Business Strategy | ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Restoring and enhancing natural, social, and economic systems | Managing risks and opportunities related to environmental, social, and governance factors |
| Objective | Create net positive impact for ecosystems and communities | Ensure compliance, reduce risks, and improve sustainability performance |
| Approach | Systemic transformation and innovation to regenerate resources | Measurement, reporting, and governance frameworks |
| Time Horizon | Long-term regenerative outcomes | Medium to long-term risk mitigation and value creation |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Deep involvement with communities and ecosystems | Focus on investors, regulators, and customers |
| Measurement Metrics | Qualitative and quantitative impact on ecosystem health and social well-being | ESG scores, compliance metrics, and sustainability reporting standards |
| Examples | Circular economy, regenerative agriculture, restorative supply chains | Emission reductions, diversity & inclusion policies, board oversight |
Which is better?
Regenerative business strategy focuses on restoring and enhancing natural ecosystems while creating long-term economic value, often leading to innovation and resilience in companies. ESG strategy emphasizes measurable criteria related to environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices, which helps attract investors and ensure regulatory compliance. Companies pursuing regenerative approaches can outperform ESG by integrating sustainability deeply into their core operations, fostering systemic change beyond compliance.
Connection
Regenerative business strategy integrates ESG principles by focusing on restoring natural systems, enhancing social well-being, and ensuring transparent governance to create long-term value. ESG frameworks provide measurable criteria that guide regenerative initiatives toward sustainability and ethical impact. This connection drives corporations to adopt practices that not only minimize harm but actively improve environmental and social conditions while maintaining robust governance standards.
Key Terms
Sustainability Reporting
ESG strategy emphasizes environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance transparency through comprehensive sustainability reporting standards like GRI and SASB. Regenerative business strategy goes beyond reporting, seeking to restore and renew natural systems by integrating circular economy principles and regenerative agriculture practices. Explore how these approaches differ in driving corporate sustainability goals and reporting frameworks.
Circular Economy
ESG strategies prioritize compliance, risk management, and stakeholder value through environmental, social, and governance criteria, while regenerative business strategies actively restore ecosystems and promote circular economy principles such as resource efficiency, zero waste, and closed-loop systems. Circular economy under regenerative strategies seeks to design out waste, extend product life cycles, and regenerate natural capital, going beyond traditional ESG metrics. Explore how integrating regenerative approaches into ESG frameworks can drive innovation and sustainability impact.
Stakeholder Value Creation
ESG strategy emphasizes compliance and risk management across environmental, social, and governance factors to protect stakeholder interests and enhance corporate reputation. Regenerative business strategy prioritizes restoring and enriching ecosystems, communities, and economies, aiming for long-term stakeholder value through innovation and systemic impact. Explore how shifting from ESG to regenerative approaches can unlock transformative benefits for stakeholders and the planet.
Source and External Links
ESG Strategy: Best Practices, Challenges, Tips for Success - An ESG strategy integrates environmental, social, and governance factors into a business's core operations and decision-making, involving assessment of impacts, risks, and stakeholder engagement to drive long-term growth.
A beginner's guide to developing your ESG strategy in 2024 - ESG strategies provide guidelines on environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance transparency to ensure sustainable and ethical business practices, covering areas like carbon footprint, employee well-being, and governance ethics.
Environmental, Social & Governance | Sustainability - McKinsey - ESG strategy creates opportunities and challenges for sustainable and inclusive growth by setting measurable goals, managing stakeholder interests, and driving value creation through initiatives and communications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com