Ghost commerce operates by selling products without holding inventory or managing fulfillment, relying on third-party suppliers to handle shipments directly to customers, similar to dropshipping but often focusing on branded or private-label items. Dropshipping involves listing products from suppliers on an online store, where orders are forwarded to suppliers who ship items directly to buyers, minimizing upfront investment and inventory risk. Explore more to understand how these models can optimize your e-commerce strategy and profitability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost commerce and dropshipping is crucial for optimizing e-commerce strategies and maximizing profits. Ghost commerce involves selling products without holding inventory or direct supplier relationships, relying heavily on digital marketing and fulfillment services. Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where the seller forwards customer orders to suppliers who then ship products directly to consumers. Knowledge of these models allows entrepreneurs to select the best operational framework, reduce risks, and enhance supply chain efficiency.
Comparison Table
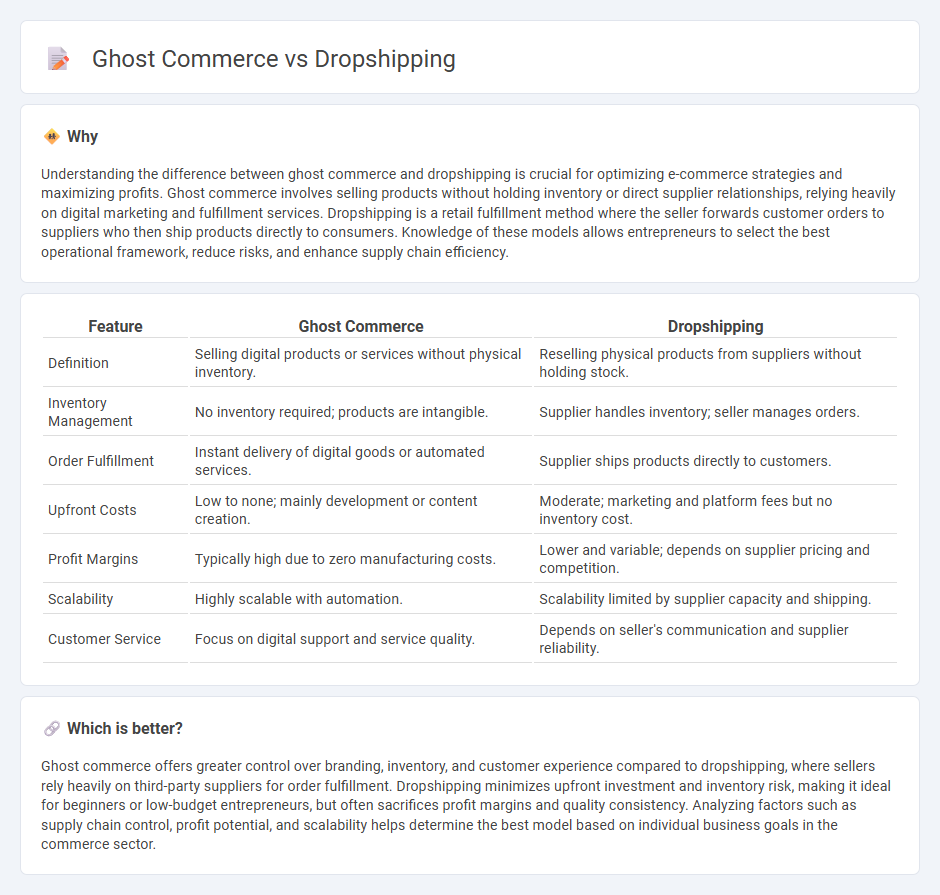
| Feature | Ghost Commerce | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Selling digital products or services without physical inventory. | Reselling physical products from suppliers without holding stock. |
| Inventory Management | No inventory required; products are intangible. | Supplier handles inventory; seller manages orders. |
| Order Fulfillment | Instant delivery of digital goods or automated services. | Supplier ships products directly to customers. |
| Upfront Costs | Low to none; mainly development or content creation. | Moderate; marketing and platform fees but no inventory cost. |
| Profit Margins | Typically high due to zero manufacturing costs. | Lower and variable; depends on supplier pricing and competition. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with automation. | Scalability limited by supplier capacity and shipping. |
| Customer Service | Focus on digital support and service quality. | Depends on seller's communication and supplier reliability. |
Which is better?
Ghost commerce offers greater control over branding, inventory, and customer experience compared to dropshipping, where sellers rely heavily on third-party suppliers for order fulfillment. Dropshipping minimizes upfront investment and inventory risk, making it ideal for beginners or low-budget entrepreneurs, but often sacrifices profit margins and quality consistency. Analyzing factors such as supply chain control, profit potential, and scalability helps determine the best model based on individual business goals in the commerce sector.
Connection
Ghost commerce and dropshipping intersect by enabling sellers to operate online stores without holding inventory, relying on third-party suppliers to fulfill orders directly to customers. This model minimizes upfront costs and logistics management, streamlining e-commerce operations and maximizing profit margins. Both approaches leverage digital platforms and supplier networks to create scalable and flexible retail businesses in the competitive commerce landscape.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dropshipping relies on third-party suppliers to handle inventory management, eliminating the need for upfront stock investment and reducing storage risks. Ghost commerce involves maintaining a private inventory managed through automated fulfillment centers, offering greater control over product quality and shipping speed. Explore more to understand which inventory strategy best aligns with your business goals.
Branding Ownership
Dropshipping involves selling products without holding inventory, relying on third-party suppliers, which often limits branding control and customer experience customization. Ghost commerce, on the other hand, emphasizes full branding ownership with businesses managing product design, packaging, and a direct relationship with consumers, enhancing brand identity and loyalty. Explore the advantages of branding ownership in ghost commerce to elevate your e-commerce strategy.
Order Fulfillment
Dropshipping relies on third-party suppliers to handle order fulfillment, where products are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer, minimizing inventory management for the retailer. Ghost commerce operates by creating a branded storefront but leverages automated systems and multiple suppliers to fulfill orders efficiently, often using advanced logistics software for tracking and delivery optimization. Explore how each model impacts customer experience and operational efficiency by diving deeper into their order fulfillment processes.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment model where the seller does not stock inventory but purchases products from a third-party supplier who handles storage, packaging, and shipping directly to the customer, allowing the seller to focus on marketing and pricing.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Dropshipping involves partnering with suppliers to sell products through your online store, forwarding customer orders automatically to these suppliers who then ship products directly to customers, enabling sellers to operate without inventory management.
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail model where the seller accepts orders without holding stock, transferring order details to manufacturers or wholesalers who ship directly to customers, minimizing overhead but with less control over quality and shipping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com