Drop servicing involves selling services performed by third-party providers, while product flipping focuses on buying and reselling physical goods for profit. Entrepreneurs leverage drop servicing to scale without inventory, whereas product flipping requires effective sourcing and market timing. Discover how each model can amplify your commerce strategy.
Why it is important
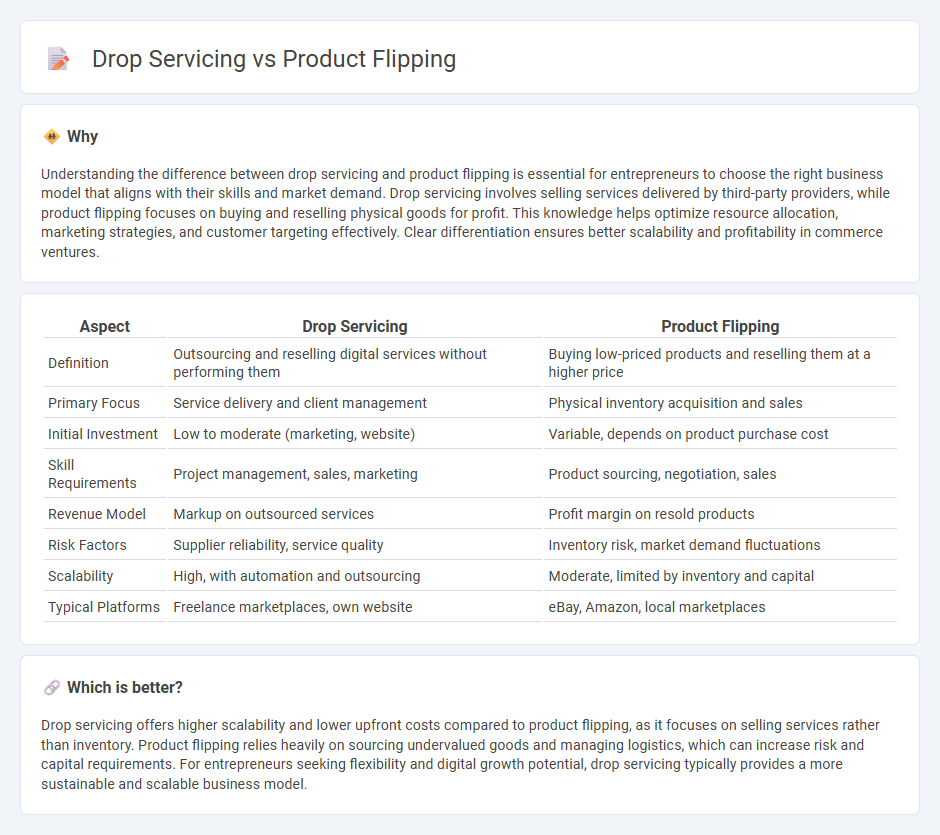
Understanding the difference between drop servicing and product flipping is essential for entrepreneurs to choose the right business model that aligns with their skills and market demand. Drop servicing involves selling services delivered by third-party providers, while product flipping focuses on buying and reselling physical goods for profit. This knowledge helps optimize resource allocation, marketing strategies, and customer targeting effectively. Clear differentiation ensures better scalability and profitability in commerce ventures.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Drop Servicing | Product Flipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourcing and reselling digital services without performing them | Buying low-priced products and reselling them at a higher price |
| Primary Focus | Service delivery and client management | Physical inventory acquisition and sales |
| Initial Investment | Low to moderate (marketing, website) | Variable, depends on product purchase cost |
| Skill Requirements | Project management, sales, marketing | Product sourcing, negotiation, sales |
| Revenue Model | Markup on outsourced services | Profit margin on resold products |
| Risk Factors | Supplier reliability, service quality | Inventory risk, market demand fluctuations |
| Scalability | High, with automation and outsourcing | Moderate, limited by inventory and capital |
| Typical Platforms | Freelance marketplaces, own website | eBay, Amazon, local marketplaces |
Which is better?
Drop servicing offers higher scalability and lower upfront costs compared to product flipping, as it focuses on selling services rather than inventory. Product flipping relies heavily on sourcing undervalued goods and managing logistics, which can increase risk and capital requirements. For entrepreneurs seeking flexibility and digital growth potential, drop servicing typically provides a more sustainable and scalable business model.
Connection
Drop servicing and product flipping are connected through their shared focus on leveraging digital platforms to generate profit by reselling services or products with added value. Both business models capitalize on market demand, relying on strategic sourcing and customer acquisition to maximize margins. Utilizing efficient marketing and outsourcing techniques, entrepreneurs can scale operations without holding physical inventory or directly delivering services themselves.
Key Terms
Inventory
Product flipping requires managing physical inventory, involving sourcing, storage, and shipping of tangible goods, which can increase operational costs and risks associated with unsold stock. Drop servicing eliminates the need for inventory by selling digital services performed by third-party providers, reducing overhead and enhancing scalability. Explore the detailed advantages and challenges of each model to determine the best approach for your business needs.
Service fulfillment
Product flipping involves purchasing physical goods at a lower price and reselling them for profit, relying heavily on efficient inventory management and shipping logistics for service fulfillment. Drop servicing centers on selling digital services, where the fulfillment process includes outsourcing tasks to specialized freelancers or agencies, ensuring quality and timely delivery. Explore the nuances of service fulfillment in product flipping and drop servicing to optimize your business strategy.
Profit margin
Product flipping involves purchasing items at a low cost and reselling them for a higher price, often yielding profit margins between 20% to 50%, depending on product sourcing and market demand. Drop servicing centers on selling digital services sourced from freelancers or agencies, typically featuring profit margins around 30% to 70%, due to lower overhead and scalable service delivery. Explore more insights on maximizing profit margins and choosing the best approach for your business model.
Source and External Links
Amazon Flips : How to Find Flipping Opportunities in 2024 - Product flipping means buying items and quickly reselling them for profit, with Amazon offering large marketplace opportunities and options like Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) or Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM); success depends on decent profit margins (20%+), sufficient demand, and managing competition effectively.
Flipping on eBay | Make money flipping these 10 EASY Items on eBay - Flipping involves buying items, holding them briefly, then reselling for profit, applicable to many assets like bags, shoes, or instruments, with eBay being a common platform for this strategy.
15 Most Profitable Items to Flip in 2025 - SaleHoo - Profitable flipping items include vintage clothes, rare books, and clearance items; these can offer healthy profit margins by sourcing undervalued goods and reselling on popular marketplaces such as Amazon or eBay.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com