Recommerce focuses on the resale of pre-owned goods, leveraging sustainability and cost efficiency to attract eco-conscious consumers. Dropshipping eliminates inventory management by allowing retailers to sell products directly from suppliers, reducing overhead and increasing product variety. Explore the advantages and challenges of recommerce versus dropshipping to determine the best fit for your e-commerce strategy.
Why it is important
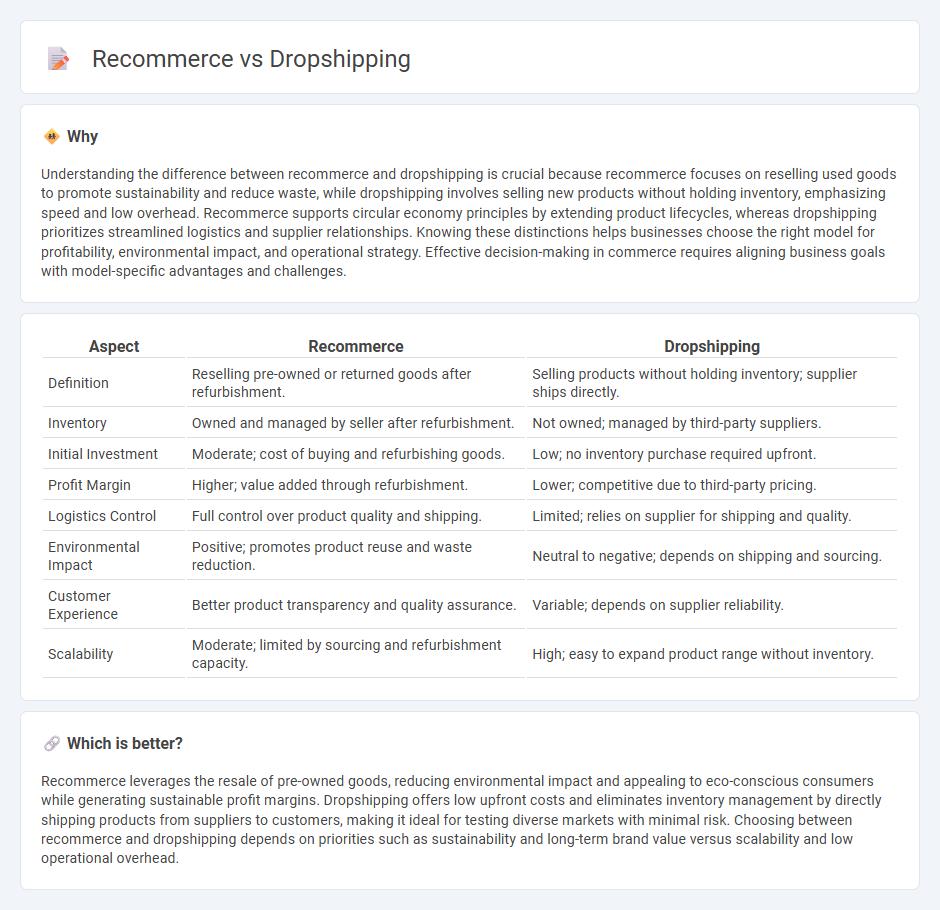
Understanding the difference between recommerce and dropshipping is crucial because recommerce focuses on reselling used goods to promote sustainability and reduce waste, while dropshipping involves selling new products without holding inventory, emphasizing speed and low overhead. Recommerce supports circular economy principles by extending product lifecycles, whereas dropshipping prioritizes streamlined logistics and supplier relationships. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses choose the right model for profitability, environmental impact, and operational strategy. Effective decision-making in commerce requires aligning business goals with model-specific advantages and challenges.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Recommerce | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reselling pre-owned or returned goods after refurbishment. | Selling products without holding inventory; supplier ships directly. |
| Inventory | Owned and managed by seller after refurbishment. | Not owned; managed by third-party suppliers. |
| Initial Investment | Moderate; cost of buying and refurbishing goods. | Low; no inventory purchase required upfront. |
| Profit Margin | Higher; value added through refurbishment. | Lower; competitive due to third-party pricing. |
| Logistics Control | Full control over product quality and shipping. | Limited; relies on supplier for shipping and quality. |
| Environmental Impact | Positive; promotes product reuse and waste reduction. | Neutral to negative; depends on shipping and sourcing. |
| Customer Experience | Better product transparency and quality assurance. | Variable; depends on supplier reliability. |
| Scalability | Moderate; limited by sourcing and refurbishment capacity. | High; easy to expand product range without inventory. |
Which is better?
Recommerce leverages the resale of pre-owned goods, reducing environmental impact and appealing to eco-conscious consumers while generating sustainable profit margins. Dropshipping offers low upfront costs and eliminates inventory management by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, making it ideal for testing diverse markets with minimal risk. Choosing between recommerce and dropshipping depends on priorities such as sustainability and long-term brand value versus scalability and low operational overhead.
Connection
Recommerce and dropshipping both leverage supply chain efficiency to minimize inventory risks by facilitating direct product delivery from suppliers to consumers. Recommerce focuses on the resale of used or refurbished goods, extending product life cycles and promoting sustainable consumption, while dropshipping enables retailers to sell products without holding stock, relying on suppliers for order fulfillment. The intersection lies in their shared reliance on third-party logistics and digital platforms to streamline commerce operations and reduce overhead costs.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory storage by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, reducing overhead and inventory risks. Recommerce involves managing returned, refurbished, or second-hand goods, requiring efficient tracking, quality control, and storage systems to maximize product lifecycle and sustainability. Discover detailed strategies to optimize inventory management for both dropshipping and recommerce models.
Supply Chain
Dropshipping eliminates inventory holding by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, streamlining supply chain efficiency and reducing overhead costs. Recommerce emphasizes the reverse logistics process, involving product returns, refurbishing, and resale, which adds complexity but promotes sustainability in the supply chain. Discover the intricacies of both models to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Product Lifecycle
Dropshipping minimizes inventory by shipping products directly from suppliers to customers, resulting in shorter product lifecycles and reduced waste. Recommerce extends product lifecycles through buying, refurbishing, and reselling used goods, promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact. Explore how these models influence product longevity and consumer behavior in evolving markets.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Wix.com - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where the seller operates an online store, markets products, and, upon receiving orders, passes them to a third-party supplier who handles inventory, packaging, and shipping directly to customers.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify - Dropshipping involves partnering with suppliers who store and ship products directly to customers, while the retailer manages the online storefront, pricing, and customer service, often using apps to automate order forwarding and inventory updates.
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail practice where a seller accepts orders without stocking inventory, forwarding order details to suppliers who ship directly to customers, offering advantages like low startup cost and flexibility but with less control over quality and shipping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com