Distributed ledger marketplaces leverage blockchain technology to enable secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions without intermediaries, enhancing trust and reducing fraud. Multi-vendor marketplaces centralize vendors on a single platform, offering diverse product selections but relying on a central authority to manage transactions and customer interactions. Explore the differences and benefits of each marketplace model to optimize your commerce strategy.
Why it is important
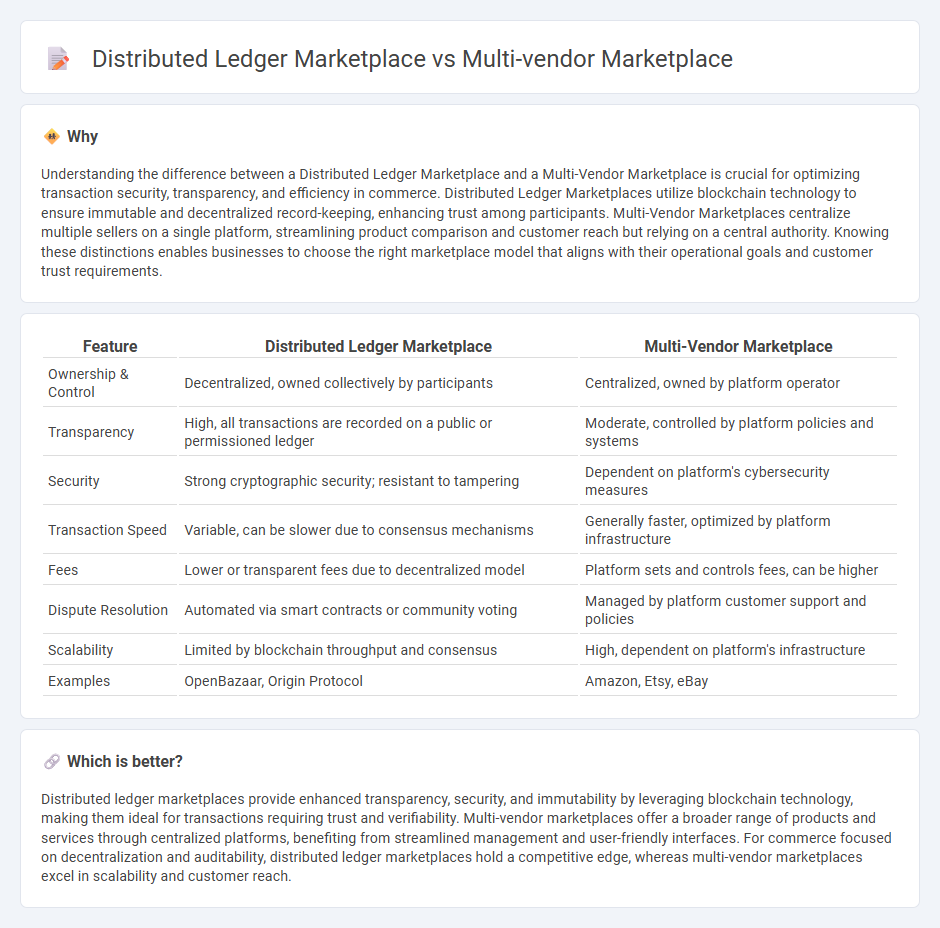
Understanding the difference between a Distributed Ledger Marketplace and a Multi-Vendor Marketplace is crucial for optimizing transaction security, transparency, and efficiency in commerce. Distributed Ledger Marketplaces utilize blockchain technology to ensure immutable and decentralized record-keeping, enhancing trust among participants. Multi-Vendor Marketplaces centralize multiple sellers on a single platform, streamlining product comparison and customer reach but relying on a central authority. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses to choose the right marketplace model that aligns with their operational goals and customer trust requirements.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Distributed Ledger Marketplace | Multi-Vendor Marketplace |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership & Control | Decentralized, owned collectively by participants | Centralized, owned by platform operator |
| Transparency | High, all transactions are recorded on a public or permissioned ledger | Moderate, controlled by platform policies and systems |
| Security | Strong cryptographic security; resistant to tampering | Dependent on platform's cybersecurity measures |
| Transaction Speed | Variable, can be slower due to consensus mechanisms | Generally faster, optimized by platform infrastructure |
| Fees | Lower or transparent fees due to decentralized model | Platform sets and controls fees, can be higher |
| Dispute Resolution | Automated via smart contracts or community voting | Managed by platform customer support and policies |
| Scalability | Limited by blockchain throughput and consensus | High, dependent on platform's infrastructure |
| Examples | OpenBazaar, Origin Protocol | Amazon, Etsy, eBay |
Which is better?
Distributed ledger marketplaces provide enhanced transparency, security, and immutability by leveraging blockchain technology, making them ideal for transactions requiring trust and verifiability. Multi-vendor marketplaces offer a broader range of products and services through centralized platforms, benefiting from streamlined management and user-friendly interfaces. For commerce focused on decentralization and auditability, distributed ledger marketplaces hold a competitive edge, whereas multi-vendor marketplaces excel in scalability and customer reach.
Connection
Distributed ledger marketplaces utilize blockchain technology to enable secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions among multiple vendors, ensuring trust without intermediaries. Multi-vendor marketplaces aggregate products from various sellers, leveraging distributed ledger systems to verify authenticity, streamline payment processes, and reduce fraud. The integration of distributed ledger technology enhances the efficiency, traceability, and trustworthiness of multi-vendor commerce platforms.
Key Terms
Intermediation
Multi-vendor marketplaces centralize intermediation, facilitating transactions through a single platform that manages payments, disputes, and trust between buyers and sellers. Distributed ledger marketplaces utilize blockchain technology to decentralize intermediation, enabling direct peer-to-peer transactions with enhanced security, transparency, and reduced reliance on third parties. Explore the evolving dynamics of intermediation in these marketplace models to understand their impact on trust and efficiency.
Decentralization
Multi-vendor marketplaces aggregate products from various sellers within a centralized platform, often controlling data and transaction processes. Distributed ledger marketplaces utilize blockchain technology to enable decentralized transactions, ensuring transparency, security, and reduced reliance on intermediaries. Explore the benefits and challenges of each model to understand their impact on decentralization.
Trust Mechanism
Multi-vendor marketplaces rely on centralized trust mechanisms, often involving third-party verification and reputation systems to ensure transaction security and buyer-seller reliability. Distributed ledger marketplaces leverage blockchain technology to create decentralized trust through cryptographic consensus, immutability, and transparent transaction histories, reducing the need for intermediaries. Explore how these trust frameworks impact efficiency, security, and user experience in various market environments.
Source and External Links
How to build a multi-vendor marketplace - A multi-vendor marketplace connects multiple sellers and buyers on one platform, offering benefits like reduced buying friction, wider choices, seller trust through ratings and reviews, and a commission-based revenue model for entrepreneurs.
The ultimate guide to choosing a multi vendor marketplace ... - Key features of a multi-vendor marketplace platform focus on the experiences of operators (vendor onboarding, contract management, payment processing), sellers (product uploads, order management, reporting), and buyers to enable smooth operation and trust.
Multi-Vendor Marketplace Platform - CS-Cart offers marketplace software tailored for multiple sellers on a single storefront, providing vendor dashboards, automated commission calculations, and full source code ownership for customization, ideal for scalable online retail.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com