Returnless refunds eliminate the need for product returns, reducing processing time and logistical costs while enhancing customer satisfaction. Cashback rewards offer immediate financial incentives without requiring returns, driving customer loyalty and increasing repeat purchases. Explore the benefits and challenges of these approaches to optimize your commerce strategy.
Why it is important
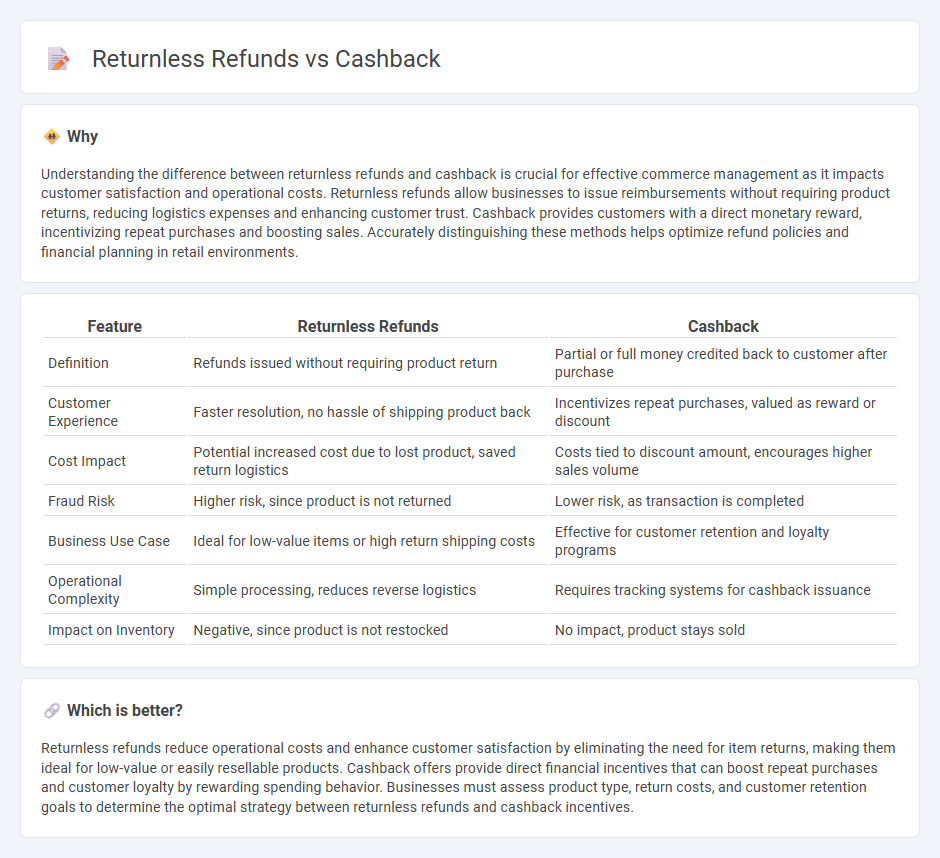
Understanding the difference between returnless refunds and cashback is crucial for effective commerce management as it impacts customer satisfaction and operational costs. Returnless refunds allow businesses to issue reimbursements without requiring product returns, reducing logistics expenses and enhancing customer trust. Cashback provides customers with a direct monetary reward, incentivizing repeat purchases and boosting sales. Accurately distinguishing these methods helps optimize refund policies and financial planning in retail environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Returnless Refunds | Cashback |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refunds issued without requiring product return | Partial or full money credited back to customer after purchase |
| Customer Experience | Faster resolution, no hassle of shipping product back | Incentivizes repeat purchases, valued as reward or discount |
| Cost Impact | Potential increased cost due to lost product, saved return logistics | Costs tied to discount amount, encourages higher sales volume |
| Fraud Risk | Higher risk, since product is not returned | Lower risk, as transaction is completed |
| Business Use Case | Ideal for low-value items or high return shipping costs | Effective for customer retention and loyalty programs |
| Operational Complexity | Simple processing, reduces reverse logistics | Requires tracking systems for cashback issuance |
| Impact on Inventory | Negative, since product is not restocked | No impact, product stays sold |
Which is better?
Returnless refunds reduce operational costs and enhance customer satisfaction by eliminating the need for item returns, making them ideal for low-value or easily resellable products. Cashback offers provide direct financial incentives that can boost repeat purchases and customer loyalty by rewarding spending behavior. Businesses must assess product type, return costs, and customer retention goals to determine the optimal strategy between returnless refunds and cashback incentives.
Connection
Returnless refunds and cashback both enhance customer satisfaction by streamlining post-purchase processes and incentivizing spending. Returnless refunds reduce logistical costs and increase convenience by allowing customers to keep products while still receiving a refund. Cashback programs boost customer retention and spending frequency by providing financial rewards tied to purchases, creating a complementary system with returnless refunds that encourages repeat business.
Key Terms
Customer Retention
Cashback programs incentivize repeat purchases by providing immediate monetary rewards, enhancing customer loyalty and boosting retention rates. Returnless refunds reduce friction in the return process, improving customer satisfaction and trust without the logistics costs. Explore how these strategies balance customer experience and operational efficiency to maximize retention.
Transaction Incentives
Cashback and returnless refunds serve as distinct transaction incentives that enhance customer satisfaction by providing immediate monetary benefits without requiring product returns. Cashback rewards encourage repeat purchases by directly crediting a percentage of the transaction value to the customer's account, while returnless refunds streamline the refund process, reducing operational costs and improving user experience. Explore how businesses leverage these incentives to optimize sales and customer loyalty.
Reverse Logistics
Returnless refunds reduce reverse logistics costs by eliminating product returns, enhancing operational efficiency. Cashback incentives encourage customer retention while minimizing the expenses associated with physical returns and restocking. Explore how these strategies optimize reverse logistics to improve profitability and customer satisfaction.
Source and External Links
Cashback - Definition, Types, How It Works, Benefits - Cashback is a credit card perk where a percentage of eligible purchases is paid back to the cardholder, typically ranging from 0.25% to 5%, encouraging more frequent credit card use.
What is cashback and how does it work? - N26 - Cashback is a rewards program offering money back on spending through credit cards, debit cards, and websites, where retailers pay a percentage to card companies that is partially returned to consumers.
How Does Cash Back Work? | Bankrate - Cash back rewards accumulate as a percentage of qualifying purchases, stored in your credit card account until redeemed as statement credits, discounts, or gift cards.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com