Dark patterns manipulate user behavior to benefit businesses often by obscuring true intentions, raising significant ethical concerns in e-commerce. Privacy-by-design embeds data protection into every stage of product development, ensuring user information remains secure and respected. Explore how contrasting strategies like these impact consumer trust and online commerce success.
Why it is important
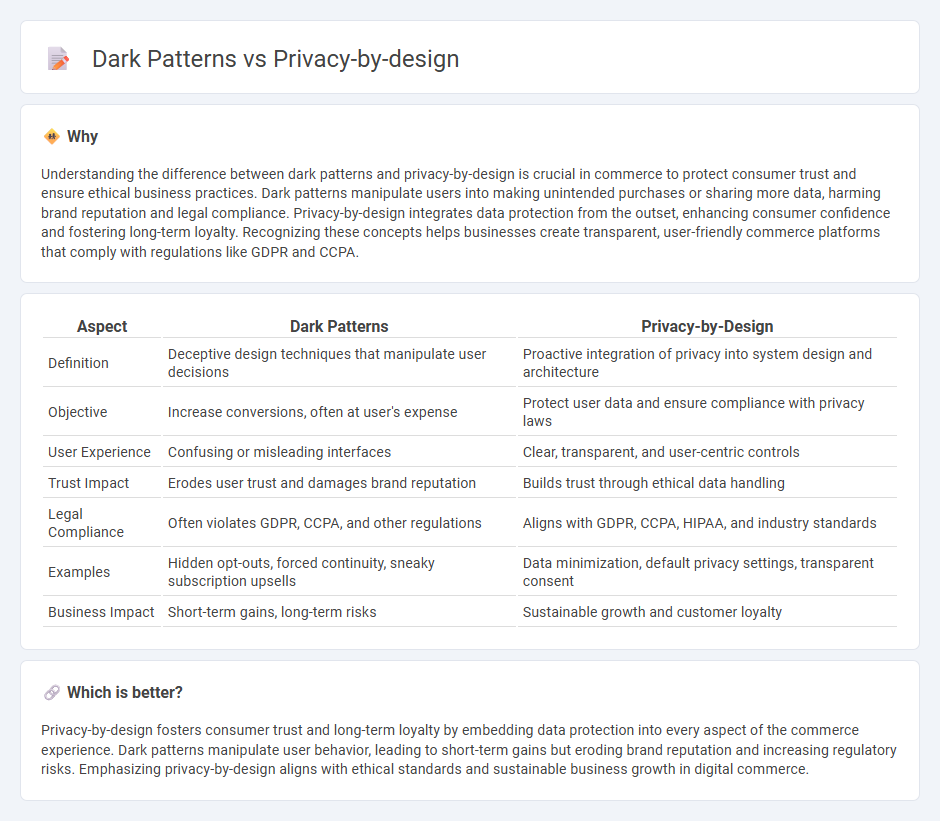
Understanding the difference between dark patterns and privacy-by-design is crucial in commerce to protect consumer trust and ensure ethical business practices. Dark patterns manipulate users into making unintended purchases or sharing more data, harming brand reputation and legal compliance. Privacy-by-design integrates data protection from the outset, enhancing consumer confidence and fostering long-term loyalty. Recognizing these concepts helps businesses create transparent, user-friendly commerce platforms that comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Patterns | Privacy-by-Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deceptive design techniques that manipulate user decisions | Proactive integration of privacy into system design and architecture |
| Objective | Increase conversions, often at user's expense | Protect user data and ensure compliance with privacy laws |
| User Experience | Confusing or misleading interfaces | Clear, transparent, and user-centric controls |
| Trust Impact | Erodes user trust and damages brand reputation | Builds trust through ethical data handling |
| Legal Compliance | Often violates GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations | Aligns with GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and industry standards |
| Examples | Hidden opt-outs, forced continuity, sneaky subscription upsells | Data minimization, default privacy settings, transparent consent |
| Business Impact | Short-term gains, long-term risks | Sustainable growth and customer loyalty |
Which is better?
Privacy-by-design fosters consumer trust and long-term loyalty by embedding data protection into every aspect of the commerce experience. Dark patterns manipulate user behavior, leading to short-term gains but eroding brand reputation and increasing regulatory risks. Emphasizing privacy-by-design aligns with ethical standards and sustainable business growth in digital commerce.
Connection
Dark patterns manipulate user behavior through deceptive design choices, undermining consumer trust and privacy. Privacy-by-design integrates data protection principles into the core of commerce platforms, ensuring transparency and user control over personal information. Implementing privacy-by-design counters dark patterns by promoting ethical data practices and enhancing consumer confidence in digital transactions.
Key Terms
User Consent
Privacy-by-design integrates user consent as a fundamental principle, ensuring transparent data collection and empowering users to make informed choices about their personal information. Dark patterns manipulate user interfaces to obscure consent options, often leading to involuntary or uninformed data sharing. Explore the ethical distinction between these approaches to understand how user consent can be genuinely respected and protected.
Data Minimization
Privacy-by-design incorporates data minimization by collecting only essential user data to enhance protection and reduce risks of breaches. Dark patterns, conversely, manipulate user consent to gather excessive personal information, undermining privacy principles. Explore how prioritizing data minimization can safeguard user trust and compliance.
Manipulative Interface
Privacy-by-design integrates user privacy through transparent, ethical interface elements that promote informed consent and data control, whereas dark patterns deploy manipulative interface techniques to deceive users into relinquishing personal data or consent unintentionally. Manipulative interfaces often exploit cognitive biases by using misleading layouts, hidden opt-outs, or confusing language to obscure privacy choices. Explore how focusing on user-centric, transparent design can combat the pervasive effects of dark patterns in digital privacy.
Source and External Links
Privacy by Design: Meaning and Its Importance - GDPR Local - Privacy by Design is a proactive approach to embed data protection into systems from the start, ensuring user privacy by default and compliance with laws like GDPR and CCPA by integrating privacy as a core system component rather than an afterthought.
Privacy by design - Wikipedia - Privacy by Design is an approach that integrates privacy into IT systems and business practices from their architecture, ensuring end-to-end security, transparency, full functionality without trade-offs, and user-centric privacy safeguards.
Privacy by Design (PDF) - Privacy by Design is based on seven principles emphasizing proactive prevention of privacy harms, privacy as the default setting, embedding privacy into design, full functionality, lifecycle security, transparency, and respect for user privacy through strong defaults and controls.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com